Acute Respiratory Failure in ESRD Patients with Diffuse Bilateral Alveolar Infiltrates
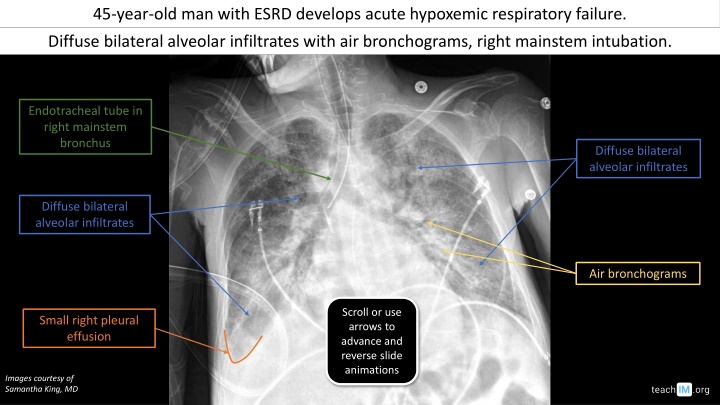
In a 45-year-old male with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, diffuse bilateral alveolar infiltrates with air bronchograms were noted, including right mainstem intubation. Correct positioning and management steps for endotracheal tube placement were discussed. Additionally, the presence of other invasive tubes and lines like a right IJ dialysis catheter and OG tube was highlighted.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
45-year-old man with ESRD develops acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. What is your overall interpretation? Diffuse bilateral alveolar infiltrates with air bronchograms, right mainstem intubation. Endotracheal tube in right mainstem bronchus Diffuse bilateral alveolar infiltrates Diffuse bilateral alveolar infiltrates Air bronchograms Scroll or use arrows to advance and reverse slide animations Small right pleural effusion Images courtesy of Samantha King, MD
46 yo M with ESRD and cirrhosis, sepsis from SBP develops acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. Diffuse bilateral alveolar infiltrates with air bronchograms, right mainstem intubation. What is your overall interpretation? What is the correct positioning for an endotracheal tube? What would be your next step in management? Endotracheal tube in right mainstem bronchus Carina The endotracheal tube should terminate 2-4 cm above the carina. Left main bronchus Right main bronchus Images courtesy of Samantha King, MD
46 yo M with ESRD and cirrhosis, sepsis from SBP develops acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. Diffuse bilateral alveolar infiltrates with air bronchograms, right mainstem intubation. What is your overall interpretation? What is the correct positioning for an endotracheal tube? What is the correct positioning for an endotracheal tube? What would be your next step in management? Retract the endotracheal tube. Endotracheal tube in appropriate position about 2.4 cm above the carina Repeat CXR after ET tube retracted 4 cm Images courtesy of Samantha King, MD
46 yo M with ESRD and cirrhosis, sepsis from SBP develops acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. Diffuse bilateral alveolar infiltrates with air bronchograms, right mainstem intubation. What is your overall interpretation? Bonus: what other invasive tubes and lines are present? Right IJ dialysis catheter terminating in the SVC Scroll or use arrows to advance and reverse slide animations OG tube terminating in the proximal stomach Images courtesy of Samantha King, MD