Computational Physics (Lecture 18)
Neural networks explained with the example of feedforward vs. recurrent networks. Feedforward networks propagate data, while recurrent models allow loops for cascade effects. Recurrent networks are less influential but closer to the brain's function. Introduction to handwritten digit classification
0 views • 55 slides
Evolution and Potential of 5G Technology
Explore the evolving landscape of 5G technology, from enhanced mobile broadband to groundbreaking use cases and standalone networks. Learn how supportive regulations and spectrum allocation are vital for unlocking 5G's full potential. Discover the transformative impact of Standalone 5G networks on i
8 views • 10 slides
Understanding Computer Networks: Types and Characteristics
In the realm of computer networks, nodes share resources through digital telecommunications networks. These networks enable lightning-fast data exchange and boast attributes like speed, accuracy, diligence, versatility, and vast storage capabilities. Additionally, various types of networks exist tod
9 views • 12 slides
Understanding Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) are powerful tools for sequential data learning, mimicking the persistent nature of human thoughts. These neural networks can be applied to various real-life applications such as time-series data prediction, text sequence processing,
15 views • 34 slides
Graph Neural Networks
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are a versatile form of neural networks that encompass various network architectures like NNs, CNNs, and RNNs, as well as unsupervised learning models such as RBM and DBNs. They find applications in diverse fields such as object detection, machine translation, and drug d
2 views • 48 slides
Understanding Artificial Neural Networks From Scratch
Learn how to build artificial neural networks from scratch, focusing on multi-level feedforward networks like multi-level perceptrons. Discover how neural networks function, including training large networks in parallel and distributed systems, and grasp concepts such as learning non-linear function
2 views • 33 slides
Understanding Back-Propagation Algorithm in Neural Networks
Artificial Neural Networks aim to mimic brain processing. Back-propagation is a key method to train these networks, optimizing weights to minimize loss. Multi-layer networks enable learning complex patterns by creating internal representations. Historical background traces the development from early
2 views • 24 slides
Exploring Samsung SmartThings Hub and Zigbee/Zwave Networks
The Samsung SmartThings hub is a versatile device connecting Zigbee and Zwave networks, offering secure access to SkySpark via HTTPS. Zigbee and Zwave networks operate on distinct frequencies, enabling efficient communication without interference with WiFi. These networks support various devices for
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWAN) and Cellular Network Principles
Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWAN) utilize cellular network technology like GSM to facilitate seamless communication for mobile users by creating cells in a geographic service area. Cellular networks are structured with backbone networks, base stations, and mobile stations, allowing for growth and c
3 views • 17 slides
Understanding Real-Time PCR: A Modern Technique for Nucleic Acid Analysis
Real-time PCR is a powerful tool for amplifying and quantifying DNA or RNA in a sample. It allows for real-time monitoring of the amplification process, enabling precise quantitation of genetic material and gene expression studies. By combining amplification and detection in one step, real-time PCR
1 views • 13 slides
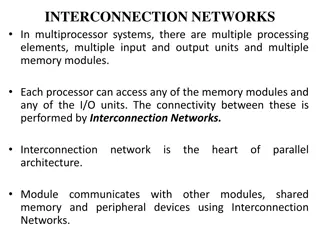
Understanding Interconnection Networks in Multiprocessor Systems
Interconnection networks are essential in multiprocessor systems, linking processing elements, memory modules, and I/O units. They enable data exchange between processors and memory units, determining system performance. Fully connected interconnection networks offer high reliability but require ext
1 views • 19 slides
Understanding Computer Networks in BCA VI Semester
Computer networks are vital for sharing resources, exchanging files, and enabling electronic communications. This content explores the basics of computer networks, the components involved, advantages like file sharing and resource sharing, and different network computing models such as centralized a
1 views • 96 slides
Understanding Real-Time Systems and Operating Systems
Real-time systems in computing refer to the concept of task execution meeting specific deadlines, with examples including process control in industrial plants, robotics, air traffic control, and more. Tasks in real-time systems have defined release, schedule, completion times, and deadlines, with ru
0 views • 46 slides
Understanding Computer Communication Networks at Anjuman College
This course focuses on computer communication networks at Anjuman College of Engineering and Technology in Tirupati, covering topics such as basic concepts, network layers, IP addressing, hardware aspects, LAN standards, security, and administration. Students will learn about theoretical and practic
0 views • 72 slides
Enhancing Quality of Service in Ultra High Rate Wi-Fi Networks
This document explores the potential improvements in Quality of Service (QoS) for Ultra High Rate (UHR) Wi-Fi networks, focusing on the benefits of timing information sharing for traffic urgency assessment. It discusses areas such as increased reliability, lower latencies, improved manageability, an
0 views • 11 slides
Introduction to Neural Networks in IBM SPSS Modeler 14.2
This presentation provides an introduction to neural networks in IBM SPSS Modeler 14.2. It covers the concepts of directed data mining using neural networks, the structure of neural networks, terms associated with neural networks, and the process of inputs and outputs in neural network models. The d
1 views • 18 slides
Enhancing Agriculture Through Global Knowledge Networks and Information Management Systems
Global and regional knowledge networks play a vital role in agriculture by facilitating information sharing, collaboration, capacity building, and coordination among stakeholders. These networks improve access to information, foster collaboration, enhance capacity building, and strengthen coordinati
0 views • 5 slides
Introduction to Real-Time Systems and Real-Time OSes
Real-time systems are defined by the critical nature of timely results, where correctness depends not just on computation but also on when results are produced. Characteristics include timing constraints, deadlines, and different types of tasks categorized based on timing patterns. Understanding sof
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Router Routing Tables in Computer Networks
Router routing tables are crucial for directing packets to their destination networks. These tables contain information on directly connected and remote networks, as well as default routes. Routers use this information to determine the best path for packet forwarding based on network/next hop associ
0 views • 48 slides
P-Rank: A Comprehensive Structural Similarity Measure over Information Networks
Analyzing the concept of structural similarity within Information Networks (INs), the study introduces P-Rank as a more advanced alternative to SimRank. By addressing the limitations of SimRank and offering a more efficient computational approach, P-Rank aims to provide a comprehensive measure of si
0 views • 17 slides
Real-time Ethernet on IEEE 802.3 Networks Tutorial
This tutorial focuses on IEEE standards for real-time Ethernet networks, enabling deterministic delivery time for applications in industrial automation and automotive control. Key topics include IEEE 802.1 Time Sensitive Networking and P802.3br Interspersing Express Traffic projects, aiming to meet
0 views • 61 slides
Understanding Advanced Classifiers and Neural Networks
This content explores the concept of advanced classifiers like Neural Networks which compose complex relationships through combining perceptrons. It delves into the workings of the classic perceptron and how modern neural networks use more complex decision functions. The visuals provided offer a cle
0 views • 26 slides
Enhancing Real-Time Network Design with WoPANets Decision-Support Tool
Addressing the increasing complexity of real-time networks, WoPANets offers a decision-support tool for designing networks with mixed-criticality data delivery, multi-hop communication, and heterogeneous architectures. By focusing on accurate timing verification and system-level performance analysis
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Relational Bayesian Networks in Statistical Inference
Relational Bayesian networks play a crucial role in predicting ground facts and frequencies in complex relational data. Through first-order and ground probabilities, these networks provide insights into individual cases and categories. Learning Bayesian networks for such data involves exploring diff
0 views • 46 slides
Understanding Real-time Debug Techniques for Embedded Development
Real-time debugging in embedded systems involves different modes like stop mode and real-time mode, each offering unique capabilities for accessing memory, registers, and handling interrupts. This technique allows developers to examine and modify memory contents while the processor is running, enabl
0 views • 32 slides
Understanding Overlay Networks and Distributed Hash Tables
Overlay networks are logical networks built on top of lower-layer networks, allowing for efficient data lookup and reliable communication. They come in unstructured and structured forms, with examples like Gnutella and BitTorrent. Distributed Hash Tables (DHTs) are used in real-world applications li
0 views • 45 slides
Understanding Networks: An Introduction to the World of Connections
Networks define the structure of interactions between agents, portraying relationships as ties or links. Various examples such as the 9/11 terrorists network, international trade network, biological networks, and historical marriage alliances in Florence illustrate the power dynamics within differen
0 views • 46 slides
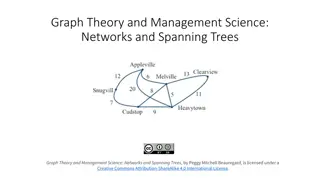
Understanding Graph Theory and Networks: Concepts and Applications
Explore the concepts of graph theory and management science, focusing on networks, spanning trees, and their practical applications. Learn about the difference between a snowplow tracing streets, a traveler visiting cities, and connecting towns with cables. Discover how networks like Facebook evolve
0 views • 15 slides
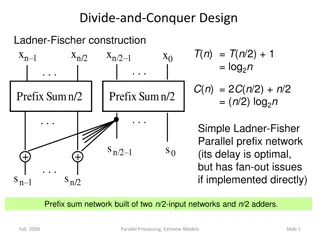
Parallel Prefix Networks in Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms
Explore the construction and comparisons of various parallel prefix networks in divide-and-conquer algorithms, such as Ladner-Fischer, Brent-Kung, and Kogge-Stone. These networks optimize computation efficiency through parallel processing, showcasing different levels of latency, cell complexity, and
1 views • 21 slides
Diverse Social Entities Mining from Linked Data in Social Networks
This research focuses on mining diverse social entities from linked data in social networks using a DF-tree structure and DF-growth mining algorithm. The study explores the extraction of important linked data in social networks and the mining of various social entities such as friends. Prominence va
0 views • 13 slides
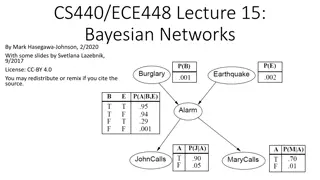
Understanding Bayesian Networks: A Comprehensive Overview
Bayesian networks, also known as Bayes nets, provide a powerful tool for modeling uncertainty in complex domains by representing conditional independence relationships among variables. This outline covers the semantics, construction, and application of Bayesian networks, illustrating how they offer
0 views • 17 slides
Machine Learning and Artificial Neural Networks for Face Verification: Overview and Applications
In the realm of computer vision, the integration of machine learning and artificial neural networks has enabled significant advancements in face verification tasks. Leveraging the brain's inherent pattern recognition capabilities, AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data to enhance face detection
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Network Analysis: Whole Networks vs. Ego Networks
Explore the differences between Whole Networks and Ego Networks in social network analysis. Whole Networks provide comprehensive information about all nodes and links, enabling the computation of network-level statistics. On the other hand, Ego Networks focus on a sample of nodes, limiting the abili
1 views • 31 slides
Evolution of Networking: Embracing Software-Defined Networks
Embrace the future of networking by transitioning to Software-Defined Networks (SDN), overcoming drawbacks of current paradigms. Explore SDN's motivation, OpenFlow API, challenges, and use-cases. Compare the complexities of today's distributed, error-prone networks with the simplicity and efficiency
0 views • 36 slides
Intersectional STEM Network Formation for Underrepresented Students
Addressing the underrepresentation of women and people of color in STEM, this study explores the impact of peer networks on the persistence of underrepresented high school students of color in STEM at the postsecondary level. It delves into how race and gender intersect to influence the creation and
0 views • 16 slides
Forecasting Short-Term Urban Rail Passenger Flows Using Dynamic Bayesian Networks
A study presented a dynamic Bayesian network approach to forecast short-term urban rail passenger flows in the Paris region. The research addresses the challenges of incomplete data, unexpected events, and the need for real-time forecasting in public transport networks. By leveraging Bayesian networ
0 views • 19 slides
New Approaches in Learning Complex-Valued Neural Networks
This study explores innovative methods in training complex-valued neural networks, including a model of complex-valued neurons, network architecture, error analysis, Adam optimizer, gradient calculation, and activation function selection. Simulation results compare real-valued and complex-valued net
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Bayesian Networks for Efficient Probabilistic Inference
Bayesian networks, also known as graphical models, provide a compact and efficient way to represent complex joint probability distributions involving hidden variables. By depicting conditional independence relationships between random variables in a graph, Bayesian networks facilitate Bayesian infer
0 views • 33 slides
Understanding Interconnection Networks in Embedded Computer Architecture
Explore the intricacies of interconnection networks in embedded computer architecture, covering topics such as connecting multiple processors, topologies, routing, deadlock, switching, and performance considerations. Learn about parallel computer systems, cache interconnections, network-on-chip, sha
0 views • 43 slides
Understanding Deep Generative Bayesian Networks in Machine Learning
Exploring the differences between Neural Networks and Bayesian Neural Networks, the advantages of the latter including robustness and adaptation capabilities, the Bayesian theory behind these networks, and insights into the comparison with regular neural network theory. Dive into the complexities, u
0 views • 22 slides