Basophil Activation Test (BAT) in Allergy Diagnosis and Monitoring
Basophil Activation Test (BAT) is a valuable tool in diagnosing and monitoring allergies. It involves taking a structured patient history, confirming allergen identity through objective tests like prick tests or sIgE measurement, and monitoring basophil sensitivity. BAT can be useful in various clinical scenarios such as confirming culprit allergens, predicting cross-reactions, and monitoring natural tolerance development. It has potential clinical utility in diagnosing drug allergies, food allergies, insect venom allergies, and more. BAT provides reproducible correlations to clinical allergy and can aid in monitoring allergic disease progression and treatment outcomes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
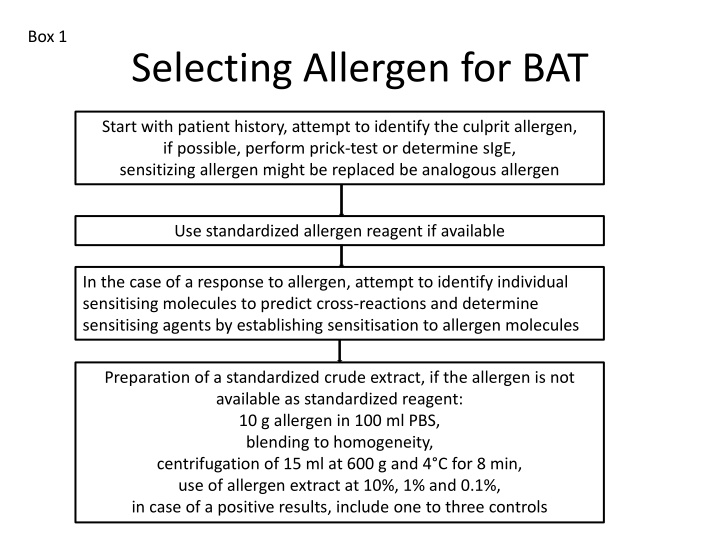
Box 1 Selecting Allergen for BAT Start with patient history, attempt to identify the culprit allergen, if possible, perform prick-test or determine sIgE, sensitizing allergen might be replaced be analogous allergen Use standardized allergen reagent if available In the case of a response to allergen, attempt to identify individual sensitising molecules to predict cross-reactions and determine sensitising agents by establishing sensitisation to allergen molecules Preparation of a standardized crude extract, if the allergen is not available as standardized reagent: 10 g allergen in 100 ml PBS, blending to homogeneity, centrifugation of 15 ml at 600 g and 4 C for 8 min, use of allergen extract at 10%, 1% and 0.1%, in case of a positive results, include one to three controls
Box 2 BAT in Allergy Diagnosis Taking a structured patients history including severity of symptoms Comfirmation of the allergen identity by an objective test a) Prick test or measurement of sIgE b) Consideration of an intradermal test in drug and insect venom allergy Consideration of a BAT a) In case the allergen is known to produce false positive results in skin testing b) In case there is no allergen source to use for skin or sIgE testing c) In case of discordance between the patient history and sIgE or skin tests (i.e. in case of IgE-mediated allergy, but negative sIgE due to extremely low total IgE) d) In case of expecting a systemic response in skin testing e) Before considering a challenge test to confirm culprit allergen
Box 3 BAT in Monitoring Allergy Taking a structured patients history including severity of symptoms Demonstration of the allergen identity by an objective test a) Prick test or measurement of sIgE b) Consideration of an intradermal test in drug and insect venom allergy Measurement of basophil sensitivity Start treatment/allow for natural tolerance development Measurement of basophil sensitivity In case BAT is negative a) A challenge can be performed b) Reintroduce allergen e.g. food
Box 4 Potential Clinical Utility of BAT Support in diagnosis of allergy Drugs (supplement for -lactam antibiotics/quinolones, unique for muscle relaxants, radio contrast media and pyrazolones) Food (reduction of number of OFC required possible) Occupational allergens (unique) Insect venom (supplement for insect venom allergen detection) Autoimmune urticaria (replacement of ASST possible) Local allergic rhinitis (possibly due to extraordinary analytical sensitivity of BAT) Monitoring allergic disease Reproducible ex vivo cor-relation to clinical allergy Identification of clinical relevant allergen in insect venom allergy Monitoring natural and induced resolution of food allergy Predicting success of allergen immunotherapy Monitoring anti-IgE-treatment Change in sensitivity: EC50 CD- sens Dichotomous decision: % pos, SI, AUC