Understanding Knowledge-Based Agents in Artificial Intelligence
Knowledge-Based Agents in AI utilize logic and knowledge representation to accept tasks, learn, and adapt to changing environments. Logic plays a crucial role in forming complex world representations and deriving actions based on inference. The central component is the Knowledge Base (KB), represent
4 views • 19 slides
Genomic Inference of Human Population Size Changes Over Time
Explore the genomic inference of a severe human bottleneck during the Early to Middle Pleistocene transition, tracing the evolution of hominins over the last 4 million years, and studying essential events in the emergence of humans in the last one million years. Discover well-known human population
4 views • 33 slides
Understanding Knowledge Management: Processes and Frameworks 2. In knowledge management, organizations create, share, and manage knowledge to enhance performance. It involves acquiring different types of knowledge through various means, such as perc
Knowledge Management, Organizational Objectives, Types of Knowledge, Tacit Knowledge, Explicit Knowledge
1 views • 17 slides
Understanding Inference and Vyapti in Logic
Inference, known as Anumana in Sanskrit, is the process of deriving knowledge based on existing information or observations. It can be used for personal understanding or to demonstrate truths to others. An inference may be SvArtha (for oneself) or ParArtha (for others). Vyapti, the invariable concom
1 views • 14 slides
Understanding Deep Generative Models in Probabilistic Machine Learning
This content explores various deep generative models such as Variational Autoencoders and Generative Adversarial Networks used in Probabilistic Machine Learning. It discusses the construction of generative models using neural networks and Gaussian processes, with a focus on techniques like VAEs and
9 views • 18 slides
Understanding Inference in Indian Philosophy
In Indian philosophy, inference is considered one of the six ways to attain true knowledge. It involves three constituents: Hetu (middle term), Sadhya (major term), and Paksha (minor term). The steps of inference include apprehension of the middle term, recollection of the relation between middle an
11 views • 8 slides
Understanding Inference Tests and Chi-Square Analysis
The content discusses the application of inference tests to determine if two variables are related, focusing on categorical and quantitative variables. It provides examples related to testing fairness of a die and comparing observed and expected distributions of Skittles colors. Additionally, it cov
1 views • 16 slides
Understanding Pramana in Indian Philosophy by Mr. Debajit Hazarika
Philosophy delves into the quest for knowledge, with Epistemology exploring sources and validity. In Indian philosophy, Prama signifies true cognition, attainable through Pramana - the means to achieve valid knowledge. This discussion covers the six pramanas within various philosophical systems and
2 views • 11 slides
Understanding Resolution in Logical Inference
Resolution is a crucial inference procedure in first-order logic, allowing for sound and complete reasoning in handling propositional logic, common normal forms for knowledge bases, resolution in first-order logic, proof trees, and refutation. Key concepts include deriving resolvents, detecting cont
2 views • 12 slides
Pedagogical Shift in Physical Science: Constructing Knowledge Through Learner-Centered Experiences
There is a significant pedagogical shift in physical science education from viewing science as a fixed body of knowledge to emphasizing the process of constructing knowledge. Learners are now placed at the center stage, engaging in inquiry-based learning, critical thinking, and collaborative interac
3 views • 21 slides
Understanding the Scope of Inference in Statistical Studies
Statistical studies require careful consideration of the scope of inference to draw valid conclusions. Researchers need to determine if the study design allows generalization to the population or establishes cause and effect relationships. For example, a study on the effects of cartoons on children'
1 views • 15 slides
DNN Inference Optimization Challenge Overview
The DNN Inference Optimization Challenge, organized by Liya Yuan from ZTE, focuses on optimizing deep neural network (DNN) models for efficient inference on-device, at the edge, and in the cloud. The challenge addresses the need for high accuracy while minimizing data center consumption and inferenc
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Nonparametric Statistics in R Short Course
Explore the application of nonparametric statistics in R Short Course Part 2, covering topics such as inference for a binomial proportion, inference for a median, and various tests for independent and paired data. Dive into hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and real-world examples like study
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Expert Systems in Computer Engineering
Expert systems are interactive computer-based decision tools that utilize facts and heuristics to solve various problems based on knowledge acquired from experts. This system consists of three main components: User Interface, Inference Engine, and Knowledge Base. The User Interface facilitates commu
4 views • 29 slides
Understanding the Difference Between Observation and Inference
Learn to differentiate between observation (direct facts or occurrences) and inference (interpretations based on existing knowledge or experience) through examples such as the Sun producing heat and light (observation) and a dry, itchy skin leading to the inference that it is dry. The distinction be
2 views • 14 slides
Introduction to Database Security and Countermeasures
Database security is essential to protect data integrity, availability, and confidentiality. Countermeasures such as access control, inference control, flow control, and encryption can safeguard databases against threats. Access control restricts user access, inference control manages statistical da
0 views • 26 slides
Database Security Measures and Controls
Database security is crucial to protect against threats like loss of integrity, availability, and confidentiality. Countermeasures such as access control, inference control, flow control, and encryption are important for safeguarding databases. Access control involves creating user accounts and pass
0 views • 35 slides
Understanding Inference for Experiments in Statistics
Learn about inference for experiments in statistics, including completely randomized design, statistical significance, and random assignment to treatments. Discover how to analyze results, determine significance, and interpret differences in responses. Explore the concept through practical applicati
1 views • 10 slides
Understanding Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) for Causal Inference
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) play a crucial role in documenting causal assumptions and guiding variable selection in epidemiological models. They inform us about causal relationships between variables and help answer complex questions related to causality. DAGs must meet specific requirements like
1 views • 63 slides
Reading Comprehension Inference Activities
Engage in reading comprehension with these inference activities. Analyze passages, make logical deductions, and answer questions to enhance critical thinking skills. Explore scenarios, draw conclusions, and strengthen your reading comprehension abilities through these interactive exercises.
2 views • 21 slides
Econometric Theory for Games: Complete Information, Equilibria, and Set Inference
This tutorial series discusses econometric theory for games, covering estimation in static games, Markovian dynamic games, complete information games, auction games, algorithmic game theory, and mechanism design. It explores topics like multiplicity of equilibria, set inference, and mechanism design
1 views • 23 slides
Navigating Statistical Inference Challenges in Small Samples
In small samples, understanding the sampling distribution of estimators is crucial for valid inference, even when assumptions are violated. This involves careful consideration of normality assumptions, handling non-linear hypotheses, and computing standard errors for various statistics. As demonstra
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Rules of Inference in Logic
Dive into the world of logic with this detailed exploration of rules of inference. Learn about different types of arguments, such as Modus Ponens and Modus Tollens, and understand how to determine the validity of an argument. Discover the purpose of rules of inference and unravel the logic behind co
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Causal Inference and Scientific Goals
Explore the significance of causal inference in science, the goals of scientific research, and the importance of developing an understanding of causal associations. Delve into topics like causal pattern recognition, mechanistic understanding, and potential outcomes frameworks to enhance your underst
0 views • 76 slides
Understanding Logical Inference: Resolution in First-Order Logic
Resolution in logic is a crucial inference procedure that is both sound and complete for unrestricted First-Order Logic. It involves deriving resolvent sentences from clauses in conjunctive normal form by applying unification and substitution. This approach covers various cases such as Modus Ponens,
3 views • 12 slides
Understanding Bayes Rule and Its Historical Significance
Bayes Rule, a fundamental theorem in statistics, helps in updating probabilities based on new information. This rule involves reallocating credibility between possible states given prior knowledge and new data. The theorem was posthumously published by Thomas Bayes and has had a profound impact on s
0 views • 34 slides
Understanding Expert Systems and Knowledge Inference
Expert Systems (ES) act as synthetic experts in specialized domains, emulating human expertise for decision-making. They can aid users in safety, training, or decision support roles. Inference rules and knowledge rules play key roles in ES, helping in problem-solving by storing facts and guiding act
0 views • 63 slides
Understanding Knowledge-Based Agents: Inference, Soundness, and Completeness
Inference, soundness, and completeness are crucial concepts in knowledge-based agents. First-order logic allows for expressive statements and has sound and complete inference procedures. Soundness ensures derived sentences are true, while completeness guarantees all entailed sentences are derived. A
0 views • 6 slides
Fast High-Dimensional Filtering and Inference in Fully-Connected CRF
This work discusses fast high-dimensional filtering techniques in Fully-Connected Conditional Random Fields (CRF) through methods like Gaussian filtering, bilateral filtering, and the use of permutohedral lattice. It explores efficient inference in CRFs with Gaussian edge potentials and accelerated
0 views • 25 slides
Probabilistic Graphical Models Part 2: Inference and Learning
This segment delves into various types of inferences in probabilistic graphical models, including marginal inference, posterior inference, and maximum a posteriori inference. It also covers methods like variable elimination, belief propagation, and junction tree for exact inference, along with appro
0 views • 33 slides
Understanding Modelling Knowledge and Knowledge Representation
Explore the significance of modelling knowledge through knowledge representation, making it explicit, independent, and reusable. Learn why knowledge representation is essential and how it facilitates exchange, query, inference, and visualization. Delve into examples of knowledge application in vario
0 views • 30 slides
Optimizing Inference Time by Utilizing External Memory on STM32Cube for AI Applications
The user is exploring ways to reduce inference time by storing initial weight and bias tables in external Q-SPI flash memory and transferring them to SDRAM for AI applications on STM32Cube. They have questions regarding the performance differences between internal flash memory and external memory, r
0 views • 4 slides
Typed Assembly Language and Type Inference in Program Compilation
The provided content discusses the significance of typed assembly languages, certifying compilers, and the role of type inference in program compilation. It emphasizes the importance of preserving type information for memory safety and vulnerability prevention. The effectiveness of type inference me
0 views • 17 slides
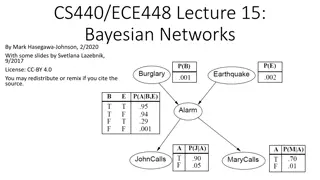
Understanding Bayesian Networks in Machine Learning
Bayesian Networks are probabilistic graphical models that represent relationships between variables. They are used for modeling uncertain knowledge and performing inference. This content covers topics such as conditional independence, representation of dependencies, inference techniques, and learnin
0 views • 14 slides
Rules of Inference Exercise Solutions in Discrete Math
This content provides solutions to exercises involving rules of inference in discrete mathematics. The solutions explain how conclusions are drawn from given premises using specific inference rules. Examples include identifying whether someone is clever or lucky based on given statements and determi
0 views • 4 slides
Modern Likelihood-Frequentist Inference: A Brief Overview
The presentation by Donald A. Pierce and Ruggero Bellio delves into Modern Likelihood-Frequentist Inference, discussing its significance as an advancement in statistical theory and methods. They highlight the shift towards likelihood and sufficiency, complementing Neyman-Pearson theory. The talk cov
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Logical Agents and Propositional Logic in AI
Designing logical agents involves forming representations of the world, using inference for deriving new insights, and deducing actions based on these representations. Knowledge Base (KB) is a crucial component, comprising known facts and current percepts to infer hidden states. Propositional logic,
0 views • 23 slides
Sequential Approximate Inference with Limited Resolution Measurements
Delve into the world of sequential approximate inference through sequential measurements of likelihoods, accounting for Hick's Law. Explore optimal inference strategies implemented by Bayes rule and tackle the challenges of limited resolution measurements. Discover the central question of refining a
0 views • 29 slides
Understanding Bayesian Networks for Efficient Probabilistic Inference
Bayesian networks, also known as graphical models, provide a compact and efficient way to represent complex joint probability distributions involving hidden variables. By depicting conditional independence relationships between random variables in a graph, Bayesian networks facilitate Bayesian infer
0 views • 33 slides
Dynamic Crowd Simulation Using Deep Reinforcement Learning and Bayesian Inference
This paper introduces a novel method for simulating crowd movements by combining deep reinforcement learning (DRL) with Bayesian inference. By leveraging neural networks to capture complex crowd behaviors, the proposed approach incorporates rewards for natural movements and a position-based dynamics
0 views • 15 slides