Enhancing IEEE 802.11 with Multi-Link Acknowledgment Mechanism
This document explores the concept of multi-link transmission in IEEE 802.11 networks as a means to enhance peak throughput. It delves into the proposal of a multi-link block acknowledgment mechanism for more efficient data transmission. The discussion includes details on existing block acknowledgment setup mechanisms and how they can be adapted for multi-link transmissions, aiming to optimize network performance.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
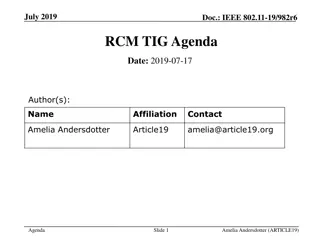
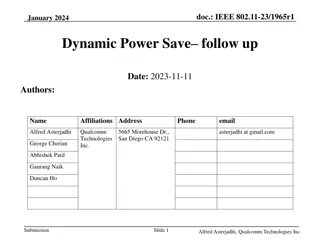
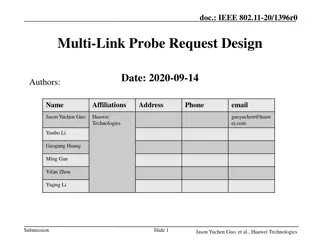
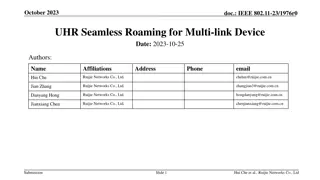
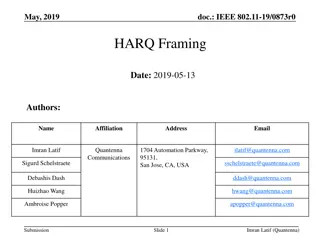
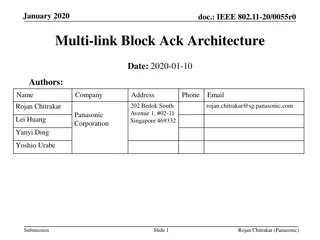
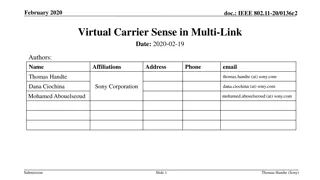
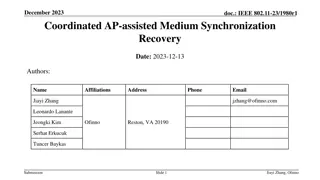
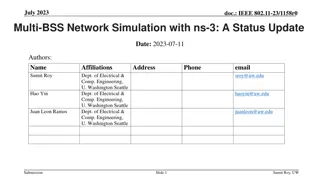
September 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Multi-link acknowledgment Date: 2019-09-10 Authors: Name Rojan Chitrakar Company Address Phone Email rojan.chitrakar@sg.panasonic.com Panasonic Corporation Lei Huang Yanyi Ding Yoshio Urabe Submission Slide 1 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Overview Multi-link transmission is being considered as one of the key technology to achieve the peak throughput goal of 802.11be. In [1], we shared our opinions on some of the topics related to multi-link transmissions. In this contribution, we will discuss the topic of acknowledgment for multi-link transmissions in more detail and propose the concept of multi-link block ack. Submission Slide 2 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 Recap: Multi-link transmission [1] doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 In order to improve the peak throughput, MPDUs belonging to the same TID may be simultaneously transmitted over multiple links. At TX side UMAC performs the allocation of MPDUs to different links. The same SN space is used across all links. At RX side UMAC consolidates the MDPUs arriving over the different links, performs BA scoreboarding, MPDUs reordering etc. A consolidated acknowledgment may be transmitted over one of the links. Submission Slide 3 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 Existing block ack setup mechanism doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Block ack mechanism is setup between an originator STA and a recipient STA by exchanging ADDBA Request/Response frames. If existing block ack setup mechanism is used for multi-link transmissions, one possible option is to perform block ack setup (in each direction) between each pair of STAs between two Multi- link Entities. 2.4 GHz Multi-link AP Multi-link STA 5 GHz 6 GHz ADDBA request (TID n) Block ACK setup for the 6GHz link ADDBA Response (TID n) ADDBA request (TID n) Block ACK setup for the 5GHz link Block ACK setup (TID n) ADDBA Response (TID n) ADDBA request (TID n) Block ACK setup for the 2.4GHz link ADDBA Response (TID n) Block Ack agreement setup for all 3 links Submission Slide 4 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 Existing Block Ack setup mechanism The parameters of the block ack mechanism is negotiated by exchanging ADDBA Request/Response frames: TID: TID for the block ack mechanism Buffer Size: number of buffer for this particular TID Block Ack Timeout Value: duration in TUs after which the block ack setup is terminated. Block Ack Starting Sequence Control: sequence number of the first MSDU to be sent under this block ack agreement. doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 ADDBA Request Frame Body MAC Header Block Ack Action Block Ack Parameter Set Block Ack Timeout Value Block Ack Starting Seq. Cntrl. Frame Control Address 1 (RA) Address 2 (TA) Address 3 (BSSID) Sequence Control HT Dialog Token Duration Category FCS Control A-MSDU Supported Block Ack Policy TID Buffer Size Once setup, each block ack agreement is uniquely identified by a tuple of Address 1 (RA), Address 2 (TA), and TID. Submission Slide 5 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 Proposal 1: Multi-link block ack Setup A single Multi-link block ack agreement is setup between two Multi-link Entities for a multi-link TID. doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 2.4 GHz Multi-link AP Multi-link STA 5 GHz 6 GHz Multi-link ADDBA request (TID n) Multi-link Block ACK setup Multi-link ADDBA Response (TID n) Block Ack agreement setup for all 3 links Example: Multi-band elements in the ADDBA Request/Response frames can indicate the links for which the Multi-link block ack applies: The block ack parameters apply to all the involved links. Buffer Size needs to account for all involved links. A common sequence number space is used for MPDUs of the same TID transmitted over multiple links; the Block Ack Starting Sequence Control field specifies the same sequence number for all links. ADDBA Request Frame Body MAC Header Block Ack Action Block Ack Parameter Set Block Ack Timeout Value Block Ack Starting Seq. Cntrl. Multi-band element (One or more) Frame Control Address 1 (RA) Address 2 (TA) Address 3 (BSSID) Sequence Control HT Dialog Token Duration Category FCS Control Submission Slide 6 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Per-link block ack Per-link block ack may be preferred for Multi-link transmissions. However, since the BA bitmaps of different links may cover the same sequence number range: Many of the bits of the BA bitmap can be expected to be 0 : Duplication/waste of bitmaps May cause confusion for the originator Reception of BlockAck frame may fail (E.g. if the multi-link originator is affected by in-device coexistence interference.) f 7 8 9 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6 GHz (160 MHz) 4 5 6 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 5 GHz (80 MHz) 1 2 3 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 2.4 GHz (20 MHz) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 t 0 1 Multi-link transmission (TID n) BlockAck bitmap BlockAck frame Legend: m n Submission Slide 7 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 Proposal 2: Multi-link BlockAck frame A single Multi-link BlockAck frame may be used to acknowledge the MPDUs received over multiple links: The BlockAck bitmap consolidates the receipt status of the MPDUs received over multiple links. A Multi-link BlockAck Request frame may be transmitted over any one link to solicit the Multi-link BlockAck frame. E.g. the Multi-link BlockAck frame may be solicited on a link that does not cause in-device coexistence interference or on the links suffering from in- device coexistence interference in a delayed manner. doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 7 8 9 f 6 GHz (160 MHz) 4 5 6 5 GHz (80 MHz) 1 2 3 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 2.4 GHz (20 MHz) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 t 0 1 BlockAck frame Multi-link BlockAck Request frame BlockAck bitmap Multi-link transmission (TID n) Multi-link BlockAck frame Legend: m n Submission Slide 8 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Multi-link BlockAck frame Example: A Multi-link bit in the BA Control field may be used to denote a Multi-link BlockAckReq/BlockAck frame. Frame Control BA Duration RA TA BA Control FCS Information Block Ack Starting Sequence Control Block Ack Bitmap BA Ack Policy BA Type Multi-Link Reserved TID_INFO The length of the BlockAck Bitmap of a Multi-link BlockAck frame may be increased (e.g. 128 octets (1024 bits) or 256 octets (2048 bits)) to acknowledge the higher number of MPDUs transmitted over multiple links. Submission Slide 9 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Conclusion In this contribution, we discussed the setup mechanism of Multi-link Block Acks. To simplify the setup process, we propose that a single Multi-link Block Ack agreement is setup between two Multi-link Entities for a multi-link TID. We also discussed the acknowledgements for multi- link transmissions. We propose that a single Multi-link BlockAck frame may acknowledge the MPDUs received over multiple links. Submission Slide 10 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Reference 1) IEEE 802.11-19/1128r0 Multi-link transmission 2) IEEE 802.11-19/818r0 - Discussion on Multi-band operation 3) IEEE 802.11-19/773r1 - Multi-link Operation Framework 4) IEEE 802.11-19/823r0 - Multi-link aggregation 5) IEEE 802.11-19/979r0 - EHT Multi-link Operation Follow-up 6) IEEE 802.11-19/1291r1 - Performance aspects of Multi-link operations 7) IEEE 802.11-19/1213r0 Discussion on Multi-link Operations Submission Slide 11 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Straw Poll 1 Do you support that a single block ack agreement is negotiated between two Multi-link devices (MLDs) for a TID that may be transmitted over multiple links? Note: The format of the setup frames is TBD. 27Y/1N/11A Submission Slide 12 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Straw Poll 2 Do you support assigning sequence numbers from a common sequence number space shared across multiple links of a Multi-link device (MLD) for a TID transmitted to peer Multi-link device. 29Y/1N/15A Submission Slide 13 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Straw Poll 3 Do you support that a single BlockAck frame may indicate the receipt status of MPDUs of a TID received over multiple links? Note: The format of the BlockAck frame is TBD. deferred Submission Slide 14 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Motion 1 Move to add the following text into IEEE 802.11be SFD: A single block ack agreement is negotiated between two Multi-link devices (MLDs) for a TID that may be transmitted over one or more links. Note: The format of the setup frames is TBD. Y/N/A Submission Slide 15 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)
September 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1512r6 Motion 2 Move to add the following text into IEEE 802.11be SFD: Sequence numbers are assigned from a common sequence number space shared across multiple links of a Multi-link device (MLD), for a TID that may be transmitted to a peer Multi-link device over one or more links. Y/N/A Submission Slide 16 Rojan Chitrakar (Panasonic)