Comprehensive Overview of Exercise Science and Training Principles
Explore various aspects of exercise science and training principles including types of practice, stages of learning, methods of practice, goal setting, energy systems, nutrition, performance components, fitness testing, and more.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
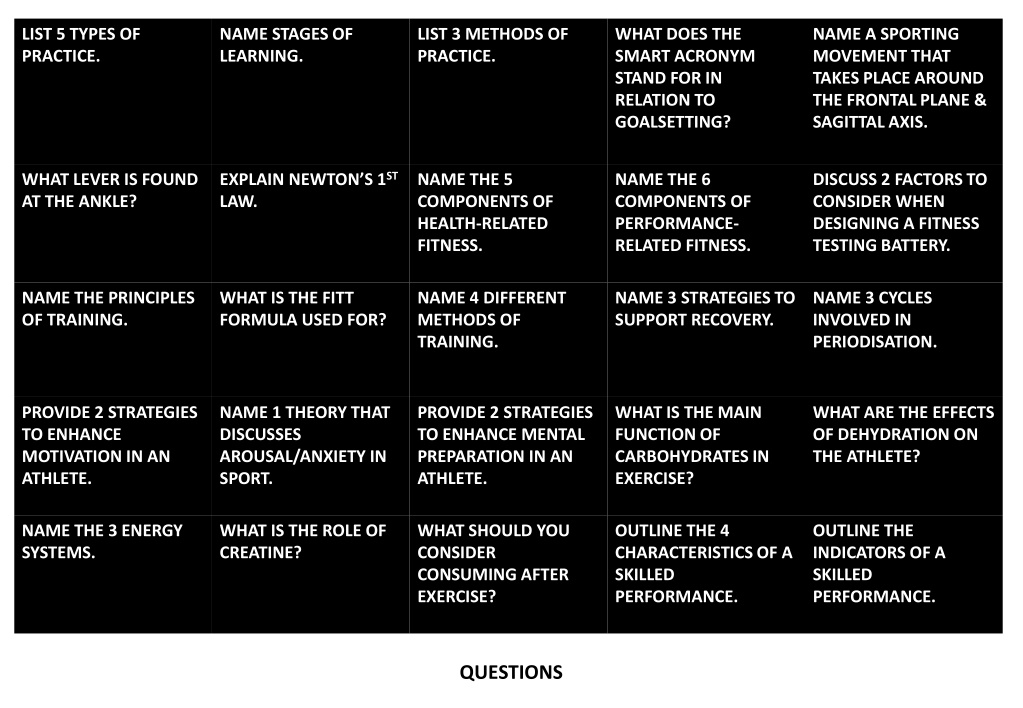
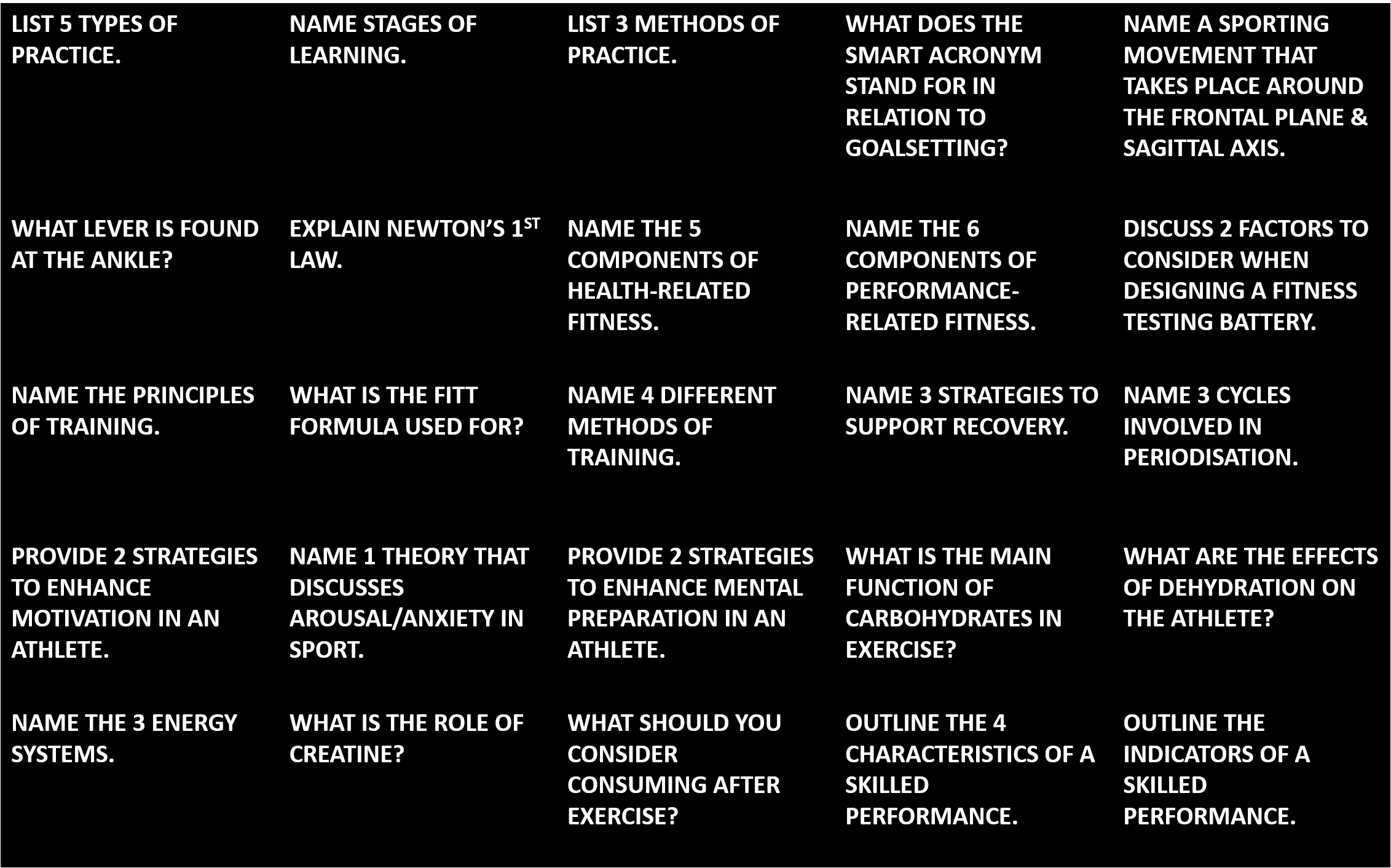
LIST 5 TYPES OF PRACTICE. NAME STAGES OF LEARNING. LIST 3 METHODS OF PRACTICE. WHAT DOES THE SMART ACRONYM STAND FOR IN RELATION TO GOALSETTING? NAME A SPORTING MOVEMENT THAT TAKES PLACE AROUND THE FRONTAL PLANE & SAGITTAL AXIS. EXPLAIN NEWTON S 1ST LAW. WHAT LEVER IS FOUND AT THE ANKLE? NAME THE 5 COMPONENTS OF HEALTH-RELATED FITNESS. NAME THE 6 COMPONENTS OF PERFORMANCE- RELATED FITNESS. DISCUSS 2 FACTORS TO CONSIDER WHEN DESIGNING A FITNESS TESTING BATTERY. NAME THE PRINCIPLES OF TRAINING. WHAT IS THE FITT FORMULA USED FOR? NAME 4 DIFFERENT METHODS OF TRAINING. NAME 3 STRATEGIES TO SUPPORT RECOVERY. NAME 3 CYCLES INVOLVED IN PERIODISATION. PROVIDE 2 STRATEGIES TO ENHANCE MOTIVATION IN AN ATHLETE. NAME 1 THEORY THAT DISCUSSES AROUSAL/ANXIETY IN SPORT. PROVIDE 2 STRATEGIES TO ENHANCE MENTAL PREPARATION IN AN ATHLETE. WHAT IS THE MAIN FUNCTION OF CARBOHYDRATES IN EXERCISE? WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF DEHYDRATION ON THE ATHLETE? NAME THE 3 ENERGY SYSTEMS. WHAT IS THE ROLE OF CREATINE? WHAT SHOULD YOU CONSIDER CONSUMING AFTER EXERCISE? OUTLINE THE 4 CHARACTERISTICS OF A SKILLED PERFORMANCE. OUTLINE THE INDICATORS OF A SKILLED PERFORMANCE. QUESTIONS
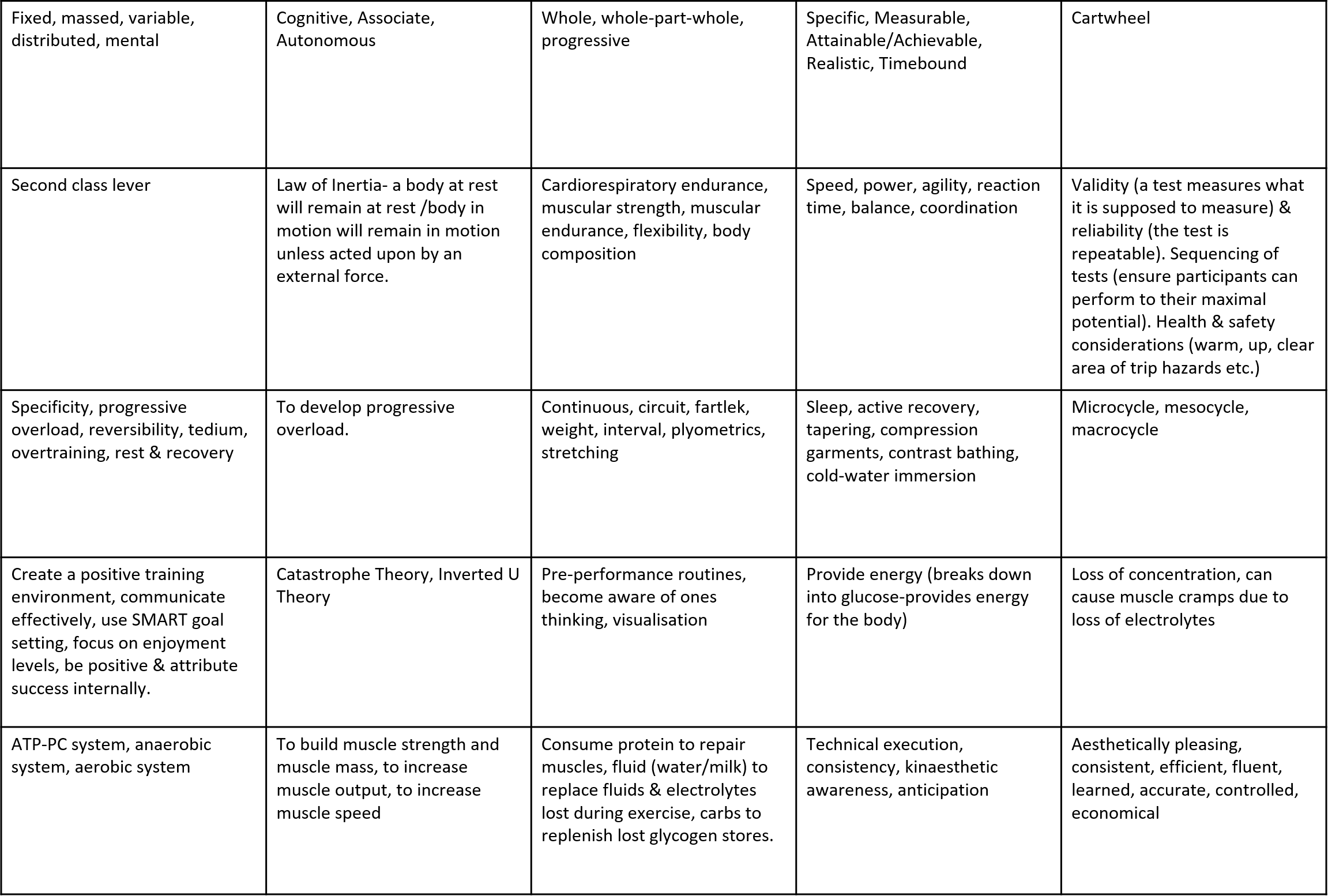
Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Cartwheel Second class lever Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force. Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery To develop progressive overload. Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores. Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical
Cartwheel Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive To develop progressive overload. Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores. Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force. Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching Second class lever Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental
Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Cartwheel Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Second class lever Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system To develop progressive overload. Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores. Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed
Second class lever Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching Cartwheel Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination To develop progressive overload. To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores.
Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous To develop progressive overload. ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores. Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental Cartwheel Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed Second class lever Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes
Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical Second class lever Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation To develop progressive overload. Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Cartwheel ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores.
Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Cartwheel Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores. Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive Second class lever Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. To develop progressive overload.
Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation Second class lever Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores. Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. To develop progressive overload. Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous Cartwheel Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes
Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores. Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle Cartwheel Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force To develop progressive overload. Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Second class lever To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed
ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical Cartwheel Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation To develop progressive overload. Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores. To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. Second class lever Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching
Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores. Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation Cartwheel Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery To develop progressive overload. Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination Second class lever Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive
Provide energy (breaks down into glucose-provides energy for the body) Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition Consume protein to repair muscles, fluid (water/milk) to replace fluids & electrolytes lost during exercise, carbs to replenish lost glycogen stores. ATP-PC system, anaerobic system, aerobic system Technical execution, consistency, kinaesthetic awareness, anticipation Cognitive, Associate, Autonomous To develop progressive overload. Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility, tedium, overtraining, rest & recovery Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable, Realistic, Timebound Aesthetically pleasing, consistent, efficient, fluent, learned, accurate, controlled, economical Speed, power, agility, reaction time, balance, coordination To build muscle strength and muscle mass, to increase muscle output, to increase muscle speed Whole, whole-part-whole, progressive Microcycle, mesocycle, macrocycle Loss of concentration, can cause muscle cramps due to loss of electrolytes Law of Inertia- a body at rest will remain at rest /body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force Create a positive training environment, communicate effectively, use SMART goal setting, focus on enjoyment levels, be positive & attribute success internally. Second class lever Sleep, active recovery, tapering, compression garments, contrast bathing, cold-water immersion Fixed, massed, variable, distributed, mental Catastrophe Theory, Inverted U Theory Cartwheel Continuous, circuit, fartlek, weight, interval, plyometrics, stretching Validity (a test measures what it is supposed to measure) & reliability (the test is repeatable). Sequencing of tests (ensure participants can perform to their maximal potential). Health & safety considerations (warm, up, clear area of trip hazards etc.) Pre-performance routines, become aware of ones thinking, visualisation