Coverage Semantics for Dependent Pattern Matching
Delve into the world of dependent pattern matching with a focus on coverage semantics. Dive deep into the concepts of denotational semantics, topologies, and coverages. Explore the interplay between patterns, values, and types in a novel way, shedding light on the essence of pattern matching.
4 views • 26 slides
Understanding Componential Analysis in Semantics
Componential analysis is a significant theory that emerged in the 20th century to analyze words based on semantic features. It helps identify word meanings by examining components and their features. This method involves representing features as either positive (+), negative (-), or unspecified (.).
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Predicators and Predicates in Sentence Semantics
Exploring the semantics of sentences, this content delves into the structure of declarative sentences in terms of predicators and arguments. It discusses various classes of items that can function as the predicator of a sentence, such as lexical verbs, the copulative verb "be" in equative sentences,
1 views • 39 slides
Understanding Grammatical Semantics in Linguistics
Grammatical semantics is the study of meaning conveyed by grammatical devices, exploring the semantics of syntax and morphology. By analyzing sentences about a mouse in the countryside, propositions are identified through a four-step analysis, revealing how meaning is constructed through linguistic
0 views • 17 slides
Exploring Arabic Semantics in Linguistics by Amir Abbas Mayouf
The article delves into the Arabic perspective in semantics as studied by linguists like Amir Abbas Mayouf. It discusses the definition of semantics, the difference between semantics and meaning, and the role of semantics in language sciences. The linguistic context, lexical reference, and phonetic
2 views • 15 slides
Exploring Knowledge Base Construction and Commonsense Knowledge in Fiction
Delve into innovative research interests focusing on knowledge base construction using fictional texts as archetypes, taxonomies for constructing knowledge bases, and extraction of commonsense knowledge from diverse sources. Challenges such as sparsity and semantics are addressed through comprehensi
3 views • 48 slides
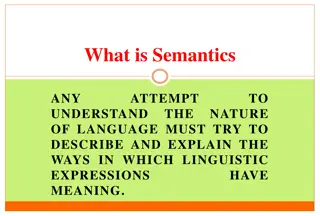
Understanding Semantics: The Study of Meaning in Linguistics
Semantics is the scientific study of meaning in language, delving into questions about definitions, ideas, objects, relations between meanings, and how meanings interact with syntactic rules. Exploring the vagueness of the term "meaning," semanticists explore sense, reference, denotation, and connot
2 views • 19 slides
Understanding Semantics: Exploring Linguistic Meaning and Expression
Exploring the realm of semantics, this content delves into how language is used to refer, denote, and express concepts in the world. It discusses the importance of linguistic meaning, different approaches to studying it, and the distinction between denotational and cognitive semantics. By examining
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Relationships in Logic and Semantics
This content explores various concepts in logic and semantics such as Loukika Sannikarsha, Sangyog Sangyukta Samavaya, and more. It delves into the intricacies of relationships and distinctions between different elements in these fields.
2 views • 5 slides
Understanding Semantics and Pragmatics in Language Study
Semantics and pragmatics are key areas of language study that focus on the meanings of words, phrases, and sentences. Semantics delves into the literal meanings and language as a system, while pragmatics explores how speakers use language in context. Understanding semantic meaning involves consideri
3 views • 77 slides
An Exploration of Linguistic Meaning: Semantics and Pragmatics
Delve into the realm of linguistic meaning through the lenses of semantics and pragmatics. Explore how words and phrases carry literal meanings, while language usage in social contexts creates both literal and nonliteral meanings. Uncover the intricate interplay between semantics, concerned with the
6 views • 70 slides
Semantics and Paradigmatic Relations of Exclusion and Opposition
The presentation explores the concepts of incompatibility, co-taxonymy, and opposition in semantics. It delves into how certain terms exclude others within a set and the various forms of opposition such as complementaries and antonymy. Examples like "Women, Queen, Mother, Servant, Teacher" illustrat
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Formal Semantics of Programming Languages: From Lambda Calculus to Separation Logic
Explore the foundational concepts of formal semantics in programming languages, covering Lambda Calculus, Untyped and Simply-typed languages, Imperative languages, Operational and Hoare logics, as well as Separation logic. Delve into syntax, reduction rules, typing rules, and operational semantics i
7 views • 14 slides
Understanding Semantics: The Study of Meaning in Language
Semantics is the branch of linguistics focusing on meaning, exploring how words, sentences, and symbols convey and represent ideas. It is crucial for language acquisition, change, social contexts, and linguistic analysis. Important aspects include symbol and referent relationships, denotation, conno
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Semantic Properties in Lexical Semantics
Explore the concept of semantic properties in lexical semantics through examples involving word meanings and relationships. Learn how semantic properties form the basic building blocks of language construction, sharing common attributes among words while also showing contrastive distinctions. Dive i
0 views • 17 slides
Clause Structure and Verb Semantics in Communication Analysis
Exploring the syntax and semantics of clausal complementation, focusing on CPs as subjects in the context of manner of speaking verbs. The discussion delves into MoS verbs like holler, yell, mumble, and shout, analyzing their role in depicting intended acts of communication and the physical characte
0 views • 48 slides
An Exploration of Semantics and Pragmatics: Classical vs. Prototype Approach
Delve into the world of semantics and pragmatics through an examination of the classical and prototype approaches to defining categories. From Aristotle's sharp boundaries to Rosch's fuzzy categories, uncover the complexities and limitations of language structure and meaning.
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Word Meaning in Lexical Semantics
Introduction to Chapter 5 Lecture 4.1 discusses the nature of word meaning, major problems of lexical semantics, and different approaches. It explains the concept of a word, prototypical words, lexical roots, lexemes, and word forms, highlighting the importance of the word as a lexeme in lexical sem
1 views • 20 slides
Natural Language Semantics: Combining Logical and Distributional Methods
Explore the integration of logical and distributional methods in natural language semantics, including the use of probabilistic logic, FOPC, Montague Semantics, semantic parsing, and more. Delve into the rich representation of knowledge, semantic compositionality, and the mapping of natural language
0 views • 43 slides
Understanding Semantics: Reference and Sense Explained
Explore the concepts of reference and sense in semantics through examples and practice questions. Learn how language expressions refer to things in the world and understand the distinction between the referent and the reference. Delve into variable and constant reference with practical scenarios to
0 views • 8 slides
Balanced Graph Edge Partition and Its Practical Applications
Balanced graph edge partitioning is a crucial problem in graph computation, machine learning, and graph databases. It involves partitioning a graph's vertices or edges into balanced components while minimizing cut costs. This process is essential for various real-world applications such as iterative
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Lexical Semantics: An Overview
Lexical semantics explores the relationships words have with each other and with our understanding of reality. It delves into reference and sense, naming theory, synonymy, and more. Reference focuses on how words relate to objects, while sense deals with relationships between lexical items. Naming t
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Semantics and Pragmatics: Exploring Extensions of Meaning
This chapter delves into the realms of semantics and pragmatics, exploring literal and non-literal meanings, naturalized, established, and nonce extensions, as well as metaphor and metonymy. It discusses how certain meanings become entrenched in language, either as naturalized or established extensi
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding the Relationship Between Language and Music: Insights from Semantics
This presentation by Winfried Lechner delves into the intricate connection between language semantics and music, exploring the meanings of linguistic expressions and the underlying concepts. It compares methodologies of linguistics and musicology, analyzing the denotation and reference in language a
0 views • 43 slides
Analyzing Big Graphs with Pregelix Dataflow Engine
Explore how Pregelix on a dataflow engine enables efficient processing of large graphs, providing insights on its system architecture, experimental results, and related work in graph analytics. Understand Pregel semantics, programming model, APIs, and graph mutations for effective analysis of big da
0 views • 38 slides
Query-Centric Framework for Big Graph Querying
A comprehensive exploration of Google's Pregel system, outlining its design, programming interfaces, vertex partitioning, vertex states, and practical examples like Breadth-First Search. The framework provides insights into large-scale graph processing by thinking like a vertex and leveraging messag
0 views • 30 slides
Understanding Semantics of Datalog With Negation
Delve into the semantics of Datalog with negation, exploring the concepts of local stratification, stable models, well-founded models, and the importance of model selection in determining the meaning of Datalog programs. Discover the significance of ground atoms and the implications for declarative
0 views • 55 slides
Understanding Pragmatics in Language Analysis
Pragmatics in language analysis involves studying utterance meaning beyond semantics, focusing on context-dependence, complete context-dependence, and pragmatic knowledge. Basic concepts include semantics, discourse, Grice's Relevance Theory, Speech Acts, Metaphor Theory, and more. Truth-conditional
0 views • 47 slides
Understanding Semantics: Basic Notions and Definitions
Semantics is a serious academic discipline focusing on the meaning of language. It delves into denotation, connotation, and the semiotic triangle, aiming to provide a clear understanding of how meaning operates in language use. Definitions from notable linguists like John Lyons and insights into sem
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Semantics: Examples and Definitions
The content covers basic ideas in semantics with an emphasis on the study of meaning in language. It includes practice examples exploring word meanings, sentence interpretations, speaker intentions, and discussions on the definitions of meaning in language. Through conversations, it illustrates how
0 views • 10 slides
Logic-Based Production System (LPS) by Robert Kowalski and Fariba Sadri
LPS, developed at Imperial College London, is a logic-based production system that combines reactive rules with logic programs to provide a logical semantics for production systems. It is used for practical programming, databases, AI knowledge representation, and problem solving. LPS is known for it
0 views • 45 slides
Exploring Semantics: Meaning of Words and Concepts
Semantics is the study of the meaning of words, ranging from their basic literal components to their associative connotations. This branch of linguistics focuses on objective meaning shared by all rather than subjective interpretations. Concepts like conceptual and associative meanings are explained
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Invariants and Abstract Interpretation in Trustworthy AI Systems
Invariants and Abstract Interpretation are crucial concepts in building trustworthy AI systems. This involves defining configurations, concrete semantics, set semantics, and handling programs with loops. Monotonic functions play a vital role in ensuring consistency in the interpretation of these sys
0 views • 22 slides
Fundamentals of English Semantics: Key Concepts and Theories
English Semantics explores the study of meaning in human language, focusing on compositional characteristics and significantly underspecified meanings. It delves into the interconnected branches of linguistics, including phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics, each playi
0 views • 13 slides
Introduction to Distributed Computing at Stanford University
A meeting at Stanford University's Gates building tonight for those interested in CS341 in the Spring. The session will cover the concept of viewing computation as a recursion on a graph, techniques like Pregel, Giraph, GraphX, and GraphLab for distributed computing, and challenges in data movement
0 views • 18 slides
Introduction to Google's Pregel Distributed Analytics Framework
Google's Pregel is a large-scale graph-parallel distributed analytics framework designed for graph processing tasks. It offers high scalability, fault tolerance, and flexibility in expressing graph algorithms. Inspired by the Bulk Synchronous Parallel (BSP) model, Pregel operates in super-steps, ena
0 views • 38 slides
Introduction to GraphLab: Large-Scale Distributed Analytics Engine
GraphLab is a powerful distributed analytics engine designed for large-scale graph-parallel processing. It offers features like in-memory processing, automatic fault-tolerance, and flexibility in expressing graph algorithms. With characteristics such as high scalability and asynchronous processing,
0 views • 26 slides
Introduction to Spark: Lightning-Fast Cluster Computing
Spark is a parallel computing system developed at UC Berkeley that aims to provide lightning-fast cluster computing capabilities. It offers a high-level API in Scala and supports in-memory execution, making it efficient for data analytics tasks. With a focus on scalability and ease of deployment, Sp
0 views • 17 slides
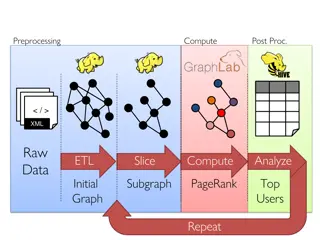
Data Processing and Analysis for Graph-Based Algorithms
This content delves into the preprocessing, computing, post-processing, and analysis of raw XML data for graph-based algorithms. It covers topics such as data ETL, graph analytics, PageRank computation, and identifying top users. Various tools and frameworks like GraphX, Spark, Giraph, and GraphLab
0 views • 8 slides
Memory Models: Enhancing Semantics for Programs with Data Races
This content delves into the importance of establishing stronger memory models to provide better semantics for programs experiencing data races. It highlights the challenges faced due to weak semantics in programming languages like C++ and Java, emphasizing the need for improved memory models to add
0 views • 61 slides