Understanding Pronouns: Types and Examples
Learn about different types of pronouns, including personal pronouns, and how they work by replacing nouns in sentences. Discover the concept of antecedents and how they relate to pronouns through examples. Explore singular and plural forms of personal pronouns with gender distinctions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
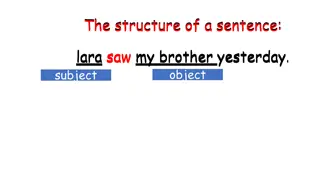
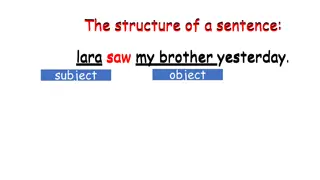
Antecedent- the noun that the pronoun replaces. Pronoun- takes the place of a noun. Example: Tom got his backpack stuck in the door. In the previous sentence, Tom is the antecedent of his. In this sentence, his replaces "Tom."
"Ante" is a root word meaning "before." If you are looking for the antecede of a particular pronoun, look at the nouns used before the pronoun in question. HINT: Sometimes the antecedent is implied. Example: Give her the shoe. In this example, the antecedent of the pronoun "her" is an implied, feminine noun. It could be replaced by Sally, your sister, or any other feminine noun.
1. Sally got her shoes today. 1. Sally 2. Get in your car. 2. You 3. Grayson looked over his homework. 3. Grayson
In your notes, write the antecedent of the pronouns in bold. 1. Colt left his sister a note because she slept in. 2. Get him a glass of water. 3. The park was closed because the contracor was working on it. 4. Your mother called to say that she will be late.
1. sister 2. Any masculine (male) noun 3. Park 4. Mother
Personal pronouns are the most common pronouns. They refer to (1) the person speaking, (2) the person spoken to, and (3) the person, place, or thing spoken about. Personal pronouns also have number (singular or plural). Finally, personal pronouns have gender (masculine, feminine, neuter)
Singular I, Me, My, Mine Plural We, Us, Our, Ours
Singular You, Your, Yours Plural You, Your, Yours Did you notice anything? That s right! Second person pronouns are the same whether the pronoun is singular or plural!
Singular He, Him, His, She, Her, Hers, It, Its Plural They, Them, Their, Theirs
Using the correct pronoun will help your reader to understand who or what you are talking about. If your reader understands who or what you are writing about, they will understand your purpose. If your reader understands your purpose, your writing will have impact.
Click on the Assignments Page of Mrs. McDs website. Complete the Assignment on your own sheet of paper.