Compliance and Risk Assessment Matrix for Electrical Safety Standards
Evaluation of compliance and risk assessment methods for adherence to electrical safety standards to prevent hazards like fires and electric shocks. The matrix includes metrics, frequency of assessments, and tools used to quantify risk levels and ensure safety measures meet industry benchmarks. Non-compliance could result in legal actions, financial penalties, and damage to company reputation. Various standards such as National Electrical Code (NEC) and IEEE are utilized to maintain safety and avoid liabilities.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
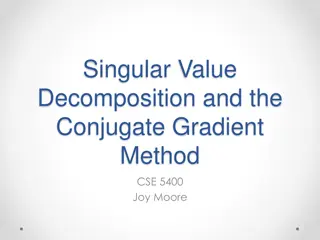
COMPLIANCE RISK ASSESSMENT MATRIX TEMPLATE RISK ASSESSMENT RECOMMENDED METRICS USED TO MEASURE COMPLIANCE AND RISK CONFIRM WHETHER OR NOT TO MONITOR RISK-LEVEL CHANGES OVER TIME AND WHY INTENDED USE OF COMPLIANCE AND RISK ASSESSMENT FRAMEWORK TOOLS UTILIZED FOR COMPLIANCE AND RISK ASSESSMENT RISK ASSESSMENT REQUIREMENTS FREQUENCY OF RISK ASSESSMENT CONFIRM WHETHER OR NOT RISK IS QUANTIFIED AND WHY TOPIC RISK Failing to adhere to electrical safety standards can result in fires, electric shocks, or other hazards that could harm users, damage property, and expose the company to significant liability and negative publicity. Evaluate the integrity, grounding, and insulation of all the company's electrical components. ELECTRICAL SAFETY STANDARDS Biannually and after any maintenance or upgrades. To ensure safety measures meet industry benchmarks. Number of incidents (fires, shocks); inspection pass rate. To identify potential wear and tear or systemic issues. To ensure user safety and reduce liability. National Electrical Code (NEC); local safety standards. YES YES PROJECT NAME Without following interconnection standards, there's a potential for grid instability. This can lead to service disruptions, possible fines from regulatory bodies, and damage to grid infrastructure. INTERCONNECTION STANDARDS Assess the quality and stability of the company's grid connectivity. To ensure seamless integration with the grid. Grid downtime duration; quality of connection scores. Especially when expanding or when the grid is undergoing major changes. To ensure stable service and avoid penalties. Annually. YES YES IEEE standards; local grid regulations. ACCESSIBILITY AND ADA (AMERICANS WITH DISABILITIES ACT) COMPLIANCE (OR EQUIVALENT LEGISLATION IN OTHER JURISDICTIONS) Failure to ensure charging-station accessibility can lead to legal complaints, potential fines, and damage to the company's reputation for lack of inclusivity. Audit charging stations for ease of access and ADA compliance. Annually and after any structural changes. Compliance is binary (i.e., either compliant or not). Number of accessibility complaints; inspection pass rate. To avoid legal actions and foster inclusivity. ADA guidelines; local accessibility standards. NO YES To ensure continued accessibility. If customer data (like payment information or usage statistics) isn't handled securely, the company could face data breaches, leading to legal action, financial penalties, and loss of customer trust. DATA SECURITY AND PRIVACY Evaluate data storage, transfer, and protection protocols. Number of security breaches; system vulnerability scores. To protect customer data and company reputation. ISO/IEC 27001; NIST cybersecurity framework. Quarterly or after any system updates. YES To measure potential vulnerabilities. YES Due to evolving cyber threats. Installing charging infrastructure without following local environmental and zoning laws can result in forced removal of charging stations, legal actions, fines, and delays in expanding the charging network. ENVIRONMENTAL AND ZONING REGULATIONS Review installation sites against environmental and zoning laws. Annually and before establishing a new station. Compliance is based on adherence to local laws. Number of legal complaints; fines incurred. To avoid legal issues and maintain community relations. Local zoning and environmental regulations; EPA guidelines. NO YES Especially when regulations change. NAME NAME, TITLE OF ASSESSOR MM/DD/YY DATE OF ASSESSMENT COMPLIANCE RISK ASSESSMENT MATRIX TEMPLATE PRESENTATION PROJECT REPORT
COMPLIANCE RISK ASSESSMENT MATRIX RISK ASSESSMENT FRAMEWORK TOOLS UTILIZED FOR COMPLIANCE AND RISK ASSESSMENT RECOMMENDED METRICS USED TO MEASURE COMPLIANCE AND RISK CONFIRM WHETHER OR NOT TO MONITOR RISK-LEVEL CHANGES OVER TIME AND WHY INTENDED USE OF COMPLIANCE AND RISK ASSESSMENT RISK ASSESSMENT REQUIREMENTS FREQUENCY OF RISK ASSESSMENT CONFIRM WHETHER OR NOT RISK IS QUANTIFIED AND WHY TOPIC RISK PROJECT REPORT
COMPLIANCE RISK ASSESSMENT MATRIX EXAMPLE RISK ASSESSMENT FRAMEWORK TOOLS UTILIZED FOR COMPLIANCE AND RISK ASSESSMENT RECOMMENDED METRICS USED TO MEASURE COMPLIANCE AND RISK CONFIRM WHETHER OR NOT TO MONITOR RISK-LEVEL CHANGES OVER TIME AND WHY INTENDED USE OF COMPLIANCE AND RISK ASSESSMENT RISK ASSESSMENT REQUIREMENTS FREQUENCY OF RISK ASSESSMENT CONFIRM WHETHER OR NOT RISK IS QUANTIFIED AND WHY TOPIC RISK Failing to adhere to electrical safety standards can result in fires, electric shocks, or other hazards that could harm users, damage property, and expose the company to significant liability and negative publicity. Evaluate the integrity, grounding, and insulation of all the company's electrical components. ELECTRICAL SAFETY STANDARDS National Electrical Code (NEC); local safety standards. Biannually and after any maintenance or upgrades. To ensure safety measures meet industry benchmarks. Number of incidents (fires, shocks); inspection pass rate. To identify potential wear and tear or systemic issues. To ensure user safety and reduce liability. YES YES Without following interconnection standards, there's a potential for grid instability. This can lead to service disruptions, possible fines from regulatory bodies, and damage to grid infrastructure. Assess the quality and stability of the company's grid connectivity. Especially when expanding or when the grid is undergoing major changes. INTERCONNECTI ON STANDARDS To ensure seamless integration with the grid. Grid downtime duration; quality of connection scores. To ensure stable service and avoid penalties. IEEE standards; local grid regulations. Annually. YES YES ACCESSIBILITY AND ADA (AMERICANS WITH DISABILITIES ACT) COMPLIANCE (OR EQUIVALENT LEGISLATION IN OTHER JURISDICTIONS) Failure to ensure charging- station accessibility can lead to legal complaints, potential fines, and damage to the company's reputation for lack of inclusivity. Audit charging stations for ease of access and ADA compliance. Number of accessibility complaints; inspection pass rate. Annually and after any structural changes. Compliance is binary (i.e., either compliant or not). To ensure continued accessibility. To avoid legal actions and foster inclusivity. ADA guidelines; local accessibility standards. NO YES If customer data (like payment information or usage statistics) isn't handled securely, the company could face data breaches, leading to legal action, financial penalties, and loss of customer trust. Evaluate data storage, transfer, and protection protocols. DATA SECURITY AND PRIVACY Quarterly or after any system updates. To measure potential vulnerabilities. Number of security breaches; system vulnerability scores. Due to evolving cyber threats. To protect customer data and company reputation. ISO/IEC 27001; NIST cybersecurity framework. YES YES Installing charging infrastructure without following local environmental and zoning laws can result in forced removal of charging stations, legal actions, fines, and delays in expanding the charging network. Local zoning and environmental regulations; EPA guidelines. ENVIRONMENTAL AND ZONING REGULATIONS Review installation sites against environmental and zoning laws. To avoid legal issues and maintain community relations. Annually and before establishing a new station. Compliance is based on adherence to local laws. Number of legal complaints; fines incurred. Especially when regulations change. NO YES PROJECT REPORT
DISCLAIMER Any articles, templates, or information provided by Smartsheet on the website are for reference only. While we strive to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability with respect to the website or the information, articles, templates, or related graphics contained on the website. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk. PROJECT REPORT