Calculations with Significant Figures
In science, precise measurements are crucial for accurate calculations. Learn how to handle significant figures when adding and subtracting measurements to ensure the precision of your results.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Calculations with Significant Figures Sig Figs meet Rounding!
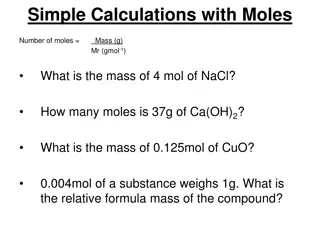
Background In Science we take measurements, but those measurements are sometimes needed to find the values that we really want. For example: Volume (Length x Width x Height) Volume by Difference using a graduated cylinder (Height of Water with object Height of water initially) Density (Mass Volume) Calculations cannot be more precise than the measurements.
Adding and Subtracting Measurements The least precise measurement dictates the precision of the answer The least precise will be the measurement with the LEAST decimal places. When adding or subtracting pretend that you are back in elementary school and line those numbers up!
Adding and Subtracting Measurements Example: Two different pieces of metal are massed separately using different balances. The first piece has a mass of 19.473 g. The second piece has a mass of 3.82 g. What is the total mass? Don t forget to use significant figures. Step 1 Line them up and do the math. 19.473 + 3.82 23.293
Adding and Subtracting Measurements Step 2 Find the LAST significant figure. Start from the right. Look for the first column that has a significant figure from both measurements. Underline the number in the answer that is in that column. 19.473 3.82 + 23.293
Adding and Subtracting Measurements Step 3 Round to that place do not forget to LOOK right! 19.473 3.82 + 23.293 Answer : 23.29 g Don t forget the Unit!!!
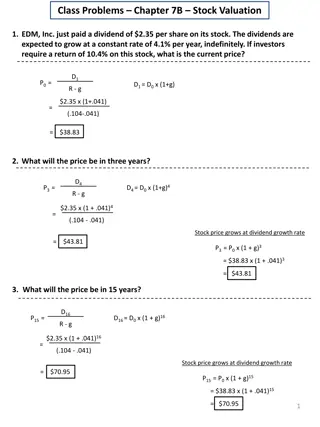
Adding and Subtracting Measurements Subtraction is the SAME!!! Example The mass of a paper cup is 1.284 g. The mass of the paper cup plus a sample of Manmium is 38.2 g. What is the mass of the Manmium sample? Step 1 What is it? 38.2 - 1.284 36.916 Yep Line them up!
Adding and Subtracting Measurements Step 2 What is it? Yep Underline the last significant figure! 38.2 - 1.284 36.916
Adding and Subtracting Measurements Step 3 What is it? Yep Look right and ROUND! 38.2 - 1.284 36.916 Answer = 36.9 g
Adding and Subtracting Practice 489.2 g + 8.03 g = ? 0.2800 L + 4.8 L =? 285.0 kg 3.82 kg = ? 0.01963 g + 0.290 g =? 926.028 kg 30.02 kg = ? 3902 L + 284.5 L = ?
Adding and Subtracting Practice 489.2 g + 8.03 g = 497.2 g 0.2800 L + 4.8 L = 5.1 L 285.0 kg 3.82 kg = 281.2 kg 0.01963 g + 0.290 g = 0.310 g 926.028 kg 30.02 kg = 896.01 kg 3,902 L + 284.5 L = 4,186 L
Multiplication and Division of Measurements The least precise measurement dictates the precision of the answer The least precise will be the measurement with the LEAST number of significant figures. The answer should be rounded to the least number of significant figures
Multiplication and Division of Measurements Example: Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 24.35 m and a width of 4.09 m. Step 1 Do the math! Area = Length x width 24.35 m x 4.09 m = 99.5915 m2 Step 2 Determine the number of significant figures in the original measurements 24.35 m (4 sig figs) 4.09 m (3 sig figs)
Multiplication and Division of Measurements Step 3 Determine the least number of sig figs 3 sig figs is less than 4 sig figs Step 4 round the answer to the least number of sig figs that you determined in Step 3 99.5915 m2 Final Answer 99.6 m2
Multiplication and Division of Measurements Division is the same! Example An object has a mass of 48.309 g and a volume of 9.28 mL. What is the density of this object? What is Step 1? Yep do the math! Density = mass/volume Density = 48.309 9.28 = 5.20571121 g/mL
Multiplication and Division of Measurements What is Step 2? Yep determine the number of significant figures in each of the original measurements 48.309 g (5 sig figs) 9.28 mL ( 3 sig figs) What is Step 3? Yep determine the least number of sig figs in the original measurements 3 sig figs
Multiplication and Division of Measurements What is Step 4? Yep Round to the least number of sig figs found in Step 3 5.20571121 g/mL round to three sig figs Final Answer = 5.21 g/mL
Multiplication and Division Practice 40.38 cm x 3.2903 cm = ? 0.00382 m x 0.08291 m = ? 293.0 g 3.0023 cm3 = ? 3.0193 x 104 kg 4.93 L = ? 293.0 cm x 3.28 cm = ? Challenge: 3.927 cm x 12.736 cm x 4.000 cm = ?
Multiplication and Division Practice 40.38 cm x 3.2903 cm = 132.9 cm2 0.00382 m x 0.08291 m = 0.000317 m2 or 3.17 x 10-4 m2 293.0 g 3.0023 cm3 = 97.59 g/cm3 3.0193 x 104 kg 4.93 L = 6,120 kg/L or 6.12 x 103 kg/L 293.0 cm x 3.28 cm = 89.3 cm2 Challenge: 3.927 cm x 12.736 cm x 4.000 cm = 200.1 cm3