Communication and Interpersonal Relationships
Communication is a vital element in human interaction, encompassing various levels such as intrapersonal, interpersonal, group, and public speaking. It involves sending and receiving messages to meet diverse needs and desires. Understanding different forms of communication, from internal dialogue to face-to-face conversations, enhances relationships and fosters effective information exchange.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Communication and interpersonal relationships
INTRODUCTION Communication is a dynamic, reciprocal process of sending and receiving messages. Communication is more than the act of talking and listening. From the first cry of a newborn to the whisper of a person who is dying, the primary purpose of a information and obtain a response. People use communication to meet their physical, psychosocial, emotional and spiritual needs communication is to share
DEFINITION Communication is any act by which one person gives to or receives from person information about that person s needs desires, perception, knowledge Communication may unintentional, may involve unconventional signals, may take linguistic or non-linguistic forms and may occur through spoken or other modes. or affective be intentional conventional or states . or
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION INTRAPERSONAL COMMUNICATION INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION GROUP COMMUNICATION PUBLIC SPEAKING
INTRAPERSONAL COMMUNICATION It is conscious internal dialogue, sometimes known as self-talk. It is language use or thought internal to the communicator. The individual becomes his or her own sender and receiver, providing feedback to him or herself in an ongoing internal process. It can be useful to communication occurring individual in a model which contains a sender, receiver and feedback loop. envision intrapersonal in the mind of the
INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION It is communication between two or more people. Face to Face conversation between two people is the most frequent form of interpersonalcommunication. Nurses use interpersonal communication to gather information during assessment, to teach about health issues to explain care and to provide comfort and support.
GROUPCOMMUNICATION It is interaction that occurs among several people. Small group communication occurs when you engage in an exchange of ideas with two or more individuals at the same time.
PUBLICSPEAKING It is a unique form of group communication. Generally hundreds of people, and varying degrees of interaction occur. Speaker may deliver a speech talk directly with a group of audience members or have open discussion with the group. It is at the heart of our economy,society and politics. Nurses often engage in public speaking to educate groups of people about health issues the speakeraddresses a dozen to
THE COMMUNICATION PROCESS Communication requires a sender, a message, a receiver and a response or feedback. Communication is a two-way process involving the sending and the receiving of a message. Because the intent of communication is to elicit a response the process of ongoing; the receiver of the message then becomes the sender of a response, and the original sender then becomes the receiver.
CommunicationProcess Message Source (sender) Channel Receiver Feedback(response)
The Communication Process Message Barrier SENDER (encodes) RECEIVER (decodes) Barrier Feedback/Response
Modes Modes of of communication communication Verbal communication Nonverbal communication
Characteristics of verbal and nonverbal modes of communication VERBAL Pace and intonation Simplicity Clarity and brevity Timing and relevance Adaptability Credibility Humor NONVERBAL Facialexpression Posture and Gait Personal Appearance Gestures Touch
Characteristics of effective communicator An effective nonverbal communicator: Relaxes Opens up Leans toward the other person Establishes eye contact Shows appropriate facial expressions An effective verbal communicator: Clarifies Listens Encourages empathically Recognizes Restates/repeats
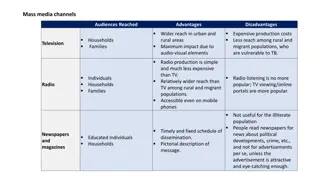
What are the most common ways we communicate? Written Word
Factors influencing the communication process Development, Gender Values And Perceptions Personal Space Territoriality Roles And Relationships, Time Environment Congruence Interpersonalattitudes.
THERAPEUTIC COMMUNICATION Therapeutic nurses use their communication in such a way that it will be benefit to their patient. communication means that Therapeutic normal communication in that it introduces an element of empathy into what can be traumatic experience for the patient and also the patient are made to feel validated. communication differs from
Importance of therapeutic communication It impels a feeling of comfort in the face of patient. To increase psychological distress information to determine the illness, assessing and modifying the behaviour and providing health information. self-worth or decrease collecting by
Therapeutic communication techniques Using silence Being specific and tentative Using open-ended questions Using touch Restating or paraphrasing Seeking clarification Perception checking or seeking consensual validation Offering self Acknowledging Giving information Clarifying time or sequence Presenting reality Focusing Reflecting Summarizing and planning
Barriers to communication Stereotyping Agreeing and disagreeing Being defensive Challenging Probing Testing Rejecting Changing topics and subjects Unwanted reassuarence Passing judgement Giving common advice
Five ways to facilitate therapeutic communication Maintain patient centered teaching Suppress prejudices Create a therapeutic environment Be alert to non verbal clues Establish a trusting relationship
Interpersonal relationship An interpersonal relationship is a strong deep or close association / acquaintance between two or more people that may range in duration from brief to enduring. The nurse is an important of the health care team that must work in co-operation and harmony for the care of the patient. This co-operation and harmony depends upon the IPR that is maintained among the members of the health care team.
Theoretical assertion The purpose of nursing achieved though the establishment of a human to human relationship. The human condition is shared by all human being. Most people at one time or another and in varying degrees will experience joy,contentment, happiness and love. All persons, at sometime in their lives will be confronted by illness and pain. The quality and quantity of nursing care delivered to an ill human being is greatly influenced by nurse s perception of the client. The term patient and nurses are stereotyped and only useful for communicate economy.
Theoretical assertion (cont.) The roles of the nurse and patients must be establish a human to human relatedness. Illness and suffering are spiritual encounters as well as emotional physical experience. Communication process enables the nurses to establish a human to human relationship and thereby fulfil the purpose of the nursing profession. Individual can be assisted top find meaning in the experience of illness and suffering then individual can cope with the problem exchanged by these experience. transcended to
Theoretical assertion (cont.) The spiritual and ethical values of the nurse, about illness suffering will determine the excellent top which she will be able to assist individuals and families to find meaning these difficult experiences. It is the responsibility of the professional nurse practitioner to assist individuals and families to find meaning in illness and suffering.
Principles of IPR Learn everyone s, name and never address anyone by nick name. Respect every one s individually. Each member of a team is as important as other.( Keep up the status of every member) Do not force anything on anybody. Keep emotions under control. Do not give and take personal favour. Don t be afraid to admit ignorance
Principles of IPR (cont.) The team leader should not make any excuse regarding his or her responsibility. Develop the habits attention on the problem. Do not do or say anything others faith. Give importance to others and practice justice of listening and focus that will disturb
Characteristics of IPR Helping relationship is a therapeutic relationship in nursing which promoting a psychological climate that brings a positive change in the client and promote his group. Facilitative characteristics Action oriented
Facilitative characteristics Trust It may be defined as the belief that other will provide in terms of need and distress trust fosters open therapeutic communication to foster the nurse sact consistently, reliably and competently. Empathy It s the ability to understand and enter the client s frame of reference. comprehensive and sharing the client s frame of reference beginning with the problem that the client recognises in other words. It is a phase of sensitive and objective look at experiences. Empathy is sensing, what another person
Facilitative characteristics (cont.) Caring It is having a positive regard for another person. It is basic in helping relationship. Nurses can show caring by expediting clients as who they are and respecting them as individuals. It promotes trust and decrease anxiety and distress. Autonomy and mutuality It is the ability to the self director. Mutuality involves sharing with important in any helping relationship. another. These are
Facilitative characteristics (cont.) Genuiness It is considered to be most basic of helping conditions. The helper needs you be aware of his own feelings. He should be comfortable with who he is so that he does not lookout his own feelings from himself. Non possessive warmth It simply means unconditional positive regard, respect for others and praising the other
Interpersonal communication It occurs between two or more person with a goal to exchange messages. Most of the nurse s day is spent communicating with the patient, family members and member of health care team. The nurses ability to communicate effectively at this level influences the nurses interpersonal sharing, problem solving, goal attainment, team building and effectiveness in critical nursing roles. (E.g.:- care giver, teacher, counsellor, leader, manager, and patient advocate)
Mid-range theory of IPR Hildegard Peplau s (1952:1997) mid-range theory of interpersonal relationships is considered an essential theory frame work for the study of interpersonal relationships. The model describes how the nurse-client relationship can identification and accomplishments of therapeutic goals top enhance client and family well-being. facilitate the In today s health care environment nurse-client relationships are of short duration concise and effective. Despite the brevity of the relationship, Peplau s basic principles partnership and terminating a relationship remain relevant. Peplau s frame work for interpersonal relationships is applicable to all areas of nursing.
Major concepts the theory explains the purpose of nursing to help others identify their felt difficulties. nurses should apply principles of human relations to the problems that arise at all levels of experience. Peplau s theory explains the phases of interpersonal process, roles in nursing studying nursing as an interpersonalprocess. Nursing is an interpersonal process because it involves interaction between two or more individuals with a common goal. The attainment of goal is achieved through the use of a series of steps following a series of pattern. The nurse and patient work together so both become mature and knowledgeable in theprocess. situations and methods of
Definitions Person-A developing organism that tries to reduce anxiety caused by needs. Environment- Existing forces outside the organism and in the context of culture. Health-A word symbol that implies forward movement of personality and other ongoing human process in the direction of creative, constructive, productive, personal and community living. Nursing-A significant therapeutic interpersonal process. It functions cooperatively with other human process that makes health possible for individuals in communities
Peplaus six nursing roles Stranger: Receives the client the same way one meets a stranger in other life situations, provides an accepting climate that buildstrust. Resource role: Answers questions, interprets clinical treatment data, and givesinformation. Teaching role: Gives instructions and provides training, involves analysis and synthesis of the learnerexperience. Counselling role: Helps client understand and integrate the meaning of current life circumstances provide guidance and encouragementto makechanges. Surrogate role: Helps dependence, interdependence and independence and acts on client s behalf as anadvocate. Leadership role: Helps responsibility for meeting treatment goals in a mutually satisfying way. client clarify domains of client assume maximum
ADDITIONAL ROLES INCLUDE Technicalexpert Consultant Health teacher Tutor Socializing agent Safetyagent Manager of environment Mediator Administrator Recorder observer Researcher
Phases of interpersonal relationship The nurse-client relation is therapeutic not social in nature. It is always client centred and goal directed. It is objective rather than subjective. The intent of a professional relationship is for client behaviour to change. It is a limited relationship, with the goal of helping the client find more satisfying behaviour patterns increase self worth. It is not for mutual satisfaction. and coping strategies and
Phases of interpersonal relationship (cont.) Peplau s developmental stages parallel to the nursingprocess. The orientation phase assessment phase of the nursingprocess. The identification component of the working phase corresponds to the planning phase, where as the exploitation implementation phase. The final resolution phase of the relationship corresponds to the evaluation phase of the nursing process. correlates with the phase parallels the
Pre interaction phase The pre interaction phase is the only one in which the client does not directly participate. Awareness of professional goal is important. The preinteraction phase occurs before you meet the client. In this phase you will gather information about the client. In this phase, the nurse and client do not have direct communication. First phase in Peplau s theory is orientation phase.
Orientation phase The nurse enters the relationship in the Stranger role and begins the process of developing trust by providing the client with basic information about the nurse and essential information about the purpose, nature, and time available for the relationship. It is also referred to as the introductory or the prehelping phase is important because it sets the tone for the rest of the relationship.
Orientation phase (cont.) It begins when you meet the client. The goal in this phase is and trust. This phase followed by an initial exchange of information. During this phase communication occurs. to establish rapport begins with introductions, verbal and nonverbal
Working phase / identification phase It is the planning phase. The conversation in the working phase turns active problem solving related to assess health care needs. Clients are able to discuss deeper, more difficult issues and experiment with new role and actions.
Working phase/ identification phase (cont.) Working phase focuses on self direction and self management to whatever extent is possible in promoting the clients health and well-being. It is the active part of the relationship. During this phase, caring is communicated, feelings are expressed, mutual honest verbal and nonverbal expression occurs. Key communication goals are to assist the client feelings and concerns thoughts and respect is maintained, and to clarify
EXPLOITATIONPHASE Use of professional assistance for problem solving alternatives. Individual feels as an integral part of the helping environment. The principles of interview techniques must be used in order to explore, understand and adequately, deal with the underlying problem. Patient may fluctuate on independence. Nurse aids the patient in exploiting all avenues of help and progress made towards the final step.
Termination phase In the termination phase, the nurse and client evaluate the client s responses to treatment, and explore the meaning of the relationship and what goals have been achieved. Nurses need to be sufficiently aware of their own feelings so that they may use them constructively without imposing them on the client. Patient drifts away and breaks bond with nurse and healthier emotional balance is demonstrated and both become mature individuals.
Termination phase (cont.) The termination phase is the conclusion of the relationship, whether at the end of the nurse s shift or the unit, facility or discharge from service. If communication has been effective, the termination phase prepares the nurse and interactions on the client s client for future
Interpersonal theory and nursing process Both are sequential and focus on therapeutic relationship. Both use problem solving techniques for the nurse and patient to collaborate on, with the end purpose of meeting the patient needs.
ASSESSMENT Data (Continuous). May not be a felt need. ORIENTATION Non collection Felt need. Define needs IDENTIFICATION Interdependent goal setting collection and analysis continuous data NURSING DIAGNONSIS PLANNING Mutually set goals IMPLEMENTATION Plans mutually set goals May be accomplished by patient nurse or family. EXPLOITATION Patient and drawing help Patient initiated initiated towards achievement of actively seeking EVALUATION Based on mutually expectedbehaviour May led to termination and initiation RESOLUTION Occurs after other phases are completed successfully. Leads to termination.