Comparison of Protease Inhibitors in ARTEMIS Study
This study compares the efficacy and safety of different protease inhibitors (PIs) including ATV, ATV/r, LPV/r, FPV/r, DRV/r, and SQV/r in HIV treatment. The ARTEMIS study specifically focuses on comparing DRV/r and LPV/r in combination with TDF/FTC in ARV-naive patients. Results show non-inferiority of DRV/r over LPV/r at week 48, with superior virologic outcomes and similar safety profiles. Baseline characteristics, patient disposition, and response to treatment are detailed, indicating the potential benefits of DRV/r in HIV therapy.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
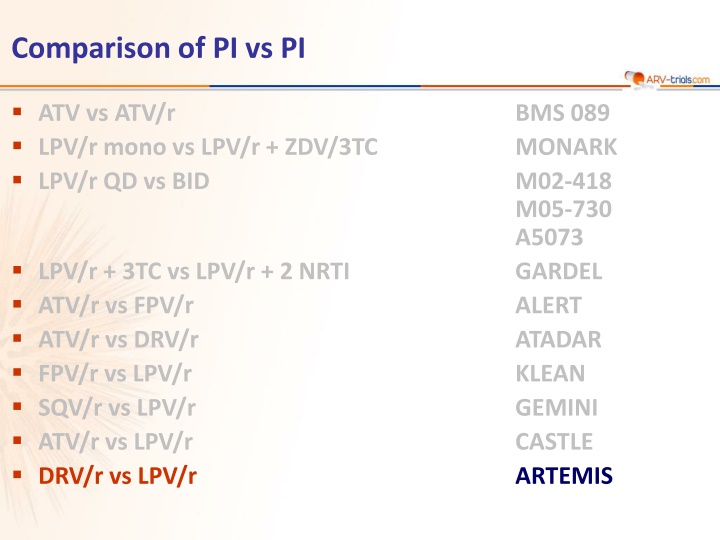
Comparison of PI vs PI ATV vs ATV/r LPV/r mono vs LPV/r + ZDV/3TC LPV/r QD vs BID BMS 089 MONARK M02-418 M05-730 A5073 GARDEL ALERT ATADAR KLEAN GEMINI CASTLE ARTEMIS LPV/r + 3TC vs LPV/r + 2 NRTI ATV/r vs FPV/r ATV/r vs DRV/r FPV/r vs LPV/r SQV/r vs LPV/r ATV/r vs LPV/r DRV/r vs LPV/r
ARTEMIS Study: DRV/r QD vs LPV/r (BID or QD), in combination with TDF/FTC Design Randomisation* 1 : 1 Open-label W48 W192 N = 343 DRV/r 800/100 mg QD > 18 years ARV-na ve TDF/FTC fdc QD LPV/r 400/100 mg BID or 800/200 mg QD TDF/FTC fdc QD HIV RNA > 5,000 c/mL Any CD4 cell count N = 346 *Randomisation was stratified by HIV RNA (< or > 100,000 c/mL) and CD4 (< or > 200/mm3) at screening Objective Non inferiority of DRV/r vs LPV/r at W48: % HIV RNA < 50 c/mL by per-protocol TLOVR analysis (lower margin of the 2-sided 95% CI for the difference = - 12%, 90% power). Superiority tested by ITT if non inferiority established Ortiz R. AIDS 2008;22:1389-97 ARTEMIS
ARTEMIS Study: DRV/r QD vs LPV/r (BID or QD), in combination with TDF/FTC Baseline characteristics and patient disposition DRV/r N = 343 * LPV/r ** N = 346 Mean age, years 36 35 Female 30% 30% Caucasian/Hispanic/Other 40% / 23% / 37% 44% / 21% / 35% HIV RNA (log10c/mL), mean CD4 cell count (/mm3), median 4.86 + 0.64 4.84 + 0.60 228 218 Hepatitis B and/or C coinfection 13% 14% Discontinuation by W48 12% 16% For virologic failure 2 (< 1%) 6 (2%) For adverse event 12 (3%) 24 (7%) * 3 patients excluded for the per-protocol analysis (did not received study medication or received disallowed therapy for more than 1 week) ** LPV/r was administered BID or QD according to investigator and/or patient preference (77% received BID, 15% QD and 8% both; 15% received soft-gel capsules, 2% tablets and 83% switched from SGC to tablets) Ortiz R. AIDS 2008;22:1389-97 ARTEMIS
ARTEMIS Study: DRV/r QD vs LPV/r (BID or QD), in combination with TDF/FTC Response to treatment at week 48 HIV RNA < 50 c/mL (TLOVR) % Per protocol ITT HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at W48 (per-protocol, TLOVR) by baseline stratification factors 100 84 84 78 78 DRV/r (%) LPV/r (%) Baseline 75 RNA < 5 log10c/mL RNA > 5 log10c/mL 86 79 * 85 67 * 50 CD4 > 200/mm3 CD4 < 200/mm3 87 79 84 70 25 * P < 0.05 N = 343 346 343 346 0 DRV/r LPV/r DRV/r LPV/r Median CD4/mm3increase at W48 (ITT, NC = F): 137 (DRV/r) vs 141 (LPV/r) 95% CI 95% CI for the difference = (- 0.1; 11) (P < 0.001) Non inferiority for the difference = (- 0.3; 11) Test for superiority (P = 0.062) Ortiz R. AIDS 2008;22:1389-97 ARTEMIS
ARTEMIS Study: DRV/r QD vs LPV/r (BID or QD), in combination with TDF/FTC Virologic failure at Week 48 Definition: HIV RNA never suppressed below 50 c/mL at W24 or confirmed HIV RNA > 50 c/mL after achieving < 50 c/mL or last observed HIV RNA > 50 c/mL followed by discontinuation Resistance data DRV/r N = 343 LPV/r N = 346 Virologic failure 34 (10%) 49 (14%) Patients in genotypic analysis (HIV RNA > 1,000 c/mL) 10 * 18 Protease inhibitor resistance mutation emergence 0 1 ** M184I/V 1 2 * 1 patient with HIV RNA > 1,000 c/mL did not have genotype available ** A71T and V77I Ortiz R. AIDS 2008;22:1389-97 ARTEMIS
ARTEMIS Study: DRV/r QD vs LPV/r (BID or QD), in combination with TDF/FTC W48 Safety: DRV/r vs LPV/r Discontinuations for adverse events (AE) were significantly less frequent in the DRV/r group: 3% vs 7% (P < 0.05) Rate of serious AE was not significantly different: 7% vs 12% Incidence of grade 2 to 4 gastrointestinal AE was significantly lower in the DRV/r group: 7% vs 14% (P < 0.01); these were mainly diarrhoea: 4% vs 10% (P < 0.01) Rash incidence was not significantly different: 3% vs 1%; 1 case of Stevens-Johnson occurred in the DRV/r group No patients discontinued because of renal events Mean increases in triglycerides and total cholesterol were less pronounced with DRV/r; grade 2 to 4 elevations in triglycerides and total cholesterol were significantly less frequent with DRV/r: 3% vs 11% and 13% vs 23%, respectively Hepatic safety was similar in both groups Ortiz R. AIDS 2008;22:1389-97 ARTEMIS
ARTEMIS Study: DRV/r QD vs LPV/r (BID or QD), in combination with TDF/FTC Summary Conclusion (W48) DRV/r QD is non inferior to LPV/r, when co-administered with TDF/FTC(1) Greater virologic response, at W48 (HIV RNA < 50 c/mL), of DRV/r as compared with LPV/r in patients with high pre treatment HIV RNA (significant difference) or low CD4 count Lower incidence of diarrhoea with DRV/r vs LPV/r Lipid elevations were less pronounced with DRV/r Ortiz R. AIDS 2008;22:1389-97
ARTEMIS Study: DRV/r QD vs LPV/r (BID or QD), in combination with TDF/FTC Overview at week 96 At W96(2), significantly more DRV/r (79%) than LPV/r (71%) patients had HIV RNA < 50 c/mL confirming non inferiority and superiority (P = 0.012; ITT) in virologic response Safety outcomes confirmed W48 results: more favourable gastrointestinal and lipid profile of DRV/r QD Lipid-lowering agents use by W96: 8% LPV/r vs 7% DRV/r Overall, discontinuation for adverse events occurred in 4% of DRV/r patients vs 9% of LPV/r patients Mills AM. AIDS 2009;23:1679-88
ARTEMIS Study: DRV/r QD vs LPV/r (BID or QD), in combination with TDF/FTC Patient disposition at W96 and W192 DRV/r N = 343 LPV/r N = 346 p Discontinuation by W48 12% 16% For virologic failure 2 (< 1%) 6 (2%) For adverse event 12 (3%) 24 (7%) Discontinuation by W96 17.2% 23.4% Discontinuation by W192 24.8% 32.9% For virologic failure 5 9 For adverse event 16 (4.7%) 44 (12.7%) 0.005 For pregnancy 9 6 Lost to follow-up 21 17 Withdrew consent/non compliance 26 26 Other 8 12 Ortiz R. AIDS 2008;22:1389-97 ; Mills AM. AIDS 2009;23:1679-88 ; Orkin C. HIV Med 2012;14:49-59 ARTEMIS
ARTEMIS Study: DRV/r QD vs LPV/r (BID or QD), in combination with TDF/FTC Final (week 192) analysis % HIV RNA < 50 c/mL (TLOVR) HIV RNA < 50 c/mL (ITT, TLOVR) by baseline stratification factors 100 Per protocol ITT DRV/ r (%) LPV/r (%) 69.1 75 Baseline p 68.8 57.1 57.2 RNA < 5 log10 c/mL RNA > 5 log10 c/mL 50 69.5 67.5 60.2 51.7 0.038 0.012 25 CD4 > 200/mm3 CD4 < 200/mm3 Median CD4/mm3increase at W192 (ITT, NC = F): + 258 (DRV/r) vs + 263 (LPV/r) 71.3 65.2 59.6 54.1 0.014 0.052 N = 340 345 343 346 0 DRV/r LPV/r DRV/r LPV/r Difference (95% CI) = 12.0% (4.8 ; 19.2) (P < 0.001) Superiority Difference (95% CI) = 11.6% (4.4 ; 18.8) (P < 0.001) Superiority Orkin C. HIV Med 2012;14:49-59 ARTEMIS
ARTEMIS Study: DRV/r QD vs LPV/r (BID or QD), in combination with TDF/FTC Resistance data at W192 DRV/r N = 343 LPV/r N = 346 Virologic failure 55 (16.0%) 71 (20.5%) Never suppressed 16 22 Rebounders 39 49 Resistance testing (HIV RNA > 50 c/mL) 43 57 Protease inhibitor resistance mutation emergence* 4** 9 Major PI mutation 0 0 4 7 NRTI resistance mutations * M184I/V = 4 M184I/V K70E = 1 * At endpoint = last time point : with available genotype ** L10V, N = 1 ; V11I, N = 1 ; I13V, N = 1 ; I13V + G16E, N = 1 Orkin C. HIV Med 2012;14:49-59 ARTEMIS
ARTEMIS Study: DRV/r QD vs LPV/r (BID or QD), in combination with TDF/FTC Safety W192 analysis Data similar to that seen at W96 No new emerging AE with longer-term follow-up Grade 2-4 treatment-related diarrhoea was significantly less frequent with DRV/r than with LPV/r (5.0% vs. 11.3%, respectively; P = 0.003) DRV/r was associated with smaller median increases in total cholesterol and triglyceride levels than LPV/r. Changes in low- and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol were similar between groups Similar increases in aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase for DRV/r and LPV/r were observed Orkin C. HIV Med 2012;14:49-59 ARTEMIS