Understanding Solutions and Concentration Units
Explore the world of solutions, the role of solvents and solutes, why solutions form, different concentration units like molarity and molality, calculations involved, colligative properties such as vapor pressure lowering, and how Raoult's Law explains changes in boiling and freezing points in solut
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Freezing Point Depression and Molality for Solutions
Introduction to molality and freezing point depression in solutions. Molality is a way to measure solution concentration, calculated using moles of solute and kilograms of solvent. By calculating the moles of NaCl in a salt solution and the mass of the solvent (ice/water), the molality can be determ
0 views • 9 slides
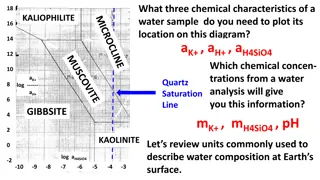
Understanding Chemical Characteristics and Units in Water Composition Analysis
Discover the essential chemical characteristics required to plot a water sample on a diagram and learn about the limitations of using molarity for concentrated solutions of divalent ions, especially when dealing with changing temperatures. Explore the concept of molality and its advantages, while al
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Molarity and Molality in Solutions
Solutions are combinations of solvent and solute, with varying concentrations affecting their properties. Molarity and molality are key measures of concentration, and saturation levels impact solubility. Explore examples to calculate molarity for solutions in different scenarios.
0 views • 12 slides
Chemical Measurements Overview
In Chapter 1 - Chemical Measurements, you will delve into SI Units, derived SI units, prefixes, unit conversions, concentrations like molarity and molality, and percent compositions. Explore how to use prefixes for calculations, convert units, and understand different concentration measurements for
0 views • 22 slides