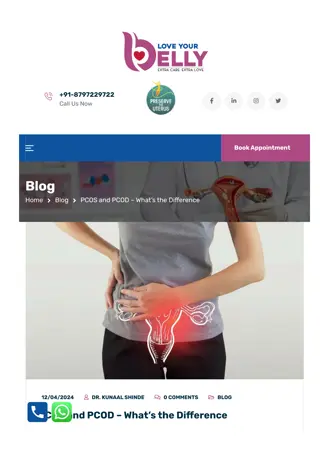
PCOS and PCOD – What’s the Difference
(PCOS and PCOD) Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Polycystic Ovary Disorder are commonly heard regarding women\u2019s health. These conditions are often used interchangeably, However, there is a difference between the two. PCOS is the more common of the two conditions and is caused by an imbalance of ho
7 views • 6 slides
Evaluation of Economic Crisis Causes in 1929-1933: Republican Policies and Factors
The economic crisis of 1929-1933 in the USA was influenced by various factors, including Republican government policies favoring laissez-faire capitalism, overproduction of goods, weaknesses in the banking system, international economic issues, and the Wall Street Crash. The prosperity of the 1920s,
0 views • 33 slides
Understanding Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Overview and Clinical Considerations
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) include a group of disorders characterized by overproduction of blood cells. The WHO classification outlines eight disorders with varied clinical presentations and potential for transformation. These disorders, such as CML, CNL, and PV, exhibit significant phenoty
2 views • 58 slides
Lean: Identifying Waste in Toyota Production Systems Lab (Grades K-5)
Industrial engineers use Lean principles to identify and eliminate waste in processes. The story of Tim Wood the woodcarver illustrates the 7 types of waste: Transportation, Inventory, Motion, Waiting, Overproduction, Overprocessing, and Downtime. Kids can learn to identify waste in their homes thro
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Waste and Kaizen in Toyota Production Systems
Industrial engineers strive to enhance processes by identifying and reducing waste. The concept of waste, known as Muda in Japanese, is central to Lean methodologies. By recognizing and addressing the seven types of waste, such as overproduction and downtime, teams can continuously improve through K
0 views • 7 slides
The USA 1920-1973: Opportunity and Inequality Part One
In the booming 1920s USA, technological advancements, mass production, and Republican policies led to economic growth, with a significant focus on consumer goods like cars, radios, and refrigerators. While the era saw a rise in prosperity for some, including business owners and investors, others, su
0 views • 6 slides
Examining State-Level and Dyadic Explanations for War in Global Politics
Understanding the reasons why certain states are more war-prone than others involves exploring factors such as economy, internal opposition, and political systems. Marxist explanations argue that capitalist economies are more prone to war due to issues like overproduction, wealth inequality, and imp
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Crystalarthropathies and Gout: A Comprehensive Overview
Crystalarthropathies encompass a group of diseases characterized by hyperuricemia and uric acid crystal formation, leading to conditions like gouty arthritis and nephrolithiasis. Primary gout, characterized by hyperuricemia without an identifiable underlying cause, primarily affects older men. Mecha
0 views • 34 slides
Causes of the Great Depression: Summary and Learning Targets
Students are tasked with summarizing specific causes of the Great Depression on index cards, with topics including overproduction in agriculture and industry, unequal distribution of wealth, and high tariffs. Learning targets include summarizing relevant facts about the causes of the Great Depressio
0 views • 16 slides
Causes of the Great Depression: An Analysis of 5 Main Factors
The Great Depression was caused by various factors including unequal distribution of wealth, overproduction in industry, uneven distribution of income, high tariffs, and war debts. The farm depression of the 1920s, stock market crash, and financial panic all contributed to the economic crisis. These
0 views • 16 slides