Childhood Kidney Disease
Kidney disease affects millions worldwide, including children at risk from an early age. Education, early detection, and healthy lifestyle promotion are crucial to combat preventable kidney diseases in children. Recent studies show an increase in kidney stone incidence among children, with unclear underlying causes. Diagnosis methods, symptoms, and potential genetic factors in pediatric kidney stone disease are highlighted, emphasizing the need for awareness and proactive healthcare.
Uploaded on Feb 24, 2025 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Kidney disease affects millions of people worldwide, including many children who may be at risk at an early age. It is therefore crucial that we encourage and facilitate education, early detection and a healthy life style in children, to fight the increase of preventable kidney diseases and to treat children with inborn and acquired disorders of the kidneys worldwide.
Shamir Tuchman, MD Children s National Medical Center
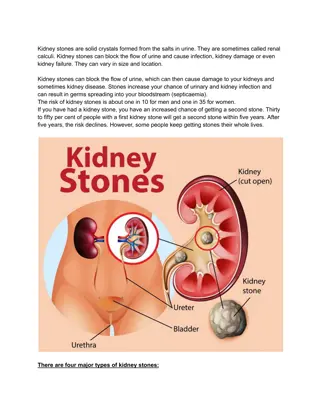
Kidney stone disease had been thought to affect primarily the adult population. Current evidence from several studies suggests a significant increase in the incidence among children. Incidence 18/100,000 patients (1999), 57/100,000 (2008) 5-fold increase in the diagnosis among children Historically, male preponderance in the incidence of pediatric kidney stone disease. More recent studies also show a rise in the incidence among females Sas et al. J Peds 2010
The underlying causes of the increased incidence of kidney stones among children are unclear. Improved diagnosis due to increased use of CT scanning Changes in activity levels among children Decreased fluid and increased sodium consumption The kidney stone trend parallels that of an increase in the incidence of obesity, though most studies suggest no relationship between high BMI and risk for kidney stones in children. 50% to 80% of children with kidney stones have been found to have a metabolic abnormality accounting for their kidney stone occurrence
The majority (50-80%) of idiopathic kidney stones in children are calcium-based Monogenetic disorders account for a small but important cause of kidney stone disease that often presents in young children. Associated with a high risk for recurrence of kidney stones May be associated with progressive chronic kidney disease
Most kidney stones are diagnosed through renal ultrasound or non-contrast CT scan after presentation with the following classic signs/symptoms: Unilateral low back or flank pain Nausea / vomiting Hematuria (microscopic or gross) Children are more likely than adults to present atypically without the above classic signs and symptoms
Children are most typically managed in the ER setting with: IV hydration IV narcotics and/or anti-inflammatory agents (ketorolac) Expulsive therapy (tamsulosin) Discussion with pediatric urologist regarding any need for acute urological intervention Kidney stone + fever is a true EMERGENCY!
In children, first-time kidney stone formation warrants a comprehensive evaluation Blood and urine testing are used to identify: 1. Abnormalities suggestive of monogenic disorder 2. Modifiable dietary risk factors The 24-hour urine stone risk factor analysis is the most important test to develop a preventative strategy Develop plan with increased water intake, dietary modifications, +/- medications to prevent further stone formation
The incidence of kidney stones in children is rising, but the reasons are unclear Suspect kidney stones in children presenting with severe back, flank, or abdominal pain, or hematuria Kidney stone + fever = true emergency Every child with a kidney stone warrants a comprehensive evaluation to help identify underlying etiology and best plan for prevention
Your pediatric nephrology community continues to work hard to improve clinical care, foster education, and advance the science regarding kidney disease in children! We appreciate your support and all you do for children s health care! Your pediatric nephrology community continues to work hard to improve clinical care, foster education, and advance the science regarding kidney disease in children! We appreciate your support and all you do for children s health care!