Bond Analysis and Valuation Techniques by Binam Ghimire
Explore the analysis and valuation of bonds in-depth with a focus on present value techniques, bond yields, and calculating future bond prices. Understand the process of pricing a bond by determining cash flows, coupon payments, and par value. Dive into the calculations involved in determining the price of a bond based on coupon rates and required yields.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Analysis and Valuation of Bonds I by Binam Ghimire 1
Objectives Present value technique to price a bond Bond Yields Current yield, Yield to maturity, Yield to call, compound realised (horizon) yield Calculating Future Bond Prices Yield for a Portfolio 2
Pricing a bond The first step to price a bond is to determine its cash flows. Knowns are: Periodic coupon interest payment to the maturity date The par value at maturity Coupons are paid semi annually Next coupon will be paid exactly six months after today Coupon interest is fixed for the term of the bond 3
Pricing a bond 20 Year bond with 10% coupon interest rate and a par value of 1,000 Annual coupon =___ Semi annual coupon = ___ Therefore there are __ semi annual cash flows of ___ and a ___ cash flows 40 six months from now. 4
Pricing a bond 20 Year bond with 10% coupon interest rate and a par value of 1,000 Annual coupon = 100 Semi annual coupon = 50 Therefore there are 40 semi annual cash flows of 50 and a 1,000 cash flows 40 six months from now. 5
Pricing a bond Price of a bond: ? ? ? ? ? + 1 + ?2+ 1 + ?3+ + 1 + ??+ 1 + ?? 1 + ? ? ? ? ? = 1 + ??+ 1 + ?? ?=1 6
Pricing a bond Price of a bond: ? ? ? ? = 1 + ??+ 1 + ?? ?=1 ( ) t + r 1 1 r C 7
Pricing a bond 20 Year bond with 10% coupon interest rate and a par value of 100 and the required yield on the bond is 11% Annual coupon = 10 Price of the bond =? 8
Pricing a bond Price of the bond: = 5*(1-(1+5.5%)^-40)/5.5% = 80.231 =1/(1+5.5%)^40 =0.1174 = 100x0.1174= 11.746 = 80.23 + 11.746 = 91.97 9
Pricing a bond What will be the price of the bond if required yield = coupon rate? i.e. 10% coupon interest rate and required rate of return 10% 10
Pricing Zero-Coupon Bonds ? ? ? ? = 1 + ??+ 1 + ?? ?=1 ? ? = 1 + ?? 11
Pricing Zero-Coupon Bonds 20 Year zero coupon bond, a par value of 100 and the required yield on the bond is 10% Annual coupon = 10 Price of the bond =? 12
Pricing Zero-Coupon Bonds 20 Year zero coupon bond, a par value of 100 and the required yield on the bond is 10% Annual coupon = 10 Price of the bond =? =100/(1+0.05)^40 = 14.20 13
Price-yield relationship 220.00 200.00 198.50 180.00 160.00 154.71 140.00 123.11 120.00 Price 100.00 100.00 82.84 80.00 69.91 60.00 60.00 52.30 40.00 20.00 - 2% 4% 6% 8% 10% 12% 14% 16% Yield 14
Pricing a bond Coupon rate < required yield = @ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ t Coupon rate = required yield = @ _ _ r Coupon rate > required yield = @ _ _ _ _ _ _ m 15
Pricing a bond Coupon rate < required yield = @ discount Coupon rate = required yield = @ par Coupon rate > required yield = @ premium 16
Pricing a bond Price Time to Maturity 17
Reasons for the change in the price of a Bond There is a change in the required yield owing to changes in the credit quality of the issuer There is a change in the price of the bond selling at a premium or discount, without any change in the required yield, simply because the bond is moving towards maturity There is a change in the required yield owing to a change in the yield on comparable bonds (i.e. a change in the yield required by the market) 18
The Yield The yield on any investment is the interest rate that will make the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ value of cash flows from the investment equal to the price (or cost) of the investment. ??1 1 + ? ??2 1 + ?2+ ??3 1 + ?3+ + ??? 1 + ?? + ? ??? 1 + ?? ? = ?=1 19
The Yield The yield on any investment is the interest rate that will make the present value of cash flows from the investment equal to the price (or cost) of the investment. ??1 1 + ? ??2 1 + ?2+ ??3 1 + ?3+ + ??? 1 + ?? + ? ??? 1 + ?? ? = ?=1 20
The Yield Investment with only one future cash flow. ??? 1+?? ? = 1/? ??? ? ? = 1 21
The Yield A financial instrument currently selling for 62,321.30 promises to pay 100,000 six years from now. What is the yield on this investment? ??? ? 1/? ? = 1 22
The Yield A financial instrument currently selling for 62,321.30 promises to pay 100,000 six years from now. What is the yield on this investment? ??? ? 1/? ? = 1 1/6 100,000 62,321.30 ? = 1 = 8.2% 23
Calculating Bond Yields Nominal Yield It is the coupon rate of a particular issue. A bond with an 8 per cent coupon has an 8 per cent nominal yield. Current Yield It is the ratio of the annual coupon interest to the market price. It can be calculated as: Annual pound coupon interest/ price 24
Calculating Bond Yields Current Yield What is the current yield for a 15-year 7% coupon bond with a par value of 1,000 selling for 769.40 25
Calculating Bond Yields Current Yield What is the current yield for a 15-year 7% coupon bond with a par value of 1,000 selling for 769.40 =70/769.40 = 9.10% 26
Yield to Maturity Two conditions Hold the bond to maturity Reinvest all the interim cash flows at the calculated YTM rate ? ? ? ? ? + 1 + ?2+ 1 + ?3+ + 1 + ??+ 1 + ?? 1 + ? ? ? ? ? = 1 + ??+ 1 + ?? ?=1 27
Yield to Maturity Find the YTM for a 15-year 7% coupon bond with a par value of 1,000 selling for 769.40 ? ? ? ? = 1 + ??+ 1 + ?? ?=1 28
Yield to Maturity Find the YTM for a 15-year 7% coupon bond with a par value of 1,000 selling for 769.40 15?2 70/2 1 + ??+ 1000 1 + ?30 769.40 = ?=1 y = 5% 29
Yield to Maturity YTM for a zero coupon bond is simpler. 1 ? 1 ? ? ? = Example 10 year zero coupon bond with a maturity value of 1,000 selling for 439.18. y can be calculated as 30
Yield to Maturity YTM for a zero coupon bond is simpler. 1 ? 1 ? ? ? = Example 10 year zero coupon bond with a maturity value of 1,000 selling for 439.18. y can be calculated as 1 20 1 1,000 439.18 ? = = 4.2% 31
Yield to Call Issuer may be entitled to call a bond prior to the stated maturity date. The price at which the bond may be called is referred to as the Call price. The procedure for calculating the yield to any assumed call date is the same as for any yield calculation: determine the interest rate that will make the present value of the expected cash flows equal to the bond s price. ? ? ? 1 + ?? ? = 1 + ??+ ?=1 Where M* is call price and n* is number of periods until the assumed call date (number of years x 2) 32
Yield to Put An issue can also be putable. This means that the bondholder can force the issuer to buy the issue at a specified price. Yield to Put 33
Yield to Worst A practice in the industry is for an investor to calculate the yield to maturity, yield to every possible call date and the yield to every possible put date. The minimum of all of these is known as Yield to worst. 34
Horizon Yield AKA Horizon yield It is the yield of a bond that you anticipate to sell prior to the maturity date. Same formula ? ?? 1 + ??+ ?? ? = 1 + ?? ?=1 M is replaced by Pf which is the future selling price and coupon C is replaced by Ci to denote the coupon available until before selling. 35
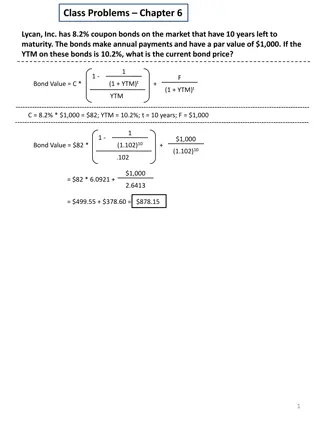
Calculating Future Bond Prices Consider a 10%, 25 year Bond with a YTM of 12%. The price will be: ? ? ? ? = 1 + ??+ 1 + ?? ?=1 36
Calculating Future Bond Prices Consider a 10%, 25 year Bond with a YTM of 12%. The price will be: 25?2 50 1,000 ? = 1 + 12%/2?+ 1 + 12%/250 ?=1 = 50x15.76 + 1,000 x 0.0543 = 842.4 Assume you bought this bond Let us assume based on analysis of economy and capital market, you now expect this bond s market YTM to decline to 8% in five years. Therefore you want to estimate the market price of the bond in five year time to estimate your expected rate of return 37
Calculating Future Bond Prices Here, you estimated a holding period of five year which implies a remaining life of 20 years and estimated YTM of 8% 20?2 50 (1 + 8%/2)?+ 1,000 ??= 1 + 8%/240 ?=1 = 50x19.79 + 1,000 x 0.2083 Future Price= 1,197.9 38
Yield for a Portfolio Bond Coupon rate (%) Maturity (Years) Par Value ( ) Price ( ) YTM (%) A B C 7 5 7 3 10,000,000 20,000,000 30,000,000 9,209,000 20,000,000 28,050,000 57,259,000 9 10.5 10.5 8.5 6 Period Cash Flow Received Bond A Bond B Bond C Portfolio 1350,000 1,050,000 900,000 2,300,000 2350,000 1,050,000 900,000 2,300,000 3350,000 1,050,000 900,000 2,300,000 4350,000 1,050,000 900,000 2,300,000 5350,000 1,050,000 900,000 2,300,000 6350,000 1,050,000 30,900,000 32,300,000 7350,000 1,050,000 1,400,000 8350,000 1,050,000 1,400,000 9350,000 10 11 12 13 14 1,050,000 1,050,000 1,050,000 1,050,000 1,050,000 21,050,000 1,400,000 11,400,000 1,050,000 1,050,000 1,050,000 21,050,000 10,350,000 39
Thank You 40