Cucumber Green Mottle Mosaic Virus: Disease Cycle and Testing Methods
This content provides detailed information on Cucumber Green Mottle Mosaic Virus, including its nucleotide genome, disease cycle, testing methods like DAS-ELISA and RT-PCR, seed testing protocols, bioassay for virus confirmation, and symptom expression in host plants. The data covers aspects such as transmission rates, contamination, and control strategies, offering valuable insights into the management of this plant virus.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
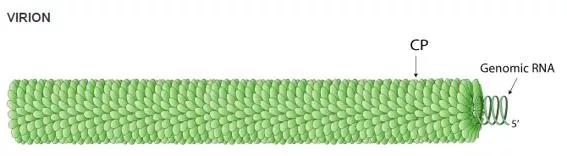
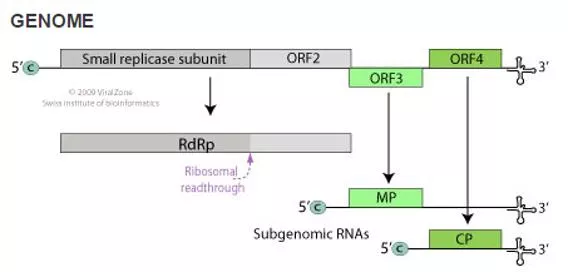
Cucumber Green Mottle Mosaic Virus 6422 nucleotide genome Group IV +ssRNA virus Top image from viralzone,expasy.org, produced by the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics. Bottom image from NCBI.NIH.gov accession NC_001801.1, National Center for Biotechnology Information.
Disease Cycle Contaminated seeds 1%-5% infected seedlings Infected fruit Secondary spread by mechanical transmission, infection rates up to 100%
Testing methods DAS-ELISA RT-PCR RT-qPCR Immunostrips
Seed Testing homogenate (v/v) Powdered seeds (w/w) Seeds (# contam./total) Isolate Yolo Yolo Yolo Yolo Yolo Yolo Yolo Yolo Yolo Yolo Yolo healthy control Yolo Buffer control SJ SJ SJ SJ SJ SJ SJ SJ SJ SJ 1/10000 SJ healthy control SJ Buffer control Dilution 1 1/10 1/50 1/100 1/200 1/500 1/1000 1/2000 1/5000 1/10000 ELISA O.D. 1.8995 2.0995 N/A 1.964 1.7415 1.9625 1.3205 1.0905 0.6385 N/A 0.085 0.08 1.496 1.3635 N/A 1.236 1.09 0.7245 0.666 0.5345 0.4035 N/A 0.084 0.08 RT-PCR positive positive N/A positive positive positive positive negative negative N/A negative negative positive positive N/A positive positive positive positive negative negative N/A negative negative ELISA O.D. 1.9255 1.987 N/A 1.403 1.5725 1.4985 0.5155 0.6745 0.364 N/A 0.082 0.08 1.444 1.377 N/A 0.9585 1.0435 1.041 0.652 0.4275 0.15645 N/A 0.082 0.08 RT-PCR positive positive N/A positive positive positive positive negative negative N/A negative negative positive positive N/A positive positive positive positive negative negative N/A negative negative ELISA O.D. 2.209 N/A 1.893 1.0745 N/A 1.69 0.7155 0.289 0.244 0.096 0.0845 0.07 1.893 N/A 1.0745 1.69 0.7155 N/A 0.289 0.244 0.096 0.0895 0.075 0.073 RT-PCR positive N/A positive positive N/A positive positive negative negative negative negative negative positive N/A positive positive positive N/A negative negative negative negative negative negative 1 1/10 1/50 1/100 1/200 1/500 1/1000 1/2000 1/5000 Dilution: # contaminated seeds/# total seeds; healthy and contaminated seeds were watermelon
Bioassay To confirm infectious virus Rub inoculate both Nicotiana benthamiana (Nb) and Chenopodiumalbum ssp. amaranticolor (Caa) Reducing inoculation buffer carborundum Symptoms take up to 10 days to develop For Nb systemic infection, test upper newest leaves with RT-PCR or ELISA Caa local lesions, excise local lesions and test with RT-PCR or ELISA
Healthy CGMMV CGMMV CGMMV CGMMV Nb 20 days post inoculation. Symptom expression begins as early as 5 dpi, if Nb are at 4th true leaf when inoculated. Not all isolates cause strong symptoms in Nb despite systemic infection.
ATCC1067 ZGMMV no local lesions Fresno local lesions ATCC391 (Japan) local lesions SJ local lesion Kern local lesion Israel local lesion 10 days post inoculation: all isolates have distinct local lesions Yolo local lesion
Isolate Collection California isolates: 3 unique isolates, 4 total American Type Culture Collection: 1 CGMMV (Japan), 1 zucchini green mottle mosaic virus Middle East: 1 isolate Europe: 26 isolates SE Asia: 4 isolates 37 total isolates
Phylogenetic analysis includes 46 full genome sequences from GenBank, and 36 sequences from international collaborators and California outbreaks. China Korea The 36 additional sequences were generated from NGS sequencing of purified virion RNA. Analyses are ongoing. Taiwan Korea Israel India Canada Israel Taiwan KoreaJapan Israel Spain Russia Spain
Full genome sequence alignment, North American isolates 1 2 3 4 5 1. Canada 2013 isolate 2. Fresno 2014 isolate 3. Kern 2014 isolate 4. Yolo 2013 isolate 5. San Joaquin 2014 isolate
Continued funding/future work Finish CGMMV recovery plan, currently under review with collaborators We received Farm Bill funding, grant #3.0323.00 Enhancing the sensitivity, efficiency and accuracy for detecting Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus in cucurbit seeds. Beginning in August Go forward with qRT-PCR work Complete sequence analyses Optimize seed RNA purification or other molecular testing method
Watermelon Cucumber Questions? Questions? Cantaloupe