Commonly Used Medications in ACLS: Adenosine, Amiodarone, Atropine, Dopamine, Epinephrine
Adenosine is used for SVT, Amiodarone for VT/VF, Atropine for bradycardia, Dopamine for shock, and Epinephrine for cardiac arrest. Each medication has specific dosages and side effects. These drugs play crucial roles in advanced cardiac life support scenarios.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Commonly Used Medications in ACLS .
Adenosine Uses : Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Dosage : 1st dose = 6 mg rapid IV push followed by saline bolus, 2nd dose = 12 mg rapid IV push in 1-2 minutes (double syringe) Side Effects : Headache, dizziness, metallic taste, dyspnea, hypotension, bradycardia or palpitations, nausea, flushing, sweating
Amiodarone Uses : Unstable VT with pulses, VF, VT without pulse and unresponsive to shock Dosage : 300 mg rapid bolus with 2nd dose of 150 mg if necessary to a maximum of 2.2 grams over 24 hours Side Effects : significant hypotension, dizziness bradycardia, torsades de pointes, tremors
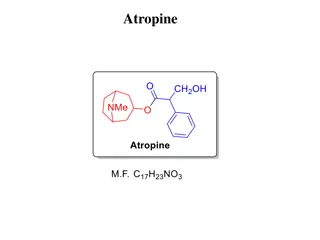
Atropine Uses : Symptomatic bradycardia, organophosphate overdoses Dosage : Bradycardia: 0.5 mg IV every 3-5 minutes with 3 mg max dose; May be given by ETT Side Effects : flushing, blurred vision, dry mouth, photophobia, pupil dilation, constipation, urinary retention
Dopamine Uses : Can be given in bradycardia after Atropine, Can be given for Systolic BP < 100 mm Hg with signs of shock Dosage : 2 to 20 mcg/kg per minute infusion titrated to response Side Effects : Headache, palpitations, PVC, VT, SVT, nausea/vomiting
Epinephrine Uses : Cardiac arrest, Anaphylaxis, Symptomatic bradycardia after atropine, Shock when pacing and atropine are not effective Dosage : (1:1000) per ETT every 3 to 5 minutes; follow with 0.1-0.5 mcg/kg/min infusion titrated to response Symptomatic bradycardia or shock: 2-10 mcg/minute infusion titrated to response Cardiac arrest: 1.0 mg (1:10000) IV or 2-2.5 mg Side Effects : Tremors, dizziness, SVT, VT, palpitations, chest pain, hypertension, nausea, vomiting, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, vasoconstriction
Lidocaine Uses : Cardiac arrest from VF or Ventricular Tachycardia, Wide complex tachycardia (QT prolong) Dosage : Cardiac Arrest: 1-1.5 mg/kg IV bolus; may repeat twice at half dose in 5-10 minutes to total of 3mg/kg; followed with infusion of 1-4 mg per minute infusion Wide complex tachycardia with pulse: 0.5-1.5 mg/kg IV; may repeat twice at half dose in 5-10 minutes to total of 3mg/kg; followed with infusion of 1-4 mg per minute infusion Side Effects : Seizures, bradycardia, dyspnea, respiratory depression, nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, tremor, drowsiness, tinnitus, blurred vision, hypotension, rash
Magnesium Sulfate Uses : Torsades de pointes; Hypo- magnesemia; Digitalis toxicity Dosage : Cardiac arrest due to hypomagnesemia or Torsades: 1-2 gram IV bolus Torsades with a pulse: 1-2 gram IV over 5-60 minutes followed by infusion at 0.5-1 gram per hour IV Side Effects : confusion, sedation, weakness, respiratory depression, hypotension