Digital Light Processing (DLP) Projectors
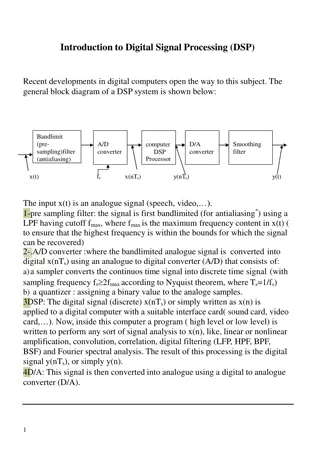
Digital Light Processing (DLP) projectors are display devices based on optical micro-electro-mechanical technology that utilize digital micromirror devices. Developed in 1987 by Larry Hornbeck, these projectors are widely used in classrooms, businesses, digital signs, and even digital cinema projection. The main features include 1-chip and 3-chip variations, with the image being created by microscopically small mirrors on a semiconductor chip known as a Digital Micromirror Device (DMD). Additionally, the projector's light source is powered by a lamp and color is produced through a color wheel or individual light sources. The lens projects the image onto the screen, completing the visual experience.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DLP Projector Evan Carlin, Michael Whitfield
What is a Digital Light Processor Projector? DLP, or Digital Light Processing Projector, is a display device based on optical micro-electro-mechanical technology that uses a digital micromirror device. It was originally developed in 1987 by Larry Hornbeck of Texas Instruments. The first DLP-based projector was introduced by Digital Projection Ltd in 1997
What are the functions of a digital light Projector? DLP projectors typically used in classrooms, business, DLP rear projection television sets, and Digital Signs. It is also used in 85% of digital cinema projection, and in additive manufacturing as a light source in some printers to cure resins into solid 3D objects.
What are the main features of digital light processing projector? 1-chip DLP projectors use a color wheel to create color 3- chip DLP projectors each chip is dedicated to the three primary colors red, green and blue, proving more power than the 1 chip projector Light source
DLP Chip In DLP projectors, the image is created by microscopically small mirrors laid out in a matrix on a semiconductor chip, known as a Digital Micromirror Device (DMD). The number of mirrors corresponds to the resolution of the projected image.
Lamp A DLP (digital light processing) lamp is the main source of light in a rear screen projection television set. DLP lamps do tend to age after a few years, with the length of time depending on the brand used and how many hours you have your TV set on
Color Wheel Colors are produced either by placing a color wheel between a white lamp and the DLP chip or by using individual light sources to produce the primary colors. The color wheel can experience what is known as the Rainbow effect The rainbow effect is caused when the mechanical spinning color wheel has brief flashes of perceived red, blue and green.
Lens The lens projects the image onto the screen.
Lens Shutter It is the gate and shutter that gives the illusion of one full frame being replaced exactly on top of another full frame. The gate holds the film still while the shutter is open. A rotating petal or gated cylindrical shutter interrupts the emitted light during the time the film is advanced to the next frame. The viewer does not see the transition, thus tricking the brain into believing a moving image is on screen. Modern shutters are designed with a flicker-rate of two times (48 Hz) or even sometimes three times (72 Hz) the frame rate of the film, so as to reduce the perception of screen flickering.
Mirror LP technology uses micro-mirrors the way an LCD use pixels to reflect color and light onto a screen. The resolution of the DLP HDTV is directly related to the number of mirrors that can have light reflected from them.
Work Cited Digital Light Processing. Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia, Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., 0 Feb. 2018, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_Light_Processing. Accessed 4 May 2018. Digital Light Processing (DLP). HomeTheaterReview.com, hometheaterreview.com/digital- light-processing-dlp/. Accessed 4 May 2018. How Long Do DLP Lamps Last? HowStuffWorks, 13 May 2011, electronics.howstuffworks.com/dlp-lamps.htm. Accessed 4 May 2018.

 undefined
undefined