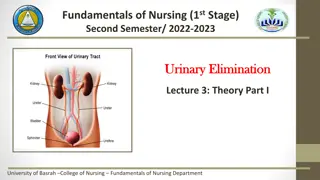
Cardiorenal Syndrome: A Complex Relationship Between the Heart and Kidneys
Cardiorenal Syndrome is a condition where dysfunction in one organ, whether acute or chronic, can lead to dysfunction in the other. This complex relationship involves intricate communication pathways between the heart and kidneys, impacting hemodynamic stability, organ perfusion, and neurohormonal interactions. Treatment involves accurate volume status assessment, aggressive management of volume overload, and optimization of renal perfusion to address underfill or overfill issues.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cardiorenal Syndrome Renal uitm
It is a syndrome! Not a diagnosis. Renal uitm
Cardiorenal syndrome definition condition whereby an acute or chronic dysfunction in one organ may induce acute or chronic dysfunction of the other Renal uitm
Relationship is complex! The heart and the kidney communicate with one another through a variety of pathways in an interdependent relationship Renal uitm
Relationship is complex! Related image wife Related image Related image girlfriend Renal uitm
Relationship is complex! Related image wife Pulmonary-renal syndrome Related image Related image Hepato-renal syndrome girlfriend Renal uitm
Neurohormonal relationship BP and Volume The heart and the kidneys are involved in maintaining hemodynamic stability and organ perfusion through an intricate network. Related image Related image Renal uitm
Pathophysiology Haemodynamic related Non-haemodynamic related hormonal and immune mediated Renal uitm
Pathophysiology underfill or overfill Haemodynamic related Renal uitm
Treatment Accurate Assessment of Volume Status Renal/Venous Congestion Aggressive Treatment of Volume Overload Removal of Fluid Accumulation in Third Spaces Diuretics and Diuretic Resistance Ultrafiltration Arterial Underfilling (Renal Hypoperfusion) Avoidance of Arterial Hypotension and Intravascular Underfilling Increasing the Effective Circulatory Volume Optimization of Renal Perfusion Renal uitm
Types of CRS Renal uitm
Types of CRS Renal uitm
RRT in haemodynamically unstable intermittent hybrid continuous HD SLEDD CVVHD SLEDD-f CVVHDF HDF Isolated UF SCUF Renal uitm
Types of RRT Conventional HD 300-350 500 4H SLEDD 150-200 200-300 6-8H CRRT 150-180 (2L/h) 33 72H Qb (ml/min) Qd (ml/min) Time UF Variations HDF SLED-F SCUF CVVHD CVVHDF Expensive Multiple inotropes Cardiogenic shock Cost Patients Cheap Fair Stable Sepsis shock Single inotropes Renal uitm
Thank you! @ Renal Uitm Renal uitm