Case Studies and Policy Framework for Cross-Policy Making and Project Planning
Explore case studies from various regions and sectors including water, agriculture, and energy, focusing on technical, nature-based, and governance solutions. Dive into the policy framework for water-energy-food coordination in Germany and the historical evolution of environmental politics, along with mechanisms and instruments for Nexus coordination in Germany.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Module III - Case Studies For cross-policy making and related project design and planning 15 September 2024 In cooperation with
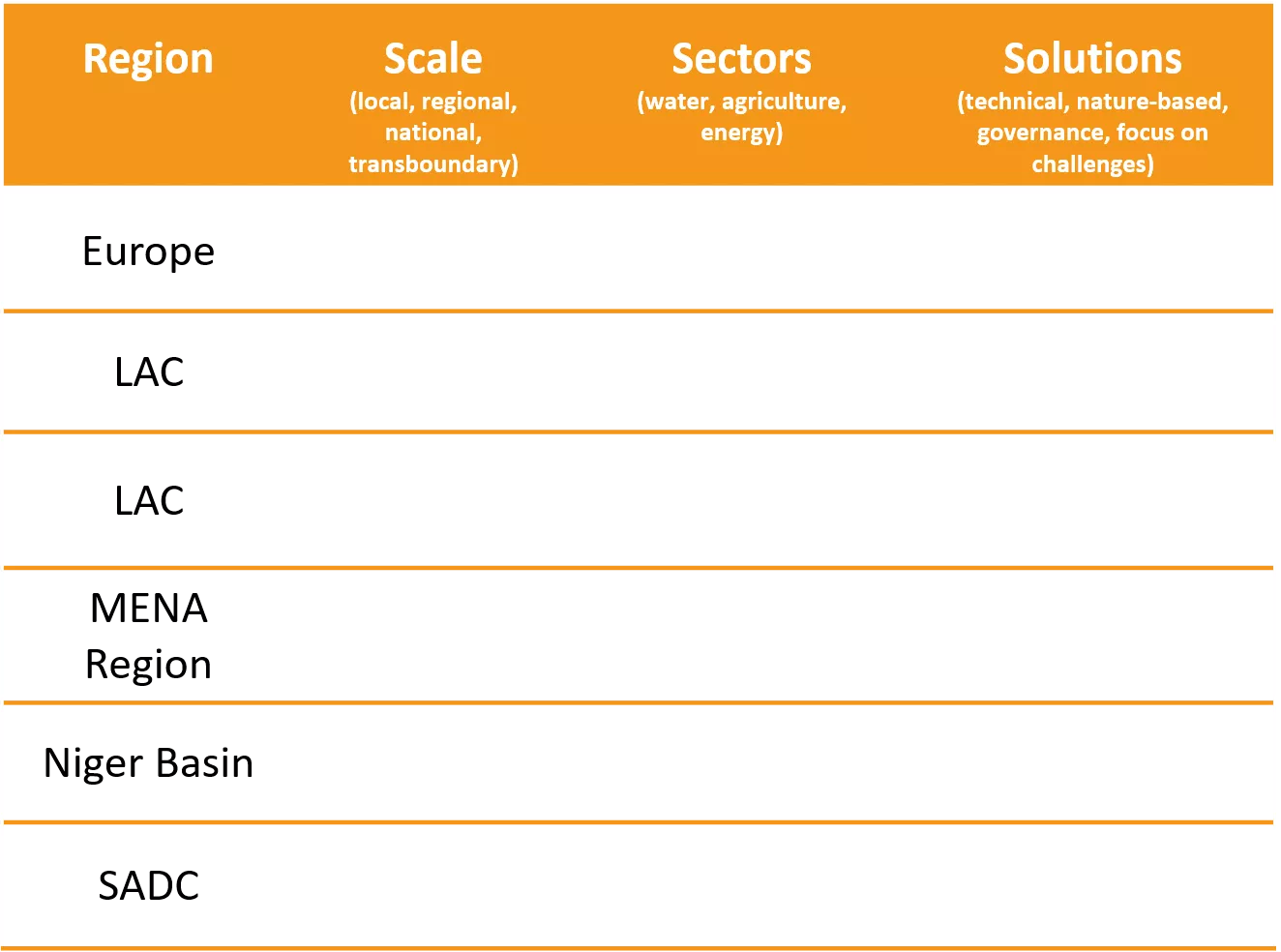
Overview of case studies Region Scale (local, regional, national, transboundary) Sectors (water, agriculture, energy) Solutions (technical, nature-based, governance, focus on challenges) Policy framework for WEF coordination, Germany Europe Hydropower in the Reventaz n River, Costa Rica LAC Mobile solar powered irrigation systems (SPIS), Bolivia LAC MENA Region The Sahara Forest Project, Jordan The Lagdo Dam in the valley of the Benue, Cameroon Niger Basin WEF-Nexus coordination in the lower Kafue basin, Zambia SADC 2
Policy Framework for WEF coordination and the amendment of the fertilizer ordinance in Germany Europe
Historical evolution of Germanys environmental politics Late 19thcentury and 1sthalf of 20thcentury Long tradition of environmental protection, 1stforest protection law in 1875 Development of common scientific and regulatory jargon Origins of environmental associations European rivers as critical for industrialisation, e.g. navigation pathways and ports Strong institutions for environmental protection at different levels Old river basin organisations Active civil engagement Rich regulatory legacies 2ndhalf of 20thcentury Federalism, decentralisation and (environmental) subsidiarity Green political parties and incorporation of environmental interests EU integration and harmonisation of environmental policies Multilevel governance Political commitment and environmental awareness Better incorporation of transboundary pressures 21st century Reorientation of policies towards ecological and energy transition Promotion of more integration to promote renewables, sustainable consumption & production, digitalisation and security of vital infrastructure Policy coherence and coordination as overarching challenge Increased use of coordination instruments Promotion of the Nexus of water, energy and land 4
Mechanism and Instruments for Nexus Coordination in Germany Joint Rules of Procedure of the Federal Ministries (GGO) Inter-ministerial committees and working groups as coordination institutions between discipline-specific ministries Federal Government as primary arbitration, mediation and coordinating body Ministerial conferences as coordination amongst ministries at state level Involvement of subject matter experts, relevant stakeholders and the general public in national policy processes 5
Coordination in decision-making processes in Germany Federal Government Overriding coordination function for policy Federal government acts in a mediating role Lead ministry (responsible for the concern) Inter-ministerial committees and working groups Interdisciplinary ministerial coordination Joint Rules of Procedure of the Federal Ministries Consultation process before law formulation Feedback provided Presentation of draft law Federal states AND Communal organisations Involvement of technical expertise Governed by underlying sector related laws Public Involvement Processes and functions Procedural instruments and policies Institution 6
Vertical Nexus Coordination in Germany Federal Government Federal States Main INFORMAL mechanism for vertical cooperation Main FORMAL mechanisms for vertical cooperation Special Ministerial Conferences Working groups Federal and state discussions Example: Conference of Environment Ministers Example: German Working Group on Water Issues Examples: political top-level talks, federal and state discussions Discuss common approaches and determine official positions of the involved sectors Discuss procedures in the enforcement of laws and law implementation problems, as well as design guidelines for the implementation of legislation The Conference of Environmental Ministers: coordination of implementation of existing environmentally relevant laws in the federal states 7
Intersectoral Coordination in Germany Example of the Fertilizer Ordinance Amendment 8
Fertilizer Ordinance Amendment Nitrogen in the Water-Energy-Security Nexus 9
Nitrate pollution of groundwater in Europe Annual average nitrate concentration in groundwater, 2016-2019 (EC 2021) 10
Fertilizer Ordinance Amendment Fertilizer Ordinance Regulates use of fertilizers (type, amount, methods of fertilizer application) Central instrument for the implementation of the European Nitrates Directive Objective: Prevent/reduce pollution of water bodies by nitrate All EU member states are obliged to document nitrate pollution In 2013 the EU initiated infringement proceedings against Germany and filed a complaint with the ECJ in 2016 because of non- compliance Trigger for the Fertilizer Ordinance Amendment 11
Objectives and trade-offs between agriculture and water sectors Provide nutrients for plants Increase agricultural yields Ensure food security Dispose of/use of manure Prevent high bureaucratic charges and additional investment costs (e.g. for storage of manure) Protect water sources from pollution Provide clean drinking water Minimize costs for drinking water supply Protect the environment and biodiversity 12
Amendment of the Fertilizer Ordinance: Intersectoral coordination 1. The working group was convened by the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (BMEL) to analyze the effectiveness of the D V and submitted significant proposals for changes Composed of representatives of various ministries, authorities, stakeholders and science (BMEL, BMUB, UBA, Chambers of Agriculture) Federal-state working group for the evaluation of the Fertilizer Ordinance (BLAG-D V) 2. Based on BLAG-D V working group results BMEL drafted first version of regulation Coordination with 2 ministries responsible for environment and economy (obligation to sign according to GGO): At all levels (head of division, head of department, state secretary, minister level) Hearings in the ministries (federal state and association representatives, science, interest groups such as environmental NGOs) Great motivation to reach an agreement due to the threat of lawsuits Interministerial coordination 13
Amendment of the Fertilizer Ordinance: Intersectoral coordination 3. Representatives present at hearings in government departments Joint statements by several scientific councils (including SRU, WBD and WBAE), supporting several points in the proposals of the BLAG-D V and calling for more far-reaching measures in other aspects Scientific Councils 4. Expert hearings in parliamentary bodies Hearing of representatives from science and associations (e.g. from chambers of agriculture, water associations, research) in the Bundestag Committee for Food and Agriculture and the Committee for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Building and Nuclear Safety 14
Amendment of the Fertilizer Ordinance: Intersectoral coordination 5. As part of the strategic environmental assessment, an environmental report was prepared that was made available to the public for comments The public was also given the opportunity to submit comments on the draft ordinance of the D V itself Public Participation 15
European Commission sues Germany before the European Court of Justice Federal Government: Involvement of Parliament and Federal Council: Public Expert Hearing in German Parliamentary Committee for Food and Agriculture / Regulative hearings / meetings discussions Overriding coordination function for policy Federal government acts in a mediating role Interdisciplinary ministerial coordination: involved ministries were: Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Building and Nuclear Safety; Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy Procedural Instrument Joint Rules of Procedure of the Federal Ministries Lead ministry : Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture Involvement and consultations with: Federal states AND Communal organisations: Federal States Working Group Evaluating the Fertiliser Ordinance Technical expertise: The Scientific Advisory Council for Fertiliser; the Scientific Advisory Board on Agricultural Policy, Food and Consumer Health Protection; German Advisory Council on the Environment The fertiliser law stipulates that the public are to be consulted regarding any changes to the fertiliser ordinance. Public Involvement Processes and functions Procedural instruments and policies Institution 16
Conclusions 1. A number of mechanisms are available to coordinate nexus issues at various levels in Germany. In principle, these instruments can be transferred to other countries, but must be adapted to the respective institutional and political structures. Coordination through negotiation processes between affected sectors predominates. However, strategic cross-sector approaches are gaining in importance. 2. 3. 17
Conclusions 4. In addition to horizontal coordination, vertical coordination between different political levels is also necessary to ensure conflict-free implementation. A binding regional regulatory framework (such as the European Water Framework Directive) can be an important stimulus for coordination at national level and possibly strengthen weaker interest groups. 5. 18
Conclusions 6. A broad, interdisciplinary consensus on the part of science can promote coordination between the sectors. Differing interests cannot always be resolved in the coordination process. 7. 19
Thank you for your time! 15 September 2024 In cooperation with

 undefined
undefined