Causes, Pathology, and Treatments
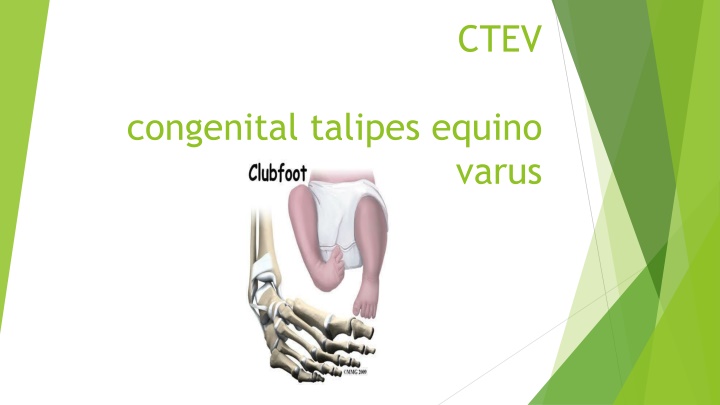
Clubfoot, also known as Congenital Talipes Equino Varus (CTEV), is a common foot deformity caused by muscular imbalance, resulting in ankle joint deformity and midtarsal joint normality. Pathologically, ligaments are stretched with muscle group changes. Treatment involves conservative methods, surgical intervention for severe cases, and physiotherapy management post-surgery.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CTEV congenital talipes equino varus
INTRODUCTION It is the commonest type of acquired foot deformity following muscular imbalance. It is produced either due to the weakness or paralysis of the dorsiflexors or spasticity in the planter flexion. The deformity is at the ankle joint while the midtarsal joint is normal. There is exaggeration of the longitudinal arch and broadening of the heads of the metatarsal due to the constant pressure of body weight on the forefoot as the heel is off the ground.
PATHOLOGY There is stretching of the ligaments on the dorsum of the foot,with shortening of the inferior-calcaneo-navicular or spring ligament,plantar fascia and other plantar ligaments. There is the lengthening of the anterior tibial group of muscles with shortening of the long toe flexors,peroneus longus and especially tendoachilles.
Treatment Conservative treatment:- Relaxed full range passive movement worked up to get maximum dorsiflexion and its passive maintenance is important. Whenever possible efforts should be made to get active contractions in the anterior tibial group of muscles to strengthen them. Gait training should be initiated with toe-pickup orthosis or Bkorthosis. Assisted standing on the affected foot stretches the tight plantar flexors with body weight.
Surgical Treatment:- Severe cases of fixed equinus deformity need surgical intervention. The surgical procedures performed are as follows:- Tendon release Triple arthrodesis
Physiotherapy management:- During immobilization,The joints free from immobilization are exercised vigorously. Toe movement are encouraged with the operated leg in elevation. Non-weight bearing crutch walking could be begun immediately. After removal of the plaster,maximum emphasis has to be placed on controlled passive,active assisted and eventually active dorsiflexion of the foot with toe extension. When weight bearing is allowed,weight transfers,balance and gait training and other modes of ambulation are taught.