Inference and Vyapti in Logic
Inference, known as Anumana in Sanskrit, is the process of deriving knowledge based on existing information or observations. It can be used for personal understanding or to demonstrate truths to others. An inference may be SvArtha (for oneself) or ParArtha (for others). Vyapti, the invariable concom
1 views • 14 slides
Inference in Indian Philosophy
In Indian philosophy, inference is considered one of the six ways to attain true knowledge. It involves three constituents: Hetu (middle term), Sadhya (major term), and Paksha (minor term). The steps of inference include apprehension of the middle term, recollection of the relation between middle an
13 views • 8 slides
Resolution in Logical Inference
Resolution is a crucial inference procedure in first-order logic, allowing for sound and complete reasoning in handling propositional logic, common normal forms for knowledge bases, resolution in first-order logic, proof trees, and refutation. Key concepts include deriving resolvents, detecting cont
3 views • 12 slides
Scope of Inference in Statistical Studies
Statistical studies require careful consideration of the scope of inference to draw valid conclusions. Researchers need to determine if the study design allows generalization to the population or establishes cause and effect relationships. For example, a study on the effects of cartoons on children'
1 views • 15 slides
DNN Inference Optimization Challenge Overview
The DNN Inference Optimization Challenge, organized by Liya Yuan from ZTE, focuses on optimizing deep neural network (DNN) models for efficient inference on-device, at the edge, and in the cloud. The challenge addresses the need for high accuracy while minimizing data center consumption and inferenc
1 views • 13 slides
The Difference Between Observation and Inference
Learn to differentiate between observation (direct facts or occurrences) and inference (interpretations based on existing knowledge or experience) through examples such as the Sun producing heat and light (observation) and a dry, itchy skin leading to the inference that it is dry. The distinction be
2 views • 14 slides
Navigating Statistical Inference Challenges in Small Samples
In small samples, understanding the sampling distribution of estimators is crucial for valid inference, even when assumptions are violated. This involves careful consideration of normality assumptions, handling non-linear hypotheses, and computing standard errors for various statistics. As demonstra
1 views • 19 slides
Rules of Inference in Logic
Dive into the world of logic with this detailed exploration of rules of inference. Learn about different types of arguments, such as Modus Ponens and Modus Tollens, and understand how to determine the validity of an argument. Discover the purpose of rules of inference and unravel the logic behind co
0 views • 17 slides
Stars: The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and Stellar Properties
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram is a tool that plots the luminosity or absolute magnitude of stars against their surface temperatures, revealing distinct groups that represent stages in the stars' life cycles. Apparent magnitude measures how bright a star appears from Earth, while absolute magnitude
1 views • 16 slides
Expert Systems and Knowledge Inference
Expert Systems (ES) act as synthetic experts in specialized domains, emulating human expertise for decision-making. They can aid users in safety, training, or decision support roles. Inference rules and knowledge rules play key roles in ES, helping in problem-solving by storing facts and guiding act
1 views • 63 slides
Knowledge-Based Agents: Inference, Soundness, and Completeness
Inference, soundness, and completeness are crucial concepts in knowledge-based agents. First-order logic allows for expressive statements and has sound and complete inference procedures. Soundness ensures derived sentences are true, while completeness guarantees all entailed sentences are derived. A
0 views • 6 slides
Fast High-Dimensional Filtering and Inference in Fully-Connected CRF
This work discusses fast high-dimensional filtering techniques in Fully-Connected Conditional Random Fields (CRF) through methods like Gaussian filtering, bilateral filtering, and the use of permutohedral lattice. It explores efficient inference in CRFs with Gaussian edge potentials and accelerated
1 views • 25 slides
Probabilistic Graphical Models Part 2: Inference and Learning
This segment delves into various types of inferences in probabilistic graphical models, including marginal inference, posterior inference, and maximum a posteriori inference. It also covers methods like variable elimination, belief propagation, and junction tree for exact inference, along with appro
1 views • 33 slides
Stellar Brightness and Magnitude Distances
Explore the relationship between a star's brightness as observed from Earth and its actual brightness, distance, apparent magnitude, and absolute magnitude. Learn how to calculate these values using data and formulas. Gain insights into the variations in star distances, brightness, and magnitudes to
2 views • 6 slides
Optimizing Inference Time by Utilizing External Memory on STM32Cube for AI Applications
The user is exploring ways to reduce inference time by storing initial weight and bias tables in external Q-SPI flash memory and transferring them to SDRAM for AI applications on STM32Cube. They have questions regarding the performance differences between internal flash memory and external memory, r
1 views • 4 slides
Typed Assembly Language and Type Inference in Program Compilation
The provided content discusses the significance of typed assembly languages, certifying compilers, and the role of type inference in program compilation. It emphasizes the importance of preserving type information for memory safety and vulnerability prevention. The effectiveness of type inference me
1 views • 17 slides
Magnitude-Based Inference (MBI) - A New Approach to Analyzing Study Results
Magnitude-Based Inference (MBI) offers a novel perspective on interpreting study outcomes by focusing on confidence intervals rather than solely relying on p-values. This approach helps researchers make more informed decisions, especially in studies with small samples where p-values may lead to misl
0 views • 22 slides
Rules of Inference Exercise Solutions in Discrete Math
This content provides solutions to exercises involving rules of inference in discrete mathematics. The solutions explain how conclusions are drawn from given premises using specific inference rules. Examples include identifying whether someone is clever or lucky based on given statements and determi
0 views • 4 slides
Modern Likelihood-Frequentist Inference: A Brief Overview
The presentation by Donald A. Pierce and Ruggero Bellio delves into Modern Likelihood-Frequentist Inference, discussing its significance as an advancement in statistical theory and methods. They highlight the shift towards likelihood and sufficiency, complementing Neyman-Pearson theory. The talk cov
1 views • 22 slides
Sequential Approximate Inference with Limited Resolution Measurements
Delve into the world of sequential approximate inference through sequential measurements of likelihoods, accounting for Hick's Law. Explore optimal inference strategies implemented by Bayes rule and tackle the challenges of limited resolution measurements. Discover the central question of refining a
0 views • 29 slides
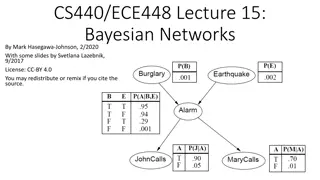
Bayesian Networks for Efficient Probabilistic Inference
Bayesian networks, also known as graphical models, provide a compact and efficient way to represent complex joint probability distributions involving hidden variables. By depicting conditional independence relationships between random variables in a graph, Bayesian networks facilitate Bayesian infer
0 views • 33 slides
Dynamic Crowd Simulation Using Deep Reinforcement Learning and Bayesian Inference
This paper introduces a novel method for simulating crowd movements by combining deep reinforcement learning (DRL) with Bayesian inference. By leveraging neural networks to capture complex crowd behaviors, the proposed approach incorporates rewards for natural movements and a position-based dynamics
0 views • 15 slides
Inference Proof
Abstract reasoning in computer science involves inference proofs where facts are combined to derive new information. The process is formal yet flexible, allowing for complex proofs to be verified with precision. Understanding and utilizing inference rules expand the boundaries of provable statements
0 views • 51 slides
Knowledge-Based Agents: Logic, Inference, and Reasoning Strategies
The foundations of knowledge-based agents, this content delves into logic, inference, and diverse human reasoning strategies. It explores the power of logical reasoning in solving AI problems and discusses how people navigate logical inference challenges. Additionally, it touches on cognitive psycho
0 views • 53 slides
Probabilistic Inference and Variable Elimination in Belief Networks
Probabilistic inference plays a crucial role in computing posterior distributions in belief networks. Exact and approximate inference methods are explored, including variable elimination algorithms. Conditional probability tables are used to represent probabilities efficiently.
0 views • 49 slides
Supervised Distributional Methods for Lexical Inference Relations
This study delves into whether current supervised distributional methods effectively learn lexical inference relations. It compares supervised and unsupervised methods, evaluates the learning capabilities, and discusses the implications for lexical inference tasks. Through experiments with various w
0 views • 30 slides
Bayesian Inference in Linguistic Studies: Exploring Data Analysis Methods
Use of Bayesian inference in linguistic studies for analyzing data. Understand the differences between frequentist and Bayesian probabilities. Learn about Bayes' Theorem, Bayesian inference process, and the importance of choosing priors carefully.
0 views • 20 slides
Using Sentence-Level LSTM Language Models for Script Inference
Event Inference Motivation: Building a Question Answering system requires the inference of probable implicit events. Explore how sentence-level LSTM language models can aid in script inference for improved understanding and context analysis. Delve into the methods, experiments, and conclusions drawn
0 views • 47 slides
Trellis Coded Quantization for CSI Feedback Part 2: Magnitude Quantization
In this document, the authors delve into applying Trellis Coded Quantization (TCQ) to the magnitude of Channel State Information (CSI) feedback. They discuss converting Rayleigh-distributed samples to uniformly distributed samples for quantizing the CSI magnitude. The content covers statistics of Ra
0 views • 17 slides
Probabilistic Models of Human and Machine Learning Techniques
Explore various inference techniques, including exact inference, variable elimination, belief propagation, and more, in the context of probabilistic models of human and machine learning. Learn about common inference problems, notation, and exact inference in Bayes Nets.
0 views • 33 slides
Bayesian Inference Research at Anglia Ruskin IT Institute
Explore the cutting-edge research on Bayesian inference in waveform signals, ECG models, and qIF neuron models at Anglia Ruskin IT Research Institute. Learn about BAYSIG, a new probabilistic modeling language, and the parameter estimation for noisy quadratic integrate-and-fire neuron models using Ba
0 views • 6 slides
Calibrated Bayesian Approach for Survey Inference
Explore the Calibrated Bayesian approach for sample survey inference, including understanding different modes of inference, mechanics of Bayesian inference, and incorporating survey design features. Learn about models for complex surveys and key aspects of survey inference methods. Gain insights int
0 views • 81 slides
Understanding Statistical Parametric Mapping Techniques
Dive into the realm of Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) with insights on random field theory, model fitting, thresholding, and inference techniques. Explore the nuances of signal assessment, voxel-level inference, and cluster-level inference in neuroimaging research.
1 views • 43 slides
Understanding Resolution in Logical Inference
Learn about resolution in logical inference, a sound and complete inference procedure for first-order logic, covering cases like Modus Ponens, Chaining, and Contradiction Detection. See examples of resolution in first-order logic and how it can be used for refutation.
0 views • 12 slides
Liquid Type Inference for Verification and Data Structures
Learn about Liquid Type Inference used in verification and data structures, as discussed in the research paper by Ming Kawaguchi, Patrick Rondon, and Ranjit Jhala from UC San Diego. Explore the concepts of precise data invariants, SMT solvers, and how to retain precision in inference.
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Causal Inference in Machine Learning
Explore the realm of causal reasoning and inference in machine learning, encompassing the discovery of causal relationships from data, heterogeneous treatment effects, automated causal inference, and more. Delve into the complexities of causal discovery and the effects of causes, shedding light on h
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Knowledge-Based Agents and Logical Inference
Explore the essential concepts of knowledge-based agents, logical inference, soundness, completeness, and the importance of reasoning soundness in agent-based decision-making. Learn how intelligent agents use knowledge bases and inference mechanisms to make informed choices.
0 views • 6 slides
Logical Inference and Action Effects in Agent-Based Propositional Logic
Explore how logical inference is used by agents to construct plans based on knowledge bases without relying on inference history. Discover how to track the world's state and model action effects using a complete logical model.
0 views • 6 slides
Causal Inference Research Areas and Projects Overview
Explore a comprehensive overview of research areas in causal inference, including unmeasured confounding, network analysis, psychometrics, transfer learning, and more. Delve into notable papers and projects, such as sensitivity analysis in genomic experiments and causal inference with latent variabl
1 views • 18 slides
Invariant Inference and Complexity Analysis in Transition Systems
Explore the complexities of invariant inference in transition systems, delving into topics such as safety, inductive invariants, SAT-based inference algorithms, and the exact learning model. Discover how these methods succeed, fail, and potential enhancements for better results.
0 views • 33 slides