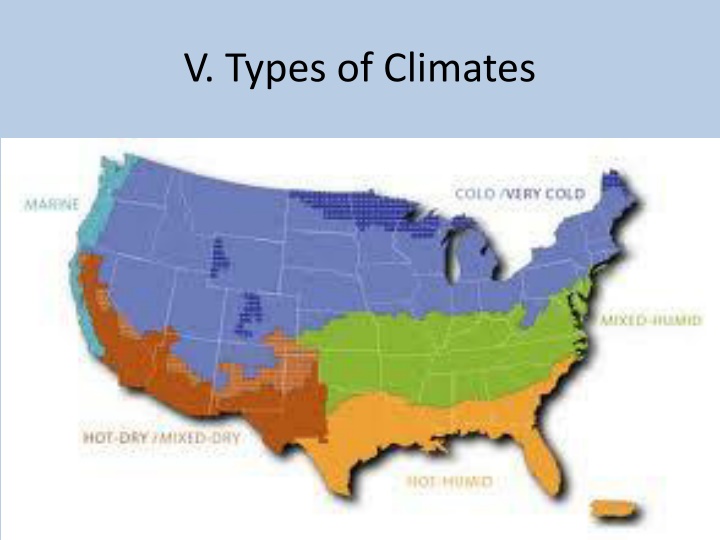
Different Climate Types and Regions
The climate is shaped by temperature, precipitation, and wind, creating global patterns and diverse climate regions. From tropical wet climates to continental warm summers, each region has unique characteristics based on temperature and precipitation. By understanding these climate types, we can appreciate the variety of climates around the world.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
A. Shapers of Climate The main shapers of climate are temperature, precipitation, and wind. These factors form global patterns Temperatures are warmest in and around the tropics and coolest near the poles. Precipitation is greatest near the Equator.
B. Climate Regions These patterns of temperature and precipitation create world climate regions. Climate regions- areas that share a similar climate
Tropical Wet climates combine hot temperatures and heavy rainfall year round and are clustered around the Equator. Tropical wet and dry climates with wet season in summer and dry season in winter Humid subtropical climates have year-round precipitation with mild winters and hot
Mediterranean climates that have hot, dry weather in the summer and a rainy season in the winter Maritime climates are wet year-round, with mild winters and cool summers. They exist where moist winds blow onshore.
Continental Warm Summer have year- round precipitation, warm summers, and cold, snowy winters. Continental Cool Summer similar, but have generally lower temperatures
Tundra have cool summers and bitterly cold, dry winters. Close to the poles, ice caps, or permanent sheets of ice covering land or sea, have bitter cold and dry climates year round. Semiarid, or dry, and Arid, or very dry occur where there is steadily sinking air. Subarctic have limited precipitation, cool summers, and very cold winters.