Efficient Scrap Recycling with Scrap Dost
Looking to recycle your scrap efficiently? Scrap Dost offers top-notch scrap recycling services, ensuring eco-friendly disposal and maximum value for your materials. Whether it's metal, plastic, or electronic waste, we handle it all. Join countless s
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
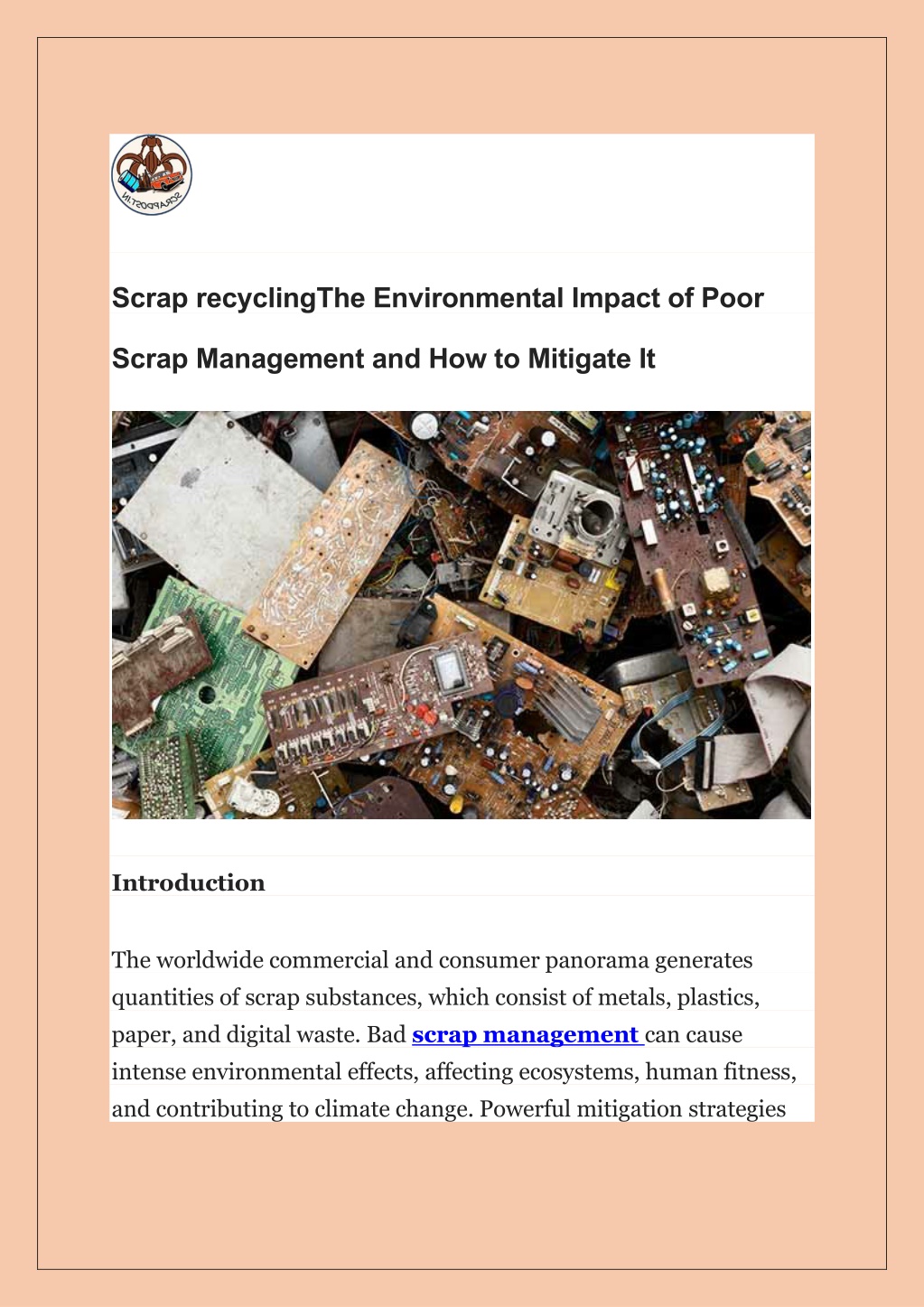
Scrap recyclingThe Environmental Impact of Poor Scrap Management and How to Mitigate It Introduction The worldwide commercial and consumer panorama generates quantities of scrap substances, which consist of metals, plastics, paper, and digital waste. Bad scrap management can cause intense environmental effects, affecting ecosystems, human fitness, and contributing to climate change. Powerful mitigation strategies
are vital to manipulating scrap sustainably, reducing environmental effects, and promoting a spherical economic device. Environmental effects of bad scrap management 1. Pollutants of Land and Water in Our Bodies Improperly disposed of scrap materials, especially electronic waste (e-waste), include risky substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium. These toxic elements can leach into soil and groundwater, contaminating drinking water resources and agricultural lands. Plastics, when not recycled, regularly emerge in landfills or water our bodies, leading to soil and water pollution. Microplastics from degraded plastic waste may be ingested with the aid of aquatic organisms, coming into the food chain and posing fitness hazards to the natural world and humans. 2. Air pollution Incineration of scrap materials, mainly plastics and e-waste, releases dangerous gasses consisting of dioxins, furans, and exceptionally risky herbal compounds (VOCs) into the environment. Those pollutants contribute to air degradation and respiration troubles in people. Open burning of scrap materials, commonplace in regions with inadequate waste control infrastructure, similarly exacerbates air pollution and releases large amounts of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas.
3. Aid Depletion Negative scrap manipulation practices often mean that valuable substances are misplaced rather than recycled. Metals like copper, aluminum, and unusual earth elements, which are finite and strength-extensive to mine, are wasted while no longer recovered from scrap. This depletion of natural belongings necessitates extra mining and extraction activities, which have their own non-public environmental impacts along with habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water infection. 4. Greenhouse Fuel Emissions
Inefficient scrap management contributes to improved greenhouse gas emissions. For example, the decomposition of natural waste in landfills produces methane, an effective greenhouse gas. The production of new merchandise from uncooked materials requires drastically more strength compared to the use of recycled substances. For that reason, terrible scrap control results in better strength intake and a larger carbon footprint. Mitigation strategies 1. Enhancing recycling structures Enhancing recycling infrastructure and systems is essential. This includes putting in greater recycling centers, improving series structures, and making sure the right sorting and processing of scrap substances. Governments and municipalities have to invest in advanced recycling technologies, which include automated sorting and processing machines, to improve growth performance and reduce contamination of recyclable substances. 2. Selling extended manufacturer duty (EPR) EPR rules maintain manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, which incorporates submit-patron waste. This incentivizes them to layout products, which is probably easier to recycle and to take back their products at the end of their useful existence. Imposing EPR can extensively reduce the quantity of
scrap entering landfills and promote the recycling and reuse of materials. 3. Public recognition and schooling Elevating public recognition of the environmental effects of horrific scrap manipulation and the advantages of recycling is crucial. Instructional campaigns can encourage individuals and organizations to adopt higher waste control practices. faculties and offices need to be targeted with records on proper waste segregation, the importance of recycling, and a way to reduce waste. 4. Regulation and coverage Enforcement More potent rules and enforcement mechanisms are needed to ensure compliance with waste control legal guidelines. Governments have to set up smooth recommendations for the disposal and recycling of numerous sorts of scrap materials. effects of illegal dumping and non-compliance with waste control guidelines want to be strictly enforced to deter environmentally risky practices. 5. Incentivizing Sustainable Practices Economic incentives, on the side of tax breaks or subsidies for undertaking sustainable scrap control practices, can inspire greater effort to put money into recycling and waste reduction technologies. Programs that praise customers for returning recyclable substances,
like deposit-refund structures for bottles and cans, can also increase recycling fees and decrease littering. 6. Advancing round economic device standards Adopting a circular financial gadget approach includes designing merchandise for durability, reparability, and recyclability. It emphasizes the reuse, refurbishment, and recycling of materials to create a closed-loop machine. ought to innovate to lessen cloth use, boom product life cycles, and create new charge from waste materials through upcycling and remanufacturing. Conclusion Powerful scrap management is essential for mitigating environmental damage and promoting sustainability. By enhancing recycling structures, enforcing EPR, raising public reputation, enforcing hints, incentivizing sustainable practices, and advancing spherical financial system requirements, the negative effects of poor scrap manipulation may be substantially reduced. the ones that not only best defend the surroundings but additionally contribute to aid conservation and monetary resilience, fostering a healthier planet for future generations. For more details:
1004 shivalik tower, Kaushambi, ghaziabad rajat@scrapdost.in For Cars - +91 98100 33550 / +91 99715 73738 For Hospitality - +91 98100 33550






















