Understanding Non-literal Meaning: Idioms, Metaphors, and Metonymy
The unpredictable world of non-literal meaning through idiomatic expressions, metaphors, and metonymy. Discover how these concepts shape language and thought.
3 views • 37 slides
Understanding Semasiology: The Study of Word Meaning
Semasiology is a branch of linguistics focused on the meaning of words. It delves into various aspects of lexical meaning, semantic development, polysemy, and semantic structure. Through exploring types of word meanings and semantic changes, semasiology helps us comprehend the intricate nuances of l
4 views • 19 slides
Understanding Translation Studies: From Origins to Cultural Turn
The exploration of translation studies, from its historical roots to the modern cultural turn, delves into the essence of translation, its typologies according to Jakobson, the role of translators through historical perspectives from Cicero to modern times, and insights from Dryden and Schleiermache
2 views • 38 slides
Understanding Semasiology: The Study of Meaning in Language
Semasiology, a branch of lexicology, focuses on the study of meaning in language through different approaches such as the referent approach and functional approach. The referent approach links the sound form with the concept denoted by the word, while the functional approach emphasizes the relations
2 views • 15 slides
TOEFL Exercise 1 Listening Practice
This TOEFL exercise focuses on listening comprehension, where you need to understand the meaning behind spoken dialogues, not just the literal translation. The exercise includes short conversations with questions about the intended meaning, testing your ability to comprehend and interpret spoken Eng
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Indirect Speech Acts in Semantics
Speech acts can be direct or indirect, with indirect speech acts relying on implicature rather than literal meaning. This concept can lead to confusion, especially in cross-cultural communication. Explore the theories of J.L. Austin and John Searle regarding speech acts and performative utterances,
1 views • 16 slides
Understanding Semantic Features in Language Study
Studying basic conceptual meaning is crucial in language analysis to explain the oddness in sentences like "The hamburger ate the boy." Semantic roles and thematic roles help identify the roles of entities in a sentence, such as agents and themes. By analyzing the components of conceptual meaning, w
1 views • 12 slides
Evolution of Translation Theory: From Literal to Sense-for-Sense
Western translation theory up to the 20th century revolved around the debate of literal, free, and faithful translation. This discussion traces back to Cicero and St. Jerome and has influenced translation practices for centuries. While some advocated for word-for-word translations, others, like St.
1 views • 13 slides
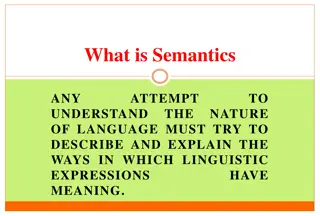
Understanding Semantics: The Study of Meaning in Linguistics
Semantics is the scientific study of meaning in language, delving into questions about definitions, ideas, objects, relations between meanings, and how meanings interact with syntactic rules. Exploring the vagueness of the term "meaning," semanticists explore sense, reference, denotation, and connot
2 views • 19 slides
Understanding PIC18 Family Instruction Set and Literal Instructions
Exploring the operation and significance of literal instructions in the PIC18 family's instruction set, including examples of bitwise operations like AND, IOR, and XOR. Learn how these instructions affect the status register and how they can be used to manipulate data effectively in programming with
1 views • 44 slides
Literal vs. Deeper Meaning in Character Inferences
Exploring the difference between literal and deeper meanings in character inferences through examples from Romeo and Juliet. By analyzing quotes and events, readers can uncover hidden motivations and emotions behind characters' actions, providing a richer understanding of the story.
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Semantics and Pragmatics in Language Study
Semantics and pragmatics are key areas of language study that focus on the meanings of words, phrases, and sentences. Semantics delves into the literal meanings and language as a system, while pragmatics explores how speakers use language in context. Understanding semantic meaning involves consideri
3 views • 77 slides
An Exploration of Linguistic Meaning: Semantics and Pragmatics
Delve into the realm of linguistic meaning through the lenses of semantics and pragmatics. Explore how words and phrases carry literal meanings, while language usage in social contexts creates both literal and nonliteral meanings. Uncover the intricate interplay between semantics, concerned with the
6 views • 70 slides
Understanding Figurative Language: A Guide to Metaphors, Similes, and More
Figurative language is a powerful tool used by writers to evoke emotions and create vivid imagery in the minds of readers. It goes beyond literal meanings, allowing for deeper interpretations and connections with the subject matter. This guide explains the difference between figurative and literal l
0 views • 40 slides
Exploring Connotative Meaning and Translation Issues in Language
Delve into the nuances of connotative meaning through allusive, collocation, and reflected meanings. Discover how translation challenges arise due to cultural nuances and connotations, as exemplified by various expressions and word associations. Explore the significance of appropriate collocations i
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Literary Appreciation and Poem Titles
Literary appreciation involves understanding and enjoying poems, while critical appreciation delves deeper into evaluating their merits and demerits. To understand a poem, one should read it aloud, decipher unfamiliar words, and focus on the overall meaning. Different types of poem titles like Liter
0 views • 14 slides
Meaning and Meaning-making in Big Q Qualitative Research
Qualitative research explores different understandings of meaning and meaning-making, providing researchers with tools, techniques, and values. Big Q qualitative research focuses on the active role of words in creating meaning beyond reflecting experiences. This lecture series delves into the founda
1 views • 20 slides
Understanding Levels of Meaning in Language
Explore the concept of denotation versus connotation and delve into the various types of connotative meanings including attitudinal, associative, affective, and allusive meanings presented by Ayat Amer AbdI.-Sattar. Discover how words can carry multiple layers of meaning beyond their literal interpr
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Denotative Meaning and Translation Issues
Denotative meaning in translation poses challenges due to the elastic and indeterminate nature of meaning, especially in dealing with the cognitive or literal sense of words. Polysemy, homonymy, and synonymy contribute to complexities in determining precise denotative meanings. The rigidity and flex
0 views • 40 slides
Understanding Constants in Programming
Constants in programming are values that remain fixed throughout the execution of a program, unlike variables whose values can change. This lesson outline covers the definition of constants, the difference between variables and constants, categories of constants (literal and named), examples of lite
0 views • 18 slides
Cultural Challenges in Translating Official Chinese Documents
Chinese official communication poses unique challenges for translation into English due to cultural differences in dialogue norms. The literal translation can fail to engage Western audiences, relying heavily on aphorisms and stock expressions. Issues like verbosity, repetition, over-conceptualizati
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Connotation and Denotation in Language
Connotation and denotation play crucial roles in assigning meaning to words. While denotation refers to the literal dictionary definition of a word, connotation involves the emotional and imaginative associations surrounding it. This distinction is exemplified through words like "house" and "home,"
0 views • 21 slides
Exploring Denotative Meaning and Translation Issues
Delve into the intricacies of denotative meaning and its implications in translation. Understand the nuances of polysemy and homonymy, along with the significance of synonymy in defining word meanings. Gain insights into the complexities of determining and translating the literal meanings of words.
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Figurative and Literal Language in English
This comprehensive guide explains the concepts of figurative and literal language, with examples of similes, metaphors, personification, hyperbole, and understatement. Learn how these devices add depth and creativity to writing.
0 views • 32 slides
Understanding Verbal Irony and Tone Through Examples
Verbal irony is the expression of words conveying the opposite of their literal meaning. It is not the same as lying and is used to emphasize a point. Tone plays a crucial role in conveying irony, as it can affect how the message is perceived. Sarcasm, though related, has a negative agenda of mockin
0 views • 7 slides
Exploring the Meaning of Life and Purpose Through Faith and Reflection
Humans are inherently curious, constantly seeking answers to questions about life's meaning and purpose. The journey involves questioning, searching for meaning in various aspects of life, exploring religious beliefs, and engaging in reflective practices.
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Connotation and Denotation in Language
Learn about the difference between connotation and denotation in language, where connotation refers to the emotional meaning of a word and denotation to the literal definition. Discover how words can have different connotations based on personal, cultural, or universal experiences, and consider exam
0 views • 9 slides
The Girl in the Lavender Dress: Literal Questions and Inferences
Retold by Maureen Scott, "The Girl in the Lavender Dress" is a mysterious tale that challenges readers with literal questions and inferences about the characters and events. From the unusual girl in a lavender dress to the gripping moments in the car, the story unravels with intriguing textual evide
0 views • 7 slides
Introduction to Meaning in Language: Semantics & Pragmatics
Meaning in language is explored in this introductory lecture, covering aspects such as communication, semiotics, linguistic channels, and approaches to studying meaning. The process of encoding messages, signal transmission, noise interference, and decoding are discussed within the context of commun
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Semantics and Pragmatics: Exploring Extensions of Meaning
This chapter delves into the realms of semantics and pragmatics, exploring literal and non-literal meanings, naturalized, established, and nonce extensions, as well as metaphor and metonymy. It discusses how certain meanings become entrenched in language, either as naturalized or established extensi
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Pragmatics in Communication
Pragmatics in communication involves recognizing not just the literal meaning of words, but also understanding the speaker's intentions and context. It delves into invisible meanings, shared assumptions, and expectations that shape communication. This includes linguistic and physical context, deixis
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Meaning in Work for Millennials: A Heuristic Study
This study explores the experience of meaning in work for millennials, considering its impact on organizational commitment, change, vision-championing, and leadership. It aims to contribute to the existing knowledge base by examining how millennials perceive and create meaning in their work, using q
0 views • 14 slides
Exploring Semantics: Meaning of Words and Concepts
Semantics is the study of the meaning of words, ranging from their basic literal components to their associative connotations. This branch of linguistics focuses on objective meaning shared by all rather than subjective interpretations. Concepts like conceptual and associative meanings are explained
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Semantics: Exploring Types and Dimensions of Meaning
Explore the complexities of semantics by delving into the types and dimensions of meaning. From descriptive to non-descriptive meaning, learn how the normality profile of linguistic items contributes to their overall meaning. Distinguish between semantic and grammatical anomalies and discover the nu
0 views • 32 slides
Approaches to Statutory Interpretation: The Literal Rule
The Literal Rule in statutory interpretation mandates that all words in a statute be given their ordinary and natural meanings, even if the result seems absurd. This approach emphasizes following the clear wording of the law as enacted by Parliament. Advantages include respecting parliamentary sover
0 views • 26 slides
Decoding Common Euphemisms: Literal vs Figurative Meanings
Explore the world of euphemisms by examining common examples used in society. Discover the literal and metaphorical meanings behind euphemisms like "gone to a better place" and "need to powder my nose." Unveil the subtle ways language softens harsh realities through colorful illustrations and explan
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding the Meaning of New Heavens and New Earth in Biblical Perspectives
The concept of New Heavens and New Earth is explored through various biblical references, highlighting the figurative and literal interpretations in the texts of Isaiah, Peter, and John. The distinction between the prophetic visions of a new order by Isaiah and the eschatological references by Peter
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Literal and Non-Literal Meanings of Words and Phrases in 3rd Grade ELA
Literal language refers to the dictionary meaning of words, while non-literal language involves expressions that go beyond literal interpretation, such as idioms. By using context clues, students can distinguish between literal and non-literal meanings, enhancing their reading comprehension skills.
0 views • 14 slides
ZAKAT 3RD PILLAR OF ISLAM: TRANSFORMING OF YOUR WEALTH INTO BLESSINGS
\/\/seribangash.com\/\nis a word in the Arabic language( Zakhat in Hindi \u091c\u0915\u093e\u0924) whose literal meaning is \u201cpurification\u201d or \u201cgrowth.\u201d It signifies that giving financial support to needy people helps purify one\u2
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Semantics, Lexical, and Grammatical Meaning
Exploring the nuances of semantics, lexical meaning, and grammatical meaning, this content delves into the distinctions between them, the role of lexemes, and the complexities associated with words. It discusses the various kinds of meanings expressed at the lexical and grammatical levels, including
1 views • 37 slides