Challenges and Opportunities in Harnessing Human Capital Amid Rapid Demographic Change
Rapid demographic changes in many countries pose challenges for harnessing human capital effectively, with labor productivity stagnating and education systems falling short. As populations age at an unprecedented pace, the need to engage young people productively becomes urgent. Policy makers must go beyond labor market reforms, as younger individuals, particularly the lower-skilled, are at risk of withdrawing from the workforce. Active policies and programs have shown promise, highlighting the importance of intermediation and counseling over skills training.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
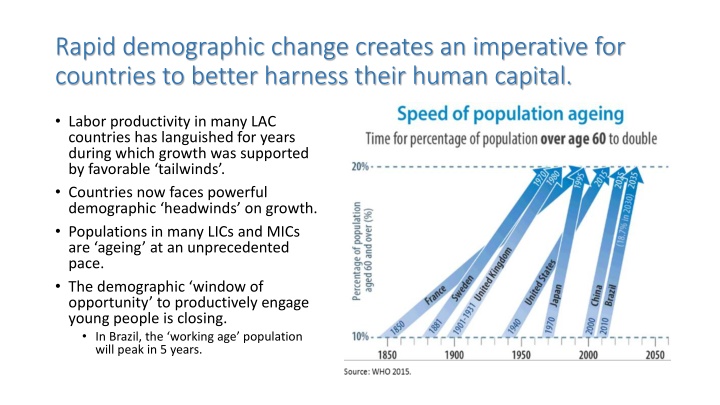
Rapid demographic change creates an imperative for countries to better harness their human capital. Labor productivity in many LAC countries has languished for years during which growth was supported by favorable tailwinds . Countries now faces powerful demographic headwinds on growth. Populations in many LICs and MICs are ageing at an unprecedented pace. The demographic window of opportunity to productively engage young people is closing. In Brazil, the working age population will peak in 5 years.
Education systems are falling short of expectations: Poor performance, repetition and dropouts. Repetition rates (lower secondary education) Structural Peers 1 BRICS 1.8 OECD 2.8 Regional Peers 5.9 Brazil 16 0.0 5.0 10.0 15.0 Drop out rates BRICS 3.1 OECD 4.1 Structural Peers 13 Regional Peers 14 Brazil 25 0.0 5.0 10.0 15.0 20.0 25.0 30.0 Source: WBG Brazil Expenditure Review, Education chapter
Younger people are more likely to withdraw from the labor force, particularly the lower skilled Change in Labor Force Participation (LFP) in Brazil - 2015-2003 (p.p.) 0.04 Skilled Skilled Skilled Skilled Skilled Skilled Skilled Skilled Skilled Skilled Unskilled Unskilled Unskilled Unskilled Unskilled Unskilled Unskilled Unskilled Unskilled Unskilled Low skilled Low skilled Low skilled Low skilled Low skilled Low skilled Low skilled Low skilled Low skilled Low skilled -0.01 15 to 18 19 to 24 25 to 54 55 to 64 65 and older 15 to 18 19 to 24 25 to 54 55 to 64 65 and older Female Male -0.06 -0.11 -0.16 Source: BR Skills and Jobs 2, using PNAD surveys
Policy makers have to look beyond reform of labor market regulation for solutions. Correlation between de- jure rigidity and youth unemployment is weak Youth unemployment versus rigidity BIH 4 SWZ MKD NAM ZAF ESP GMB MOZ GRC SRB SLB LCA LBY OMN HRV MNE ITA ARM COM TUN GAB EGY HTI LSO GEO VCT BWA CYP PRT SYR IRQ JAM JOR BHS YEM DOM HUN BRB SAU ALB IRL PRI GUY IRN LVA SWE DZA POL BGR LTU MUS FRA KEN CRI FJI BLZ STP BEL GBR Log of Youth unemployment SDN COL LBN IDN LKA 3 FIN EST URY ARG MAR SVN UKR CZE WSM UZB AFG SUR TUR LUX COG BRA CHL ZMB MRT TJK PHL MNG KGZ NZL RUS KWT SLV More active policies and programs have shown favorable results CIV AZE DNK MLT MDA SEN PAN PRY AUS ISL TON TGO ERI ECU GIN GNB ARE DJI CAF NLD AGO GNQ ISR NIC NGA PAK VUT MYS TTO CHN KOR IND AUT BGD NOR MEX PER HKG GHA BTN MLI TCD ZWE MWI HND CHE DEU 2 JPN ETH SGP MDV GTM TZA VNM PNG BFA BHR LBR NPL SLE BRN NER KAZ RWA THA UGA LAO BDI 1 MDG MMR BEN Intermediation, counseling and coaching are more cost effective than skills training. BLR QAT 0 0 .5 1 1.5 2 Log of rigidity Log of Unemp, youth total Fitted values