Amino Acids: Disposal of Nitrogen
Overview of nitrogen metabolism with a focus on the disposal of nitrogen through amino acid catabolism. It explains the process of removing the α-amino groups from amino acids, the synthesis of urea, and the conversion of carbon skeletons to energy-producing pathways.
36 views • 65 slides
Significance of Amino Acids in Biological Pathways
Amino acids play a crucial role as precursors in various biological processes, serving as building blocks for small molecules like hormones, coenzymes, nucleotides, and more. Glycine, a key amino acid, serves as the major precursor for porphyrins, essential in heme proteins. Understanding the pathwa
0 views • 21 slides
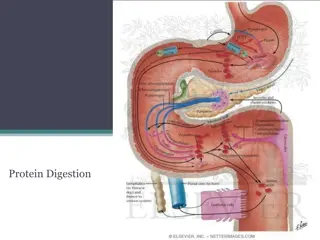
Comprehensive Overview of Protein Digestion in the Gastrointestinal Tract
Understanding the process of protein digestion is crucial for optimal nutrient absorption and overall health. In this lecture series by Professor Shraddha Singh, delve into the composition of proteins, the role of enzymes in protein digestion, sites of absorption, molecular basis of protein transpor
1 views • 28 slides
Color Tests for Proteins and Amino Acids
This experiment involves employing color tests to detect specific amino acids like tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Various reagents are used to observe distinctive color changes, indicating the presence of these amino acids. Detailed procedures, materials, and results are documented for each te
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Acids, Bases, and Buffers in Medical Biochemistry
Biologically important molecules, such as acids and bases, have significant roles in metabolism. Strong acids like hydrochloric acid ionize completely, while weak acids and bases play crucial regulatory roles. The Bronsted-Lowry theory defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. Eq
0 views • 29 slides
Amino Acid Catabolism: Pathways and Reactions
Amino acid catabolism involves removing amino groups via deamination, leading to urea synthesis and TCA cycle intermediates. The process includes transamination and oxidative deamination reactions, with specific aminotransferases catalyzing these reactions. Transamination is a key step in funneling
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding the Urea Cycle in Biochemistry
Explore the intricate process of the urea cycle, its role in removing amino groups from amino acids, converting ammonia into urea in the liver, and managing hyperammonemia. Learn about transamination, oxidative deamination, and the importance of glutamine and alanine in ammonia transport. Discover t
1 views • 26 slides
Understanding Protein Digestion and Amino Acid Metabolism
The process of protein digestion involves proteolytic enzymes produced by the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine. Pepsinogen is activated to pepsin in the stomach, breaking down proteins into oligopeptides and amino acids. After absorption, amino acids are utilized for protein synthesis and as d
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Amino Acids: Qualitative Tests and Properties
Amino acids play a crucial role as building blocks of proteins and can be converted into specialized products. There are 20 common L-α-amino acids found in mammalian proteins, each with a unique structure and classification based on their side chain properties. Amino acids exhibit optical activity,
1 views • 34 slides
Amino Acid Metabolism Pathways: Transamination, Deamination, and Clinical Significance of Transaminases
Amino acid metabolism involves pathways such as transamination, deamination, and the clinical significance of serum transaminases like ALT and AST. Transamination involves the transfer of amino groups, while deamination involves the removal of the amino group. Transaminases are important intracellul
0 views • 23 slides
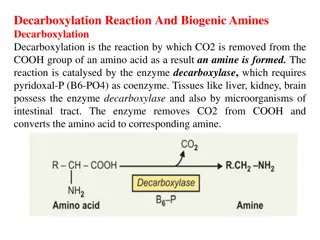
Decarboxylation Reaction and Biogenic Amines in Amino Acid Metabolism
Decarboxylation is a crucial reaction in amino acid metabolism where CO2 is removed to form biogenic amines, catalyzed by decarboxylase enzymes. Important biogenic amines include tyramine, tryptamine, and histamine, each impacting physiological functions like blood pressure regulation. Aromatic amin
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Peptide and Protein Chains Formation
Proteins and peptides are composed of 20 common amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Chains with less than 50 amino acids are known as peptides, while those exceeding 50 are considered proteins.
4 views • 23 slides
Amino Acid: Structure and Classification Overview
Amino acids are essential building blocks of proteins, with only 20 out of the 300 occurring in nature being used for protein synthesis. The structure of amino acids consists of four groups attached to a central carbon atom. At physiological pH, these groups can ionize, forming zwitterions. Amino ac
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Transamination and Deamination in Biochemistry
Transamination is a vital chemical reaction in biochemistry that transfers amino groups to ketoacids to form new amino acids, playing a crucial role in amino acid metabolism. Enzymes called transaminases facilitate this process, utilizing -ketoglutarate as a key amino group acceptor. The mechanism i
5 views • 17 slides
Understanding the Structure and Role of Amino Acids in Proteins
Amino acids are building blocks of proteins, with distinct structures and properties. There are 20 common amino acids found in mammalian proteins, each with a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a unique side chain. The side chains determine the role of an amino acid in a protein, classified as nonp
8 views • 11 slides
Understanding Amino Acids: Structure, Properties, and Classification
Amino acids are essential building blocks of proteins with unique structures and properties. They contain both carboxyl and amino groups, playing vital roles in metabolism. This article covers their general structure, zwitterion form, isoelectric point, pK values, and classification based on body re
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Proteins: Functions, Structure, and Breakdown
Explore the world of proteins, from their essential functions in living organisms to the chemistry of amino acids that form them. Learn how proteins are structured, the significance of amide links, and how they are broken down through hydrolysis. Delve into the importance of essential amino acids an
0 views • 17 slides
Amino Acid Absorption Mechanisms in Small Intestine
Amino acid absorption in the small intestine is an active process requiring energy derived from ATP hydrolysis. It involves two main mechanisms: carrier proteins transport system and glutathione transport system. The carrier proteins transport system uses ATP energy for absorption, while glutathione
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Amino Acids: Structure, Classification, and Properties
Amino acids are crucial chemical units that form proteins and play essential roles in the body. They consist of a carboxyl group and an amino group, serving as building blocks and metabolic intermediates. This article covers the general structure, zwitterions, isoelectric point, pK values, and class
0 views • 26 slides
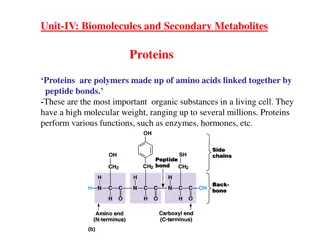
Understanding Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins in Organic Chemistry
Amino acids, peptides, and proteins are essential components in biological processes. Proteins are polymers made up of amino acid units linked by peptide bonds, while peptides are important in various biological functions. The structure and classification of amino acids play a vital role in the stru
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Acids and Bases in Chemistry
Acids donate protons, while bases accept them. Strong acids ionize completely while weak acids only partially ionize, resulting in a Ka value less than one. Water, being amphoteric, can both donate and accept protons. The ionization of water leads to a constant Kw value of 10^-14. Explore the ioniza
0 views • 15 slides
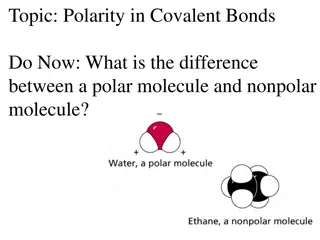
Understanding Polarity in Covalent Bonds
The difference between a polar molecule and a nonpolar molecule lies in the distribution of electrons. A polar molecule has an asymmetric electron distribution due to a significant difference in electronegativity, while a nonpolar molecule has a symmetric electron distribution. You can predict polar
0 views • 15 slides
Qualitative Tests of Proteins & Amino Acids: Overview and Analysis
In this lab, you will delve into the qualitative tests for proteins and amino acids, understanding their structures, classifications, and importance in food and human nutrition. The tests include solubility tests and identification tests for both amino acids and proteins, revealing their presence an
0 views • 13 slides
Qualitative Tests of Proteins & Amino Acids - Lab Analysis Overview
This lab analysis covers qualitative tests for proteins and amino acids, including solubility tests and identification tests for amino acids and proteins. Specific tests like Ninhydrin test for -L amino acids, Xanthoproteic test for aromatic amino acids, and lead sulfite test for sulfhydryl group de
0 views • 13 slides
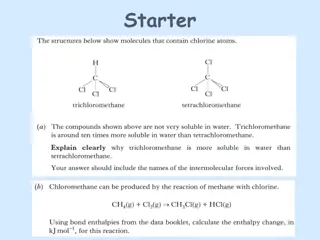
Understanding Intermolecular Forces and Dispersion Forces in Molecules
Particle diagrams of liquids, solids, and gases reflect distinct arrangements due to intermolecular forces. The existence of substances as gases, liquids, or solids at room temperature is attributed to the forces between molecules known as intermolecular forces (IMF), with dispersion forces being th
0 views • 30 slides
Overview of Amino Acidopathies in Dentistry: Defects in Amino Acid Metabolism
This lecture discusses the various amino acidopathies, including phenylketonuria, albinism, alkaptonuria, maple syrup urine disease, and homocystinuria. It covers the metabolic defects in amino acid metabolism, symptoms, causes, and treatment methods for these disorders. Emphasizing the importance o
0 views • 19 slides
Exploring the Early Earth: Origins of Life and Genetic Evolution
Delve into the mysteries of the early Earth and the origin of life through engaging categories such as the absence of certain gases in the atmosphere, the synthesis of amino acids in lab simulations, the formation of protocells using DNA, and the bombardment of space debris. Discover how reducing at
1 views • 26 slides
Overview of Alkaloids in Pharmacognosy
Alkaloids are a diverse group of compounds containing nitrogen that are derived from amino acids like phenylalanine or tyrosine. Protoalkaloids, such as ephedrine, are derived from common amino acids and do not contain a heterocyclic ring. Ephedrine, obtained from Ephedra sinica, has CNS stimulatory
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Proteins: Structure and Function
Proteins are vital organic compounds composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. They serve various functions in cells, such as enzymes and hormones. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, with 20 different types forming all proteins on Earth. Proteins have four levels of structure -
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Acids and Bases in Chemistry
Acids and bases play essential roles in chemistry, where they release hydrogen ions or hydroxide ions when mixed with water. Acids, like vinegar and lemon juice, are corrosive and can cause chemical burns. On the other hand, bases, such as bleach and dish soap, contain the hydroxide group in their f
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Amino Acids: Structure, Types, and Importance
Amino acids are essential organic molecules that serve as the building blocks of proteins. They contain unique chemical groups and play crucial roles in various bodily functions. This article discusses the structure of amino acids, their different types (D and L), and highlights their importance in
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Conjugate Acids and Bases in Chemistry
Explore the concept of conjugate acids and bases in chemistry through definitions, reactions, and examples. Learn how to identify strong and weak acids/bases based on their conjugates and understand the behavior of acids/bases in reverse reactions. Discover the significance of conjugate acids/bases
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding pH Calculations for Acids and Bases in Water
Acids and bases play crucial roles in chemical reactions by involving the transfer of protons. This lecture explains the definitions of acids and bases, general acid-base reactions in water, and how the pH scale is used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution. It covers how acids and bases
0 views • 42 slides
Mapping QTL and Selection of Soybean Lines with High Essential Amino Acids
Soybean (Glycine max L.) plays a crucial role as a crop in North Carolina, especially for its essential amino acids content critical for human and animal nutrition. This study aims to identify quantitative trait loci (QTL) for essential amino acids in soybean seeds using a genetic map from the Forre
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding the Titration of Weak Acids and Amino Acids
Titration is a crucial technique used to determine the properties of weak acids and amino acids. This process involves calculating pH values, degree of ionization, and understanding the ionization equilibrium of different acid-base systems. Various examples, including glycine hydrochloride, isoelect
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Acids and Bases: Ionization and Properties
Acids donate protons while bases accept them. Strong acids and bases ionize completely, while weak acids ionize partially. Water is amphoteric, capable of both accepting and donating protons. The equilibrium constant Kw for water is 10^-14. Understanding the ionization of weak acids and weak bases h
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Acids and Bases in Chemistry: Key Concepts and Terminology
This chapter delves into the fundamental concepts of acids and bases in chemistry, covering Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis definitions. It discusses conjugate acids and bases, acid dissociation, dissociation of strong and weak acids, and the differences between strong and weak acids/bases. The
0 views • 41 slides
Understanding the Genetic Code and Protein Synthesis
Explore the fascinating world of nucleic acids, DNA, RNA, and the genetic code. Discover how the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA translates into amino acids, forming proteins. Learn about codons, ribonucleotides, and the triplet code, and unravel the process of reading the genetic code to determine
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Translation in Genetic Processes
Translation is the process of converting RNA messages into amino acids in cells. This key step in gene expression involves decoding codons, utilizing tRNA as adaptors, and following the genetic code to produce proteins. The shared genetic code, the role of tRNA in carrying amino acids, and the conti
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Nucleic Acids and the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
In molecular biology, understanding nucleic acids like DNA and RNA is crucial for comprehending the central dogma, which explains the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to proteins. Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides, composed of pentose sugar, nitrogenous bases, and phosphate groups
0 views • 18 slides