Carbohydrates in Living Organisms
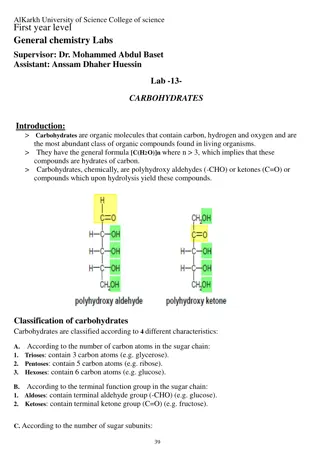
Carbohydrates, along with proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, are essential macromolecules in living organisms. They are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. Carbohydrates provide the main energy source for living things, with examples including glucose, fructose, and sucrose. Plants store carbohydrates as starch, while animals store them as glycogen. Cellulose, a complex carbohydrate, provides strength to plant structures. Carbohydrates play a crucial role in energy production and body functions, making them a vital component of a balanced diet.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic acids
Giant molecule Made from thousands or even hundreds of thousands of smaller molecules.
Formed by a process known as polymerization Large compounds are built by joining smaller ones together. Monomers joined together to form polymers
List examples of foods that contain carbohydrates Function of carbohydrates
Made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen 1:2:1 ratio
Carbohydrates provide living things their main energy source.
Simple sugar Glucose Fructose Galactose
Simple sugar Sucrose (table sugar)
Complex carbohydrate Many animals store excess sugar in the form of a polysaccharide Glycogen (stored in your liver and muscle)
Plants store their polysaccharide in the form of starch
Cellulose Tough and flexible fibers give plants much of their strength and rigidity Major component of wood and paper.
Food: energy and body functions, Calorie=heat needed to raise 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius. (1 Tbs, 1oF), 2200female, 2800male, balanced diet Nutrients: water, carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals. Water: Most important, chemical reactions take place in water. 1 liter per day Carbohydrates: energy, sugar=fast energy, starch=slow energy, fiber=not digested Fats: Need essential fatty acids, some vitamins are fat soluble, store energy, saturated=solid=bad, unsaturated=liquid=good, health risk Proteins: growth/repair, control chemical reactions, amino acids, essential amino acids Vitamins and Minerals: help chemical reactions, vitamins organic, minerals inorganic, not for energy, build body structures
What is it? Rice Bread Carrots Soda Pizza Banana Burger
Carbohydrates- energy for cells Saccharides Mono=simple Poly= starch and glycogen, Cellulose Proteins-biological function Peptide Support, enzymes, movement, hormones Fats- insulations and cell membranes Lipids
Objective: understand the structure and function of carbs (know the 3 different types of saccarhides and where they are found.) Carbohydrate Lab reports Movie (Nova)
Common Name Foods Function in body Monomer (Building blocks) Simple Polymer Complex Elements Shape Calories per Gram Other Facts saccharide (derived from the Greek sakchar, meaning sugar or sweetness
ANd9GcSnuUqNOTwVHa99sCWk6Ww6s6wQnGq1SRNOLegqcEfUXrNmDXy8JF5dHgANd9GcSnuUqNOTwVHa99sCWk6Ww6s6wQnGq1SRNOLegqcEfUXrNmDXy8JF5dHg
Common Name Foods Function in body Monomer (Building blocks) Simple Polymer Complex Elements Shape Calories per Gram Other Facts saccharide (derived from the Greek sakchar, meaning sugar or sweetness
Title Title Question: Hypothesis: Materials: Procedure: Data: Results/Analysis: Conclusion: Question: Hypothesis: Materials: Procedure: Data: Results/Analysis: Conclusion:
Objective: For students to known that different food contain different types of saccharide, Complex vs simple All sugars not created equal
Objective: For students to understand that proteins are broken down into Amino acids then put together to form new proteins in the body Proteins notes Testing for proteins
Common Name Common Name Foods Function in body Monomer (Building Block) Elements Shape Calories per Gram Other Facts
Antibodies - are specialized proteins involved in defending the body from antigens (foreign invaders). Contractile Proteins - are responsible for movement. Enzymes - are proteins that facilitate biochemical reactions. referred to as catalysts because they speed up chemical reactions. Hormonal Proteins - are messenger proteins which help to coordinate certain bodily activities Structural Proteins - are fibrous and stringy and provide support. Receptor Proteins- receives specific chemical signals from neighboring cells, allows thing in and out of cells Storage Proteins - store amino acids. Transport Proteins - are carrier proteins which move molecules from one place to another around the body.
Common Name Common Name Foods Function in body Monomer (Building Block) Elements Shape Calories per Gram Other Facts
Common Name Common Name Foods Function in body Monomer (Building Block) Elements Shape Calories per Gram Other Facts
Complete Protein All amino acids (animals) Incomplete Lack essential amino acids (plants) Animal and plant proteins same effect on body Pay attention what comes with the protein Fat or fiber
GOGGLES MUST BE ON AT ALL ALL TIMES
Cannot just eat a specific protein to have more in the body. Has to break down into AA then rebuild into a new protein.
Objective: Understand the structure and function of lipids. Notes Obesity Discussion
Common Name Foods Function in body Elements Shape (Triglycerides, phospholipids) Glycerol Fatty acid Calories per Gram Other Facts Saturated, unsaturated,
Saturated Un-saturated
Type is what matters Bad Saturated Animal fats We make all we need Tans Processed foods, fats food Hydrogenated Good Unsaturated Mono-, poly- Improve health Nuts, vegetable oil, seeds
WHAT IS IT.. Obesity means having too much body fat. It is not the same as being overweight, which means weighing too much. Cause Obesity is influenced by many other factors, also, including your family history, mental state, the type of work you do, your race, and your environment Prevention More calories out then in. Healthy eating. Being mentally and physically healthy.
Objective: For students to relate the information they have learned about different macromolecule and nutrients that our body needs to every day illnesses. Apply class information to familiar illnesses
Iron deficiency Iron deficiency anemia Zinc Growth retardation Thiamine (Vitamin B1) Beriberi Niacin (Vitamin B3) Pellagra Vitamin C Scurvy Vitamin D Osteoporosis Rickets Obesity Heart Disease Diabetes Proteins/fats/carbohydrates Protein-energy malnutrition Kwashiorkor Marasmus Mental retardation[2] [ [edit minerals Calcium Osteoporosis Rickets Tetany Iodine deficiency Goiter Selenium deficiency Keshan disease Eatting disorders Proteins/fats/carbohydrates edit] Dietary vitamins and minerals ] Dietary vitamins and
Biomolecule p.45-47 Carbohydrate Elements Monomer Polymer Lipid Protein
Casing for cells Function Properties Marker proteins Semi-perm Equalimbrium Channels vitiamns Proteins in by layers tranip
Hydrophilic- Head Water Loveing Polar Water soluble Hydrophobic - Try to avoid water Non-polar (insoluble)