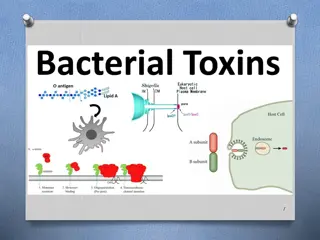
Understanding Bacterial Toxins and Cell Damage
Bacterial toxins are poisonous substances produced by microbes that can cause harm to host cells through direct damage, toxin production, and hypersensitivity reactions. Toxigenesis is a crucial mechanism used by bacterial pathogens to induce disease, with endotoxins and exotoxins playing distinct r
2 views • 28 slides
Salmonellosis: Causes, Clinical Presentations, and Transmission
Salmonellosis is caused by the gram-negative bacterium Salmonella enterica. It predominantly affects warm-blooded vertebrates, leading to carrier states, septicemia, enteritis, and other clinical presentations like abortion and arthritis. The disease is transmitted through contaminated foods of anim
0 views • 15 slides
Klebsiella Species: Characteristics and Pathogenicity
Klebsiella species, such as K. pneumoniae and K. oxytoca, are gram-negative bacilli commonly found in the microbiota of the intestines, nasopharynx, and feces. They exhibit distinct characteristics like pink mucoid colonies on MacConkey's agar and are known to cause both community-acquired and hospi
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Host-Parasite Relationship in Microbiology
In microbiology, the host-parasite relationship is crucial for understanding diseases caused by pathogens. This lecture covers definitions of terms like pathogenicity, pathogen, disease, resistance, susceptibility, infection, virulence, and transmissibility. It also delves into the division of host
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Pathogenicity in Infectious Diseases and Parasitism
Pathogenicity refers to the ability of a pathogen to cause disease in plants, humans, and animals. Infectious diseases and parasitism play key roles in the spread and development of epidemics. Parasites can hinder the normal growth of plants by extracting nutrients, while different types of parasite
0 views • 5 slides
Understanding Sarcocystis Parasites in Veterinary Parasitology
Veterinary Parasitology delves into the study of Sarcocystis parasites, focusing on their morphology, life cycle, and impact on hosts. The Sarcocystidae family, including species like Sarcocystis hominis and S. suihominis, are examined for their pathogenicity in carnivores and herbivores, shedding l
1 views • 11 slides
Insights into the Plague: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Outbreaks
The Plague, caused by Yersinia pestis, has a chilling history spanning pandemics like the Justinian Plague and the Black Death. Understanding its etiology, family, and pathogenicity is crucial. This deadly disease has had notable outbreaks in India, emphasizing the importance of recognizing its host
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Mechanisms of Viral Infection and Spread
Viral infection involves a replicative cycle within the host, leading to a range of cellular responses from no apparent effect to disease. Factors such as virulence genes, host characteristics, and viral genome influence the pathogenicity and virulence of a virus. The process includes entry into the
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Characteristics, Culture, and Pathogenicity
The genus Pseudomonas, specifically P. aeruginosa, is a well-known opportunistic pathogen found in diverse ecological niches. This bacterium, commonly associated with disease conditions in animals and humans, exhibits unique growth characteristics, pigment production, and virulence factors. Its adap
1 views • 14 slides
Understanding Mycobacteria: Human TB, Bovine TB, and Atypical Mycobacteria
The article explores characteristics and differences between Human TB, Bovine TB, and Atypical Mycobacteria, discussing their growth, biochemical reactions, pathogenicity, and disease manifestations. Additionally, it highlights the properties of Mycobacterium leprae, emphasizing its unique morpholog
0 views • 7 slides
Overview of Salmonella Infections and Pathogenicity
Salmonella bacteria, often transmitted through contaminated food or drink, can cause various infections in humans and animals. They are identified by their morphology, and classified into different species and subtypes. The pathogenesis of Salmonella infections varies, with some species infective pr
0 views • 18 slides
Overview of Enterobacteriaceae Family and Their Antigenic Structure
The Enterobacteriaceae family comprises a diverse group of gram-negative rods commonly found in the gut of humans and animals, known for causing various diseases. Key members include Escherichia coli, Shigella, Salmonella, Klebsiella, and more. They are facultative anaerobes, ferment glucose, lack c
0 views • 48 slides
Understanding Hemoflagellates: Leishmania and Trypanosoma Species
Hemoflagellates are blood and tissue parasites belonging to the genera Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma spp. This article discusses their life cycle, pathogenicity, diseases they cause like visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis, and diagnostic methods. Special focus is given to Leishmania donovani and
0 views • 14 slides
Overview of Myxoviruses: Classification, Morphology, and Orthomyxoviridae
Myxoviruses are a group of viruses that bind to mucin receptors on red blood cells, causing hemagglutination. They are classified into orthomyxoviridae and paramyxoviridae, with influenza viruses being major pathogens. Influenza viruses consist of three genera and have distinct morphological feature
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Parasitology: An Introductory Overview by Dr. Saif alshalah
Parasitology, as elucidated by Dr. Saif alshalah, delves into the science of parasites and their impact. This discipline encompasses medical parasitology, the study of parasitic agents causing diseases in humans. The definition and classification of parasites based on their nature, association with
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Fungi: A Brief Overview of Mycology in Microbiology by Dr. Esra Hassan
Fungi, classified as living eukaryotic microorganisms, exhibit diverse structural forms such as yeasts and molds in mycology. This field explores the characteristics, pathogenicity, and importance of fungi, particularly Candida in oral mycology. Discover the fundamental concepts of morphology, hypha
0 views • 32 slides
Overview of Neisseria: Morphology, Cultural Characteristics, and Pathogenicity
Neisseria, named after Dr. Albert Neisser, are gram-negative cocci known for causing gonorrhoea and other infections. They are aerobic, catalase-positive organisms usually found as commensals in the upper respiratory tract. Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis are the most significant sp
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Chicken Pox: A Seminar on the Medical Importance of Viruses
Chicken pox, caused by the Varicella-zoster virus, is a contagious infection primarily affecting children. This seminar presentation delves into the classification, route of infection, symptoms, and treatment of this viral disease common in Africa. The Varicella-zoster virus, a member of the herpes
0 views • 17 slides
Overview of Neisseria Species: Characteristics, Pathogenicity, and Laboratory Diagnosis
Neisseria species are Gram-negative diplococci known for pathogens like N. gonorrhoeae causing gonorrhea and N. meningitidis causing meningitis. They are aerobic to facultatively anaerobic, oxidase-positive, non-motile, and encapsulated cocci. N. gonorrhoeae is fastidious, requiring increased CO2 te
0 views • 20 slides
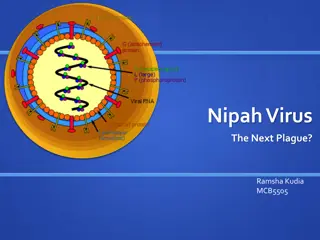
Understanding Nipah Virus: A Comprehensive Overview
Nipah virus, belonging to the Paramyxoviridae family, is a zoonotic virus with high pathogenicity and mortality rates. It falls under the Henipavirus genus, known for infecting a wide range of animal species. Its virion structure consists of non-segmented, negative-sense RNA, and the viral genome co
0 views • 22 slides