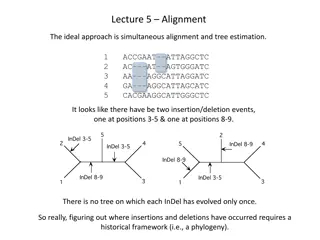
Addressing Sequencing Errors in Phylogenetics
The impact of sequencing errors on phylogenetic analysis and the strategies to mitigate these errors through probabilistic modeling and next-generation sequencing technologies. This research delves into gene evolution, convergent evolution, mutation rate variation, and divergence time estimation in the context of error-prone data. Discover how incorporating more information from sequencing data can refine phylogenetic reconstructions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ACCOUNTING FOR SEQUENCING ERROR IN PHYLOGENETICS Gregg Thomas Indiana University Society of Systematic Biologists Conference, Ann Arbor, MI 05.21.15
EVOLUTION PHYLOGENETICS GENOMICS 2
EVOLUTION PHYLOGENETICS GENOMICS Gene family evolution Convergent evolution Mutation rate variation Divergence time estimation 3
EVOLUTION Error prone! PHYLOGENETICS GENOMICS Gene family evolution Convergent evolution Mutation rate variation Divergence time estimation 4
EVOLUTION Error prone! PHYLOGENETICS GENOMICS Gene copy number error Gene family evolution Convergent evolution Mutation rate variation Divergence time estimation 5
EVOLUTION Error prone! PHYLOGENETICS GENOMICS Gene copy number error Gene family evolution Convergent evolution Mutation rate variation Divergence time estimation Base calling errors 6
ACCOUNTINGFORERRORBYPROBABILISTIC MODELING Incorporate more information from next generation sequencing into the phylogenetic reconstruction process 7
NEXTGENERATIONSEQUENCEDATAISERROR PRONE Quality Score Hu et al, 2012 8
NEXTGENERATIONSEQUENCEDATAISERROR PRONE Quality Score Philippe et al, 2012 Hu et al, 2012 9
PHYLOGENETICRECONSTRUCTIONSSTARTWITH OBSERVEDSTATEPROBABILITIESOF1OR0 A T C G A 1 0 0 0 A T C G G 0 0 0 1 A T C G A 1 0 0 0 10
NEXTGENERATIONSEQUENCINGGIVESUSMORE INFORMATION A T C G A 1 0 0 0 Aligned reads G G Assembly A T C G A 1 0 0 0 11
MODELOBSERVEDSTATESPROBABILISTICALLY A T C G A 0.8 0 0.1 0.1 A T C G G 0.6 0 0 0.4 A T C G A 0.9 0.1 0 0 12
CAPTURINGUNCERTAINTYFROM NGS Aligned reads G Assembly 13
CAPTURINGUNCERTAINTYFROM NGS Aligned reads G Assembly No quality information 14
CAPTURINGUNCERTAINTYFROM NGS Each read has a quality score Aligned reads G Assembly 15
CAPTURINGUNCERTAINTYFROM NGS Each read has a quality score Aligned reads G Assembly Map reads back to assembly and compile quality information 16
CAPTURINGUNCERTAINTYFROMNGSDATA The probability a given base is an error: ? ? = 10 ? 10 ? !? = 1 ? ? 17
CAPTURINGUNCERTAINTYFROMNGSDATA The probability a given base is an error: ? ? = 10 ? 10 ? !? = 1 ? ? The probability of each base at a position, given a set of reads: ? = ?,?,?,? ? log? ? ?? ?? ? log? !? ?? ??= ? ? ? ? = ?=1 18
CONCLUSIONS Currently benchmarking on simulated data Will add quality metric to all NGS assemblies Focus on phylogenetic reconstructions 19
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Colleagues: James Pease Simo Zhang Fabio Mendes Rafael Guerrero Jeff Adrion Ben Rosenzweig Advisor: Matt Hahn Committee: Haixu Tang Elizabeth Housworth GCMS Training Grant 20