Genetic Control of Metabolism in Microbes: Enhancing Traits for Biotechnology
Exploring the genetic control of metabolism in microbes, focusing on wild type organisms and the process of strain improvement through mutagenesis, selective breeding, and recombinant DNA techniques. The potential benefits and challenges of altering microbial genomes for biotechnological application
0 views • 27 slides
Improving Microbial Productivity and Characteristics for Industrial Applications
Efforts to enhance the productivity of natural isolates for commercial products involve genetic modifications through mutation, genetic recombination, and genetic engineering techniques. Desired characteristics include genetic stability, efficient production, versatility in carbon sources, and ease
1 views • 25 slides
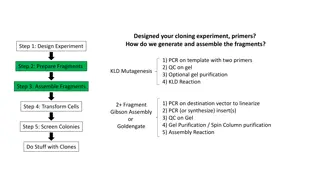
Cloning Experiment Overview and Procedures
The cloning experiment involves designing primers, generating and assembling fragments through PCR, gel purification, and KLD reaction. Further steps include fragment preparation, assembly, cell transformation, colony screening, and working with clones. Detailed instructions for KLD mutagenesis, QC
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Mutagenesis, DNA Damage, Repair, and Recombination
Mutations in DNA, caused by various factors such as radiation and chemical mutagens, can lead to permanent changes in the genetic sequence. Repair mechanisms like direct reversal, excision repair, and trans-lesion DNA synthesis play crucial roles in maintaining DNA integrity and accuracy during repl
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Site-Directed Mutagenesis in Molecular Biology
Site-directed mutagenesis is a crucial molecular biology technique used to intentionally modify DNA sequences for research purposes. By synthesizing a short DNA primer containing the desired mutation, hybridizing it with the template DNA, and then extending it using a DNA polymerase, scientists can
0 views • 10 slides
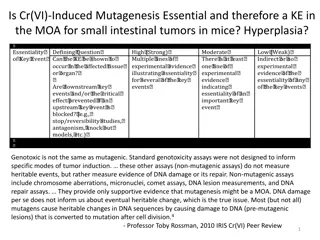
Essentiality of Cr(VI)-Induced Mutagenesis in Small Intestinal Tumor Development in Mice
Cr(VI)-induced mutagenesis is a key event in the mode of action for small intestinal tumors in mice, with the question of whether it is an essential step in tumor development. The interaction of cellular components with Cr leads to cell proliferation, hyperplasia, and ultimately mutagenesis. Differe
0 views • 4 slides