Human Adaptations to Diverse Environments: A Study in Environmental Geography
Humans exhibit various biological and behavioral adaptations to thrive in different environments, showcasing our ability to modify and adapt to diverse ecosystems. This adaptation is essential for our survival in varied habitats, ranging from humid tropical forests to arctic wastelands. Through gene
5 views • 6 slides
Understanding Food Microbiology: Sources of Contamination
Humans have broader nutritional requirements than most microorganisms. The human diet includes a wide variety of substances, making our food excellent media for microbial growth. Natural contamination of food by various microorganisms, including pathogens, is common. Food consumed by humans and anim
0 views • 51 slides
Understanding Leptospirosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Epidemiology
Leptospirosis is a bacterial disease affecting humans and animals caused by the Leptospira genus. Symptoms range from kidney damage to death if untreated. The disease has various synonyms and is caused by pathogenic leptospires. It is prevalent in both animals and humans globally, with various serov
1 views • 26 slides
Encounter with Curious Giants
In a peculiar encounter, curious and powerful giants with trees for hair bemuse running humans, leading to a conversation about whether they frightened the people. The giants observe the humans fleeing as the evening sky paints a beautiful sunset scene. The larger giant expresses confusion while the
0 views • 5 slides
Understanding Public Health Risks Associated with Zoos and Wild Animals
Zoos and wildlife parks serve as hubs for public recreation and education but can also pose public health risks due to potential transmission of zoonotic diseases by veterinarians who work closely with wild animals. Approximately 61% of infectious agents affecting humans are zoonotic in nature, with
0 views • 15 slides
Animals by Walt Whitman: Embracing the Virtues of Animals Over Humans
Walt Whitman's poem "Animals" expresses a longing to live among animals due to their peaceful and self-controlled nature, contrasting them with the perceived greed and jealousy of humans. The poet finds solace in the virtues displayed by animals and reflects on their simplicity and contentment, high
0 views • 16 slides
Bovine Tuberculosis: A Zoonotic Disease Impacting Humans and Animals
Bovine tuberculosis is a chronic bacterial disease affecting cattle and other mammals, with potential transmission to humans. Endemic in developing countries, it poses public health risks. Modes of transmission, clinical symptoms, diagnosis, and control measures are discussed, highlighting the impor
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Ambiguity in Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) faces challenges with ambiguity, which occurs due to multiple possible interpretations of language input. Humans can often resolve ambiguity, but it's complex for computers. Types of ambiguities include lexical, syntactic, pragmatic, referential, and transient. Over
2 views • 24 slides
Understanding Human-Environment Interaction: Environmental Determinism vs. Possibilism
Human-environment interaction is a two-way process shaping cultures and behaviors. Explore the theories of environmental determinism and possibilism, which offer contrasting views on the influence of physical conditions on human societies. Environmental determinism emphasizes the impact of the envir
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Homeostasis in Humans: The Key to Maintaining Internal Balance
Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to regulate and maintain a constant internal environment despite external changes. In humans, the tissue fluid plays a crucial role in this process, with factors like pH, water concentration, oxygen levels, temperature, and glucose content needing to be contr
0 views • 80 slides
Understanding Homeostasis in Humans and Mammals
Humans and mammals rely on homeostasis to maintain a constant internal environment for survival. This involves regulating core body temperature, blood glucose levels, and water levels through nervous and hormonal responses. By understanding the principles of homeostasis, we can appreciate the vital
0 views • 22 slides
Overview of Laboratory Animals and Their Uses in Biomedical Research
Laboratory animals play a crucial role in biomedical research, serving as models for studying various conditions affecting humans and animals. They must thrive in controlled conditions and are used to test hypotheses and drugs. Commonly used lab animals include rodents, lagomorphs, canines, felines,
0 views • 9 slides
Evolutionary Journey of Early Humans
Explore the evolution of early humans, from the diverse species that lived over millions of years to Darwin's Theory of Evolution. Discover how natural selection shaped human ancestors and led to the development of modern humans. Uncover the significance of Africa as the cradle of civilization and t
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Salmonellosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Salmonellosis is a bacterial infection of the gastrointestinal tract caused by various serotypes of Salmonella bacteria. It affects both animals and humans, commonly spread through contaminated food sources. Symptoms in humans include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever, with potential complicatio
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding the Impact of Mosquitoes on Humans: Causes and Solutions
Mosquitoes have been around longer than humans and play vital ecological roles. However, they also pose risks as disease vectors. The evolution of mosquitoes, human activities, and mosquito bites are explored along with ways to address this issue.
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Brucellosis: A Zoonotic Disease Impacting Animals and Humans
Brucellosis, caused by the genus Brucella, is a zoonotic disease affecting animals like goats, sheep, cattle, and humans. It is primarily transmitted through contact with infected animals or ingestion of their products. The disease manifests in various forms like Mediterranean fever and can lead to
0 views • 13 slides
TU Symposium Humans and Machines: Prospects for Our Digital Future
Julia Neidhardt from the Research Unit of E-Commerce at TU Wien in Austria presented at the TU Symposium Humans and Machines in Vienna, discussing the pervasive role of informatics in digital transformation, the impact of artificial intelligence, and critical issues like personalization and concentr
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Antibiotic Resistance in E. coli from Poultry, Humans, and the Environment in Malawi
This research project in Malawi investigates the patterns of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from poultry, humans, and the environment. Preliminary results reveal insights into knowledge, attitudes, practices, and microbiological aspects related to antibiotic use. The study aims t
5 views • 8 slides
Evolution of Division of Labor in Humans and Social Insects
Evolutionary advantages of cooperation and specialization led to a developed system of social cooperation and division of labor in humans and social insects. Despite vast differences, these species have conquered the earth due to common characteristics. The puzzle lies in why only a few species evol
0 views • 23 slides
Relationship Between Cats and Humans: Insights from Research
Explore the fascinating bond between cats and humans through the lens of scientific research. Discover the social attachment of cat owners, reasons for pet ownership, and the unique characteristics that make cats such popular companions. From independence to intelligence, cats offer a diverse array
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Human Evolution: From Ancestral Lineage to Modern Hominids
Human evolution is a fascinating journey of change and development, where humans emerged as a distinct species. The theory of evolution highlights our common ancestry with other organisms, including chimpanzees. Evidence from fossils, genetics, and culture supports the idea of a shared ancestor amon
1 views • 23 slides
Understanding Echinococcus Granulosus and Hydatid Disease
Echinococcus Granulosus, also known as the hydatid worm or dog tapeworm, causes cystic echinococcosis. The tapeworm has distinct characteristics and a complex life cycle involving canids as definitive hosts and humans as accidental hosts. Hydatid disease in humans can be dangerous, with symptoms var
0 views • 8 slides
Exploring the Existence of Causes in Nature and Human Understanding
The discussion delves into whether everything has a cause and if humans can comprehend all causes. It contrasts functional and formal approaches, questioning the universal expectation that phenomena have causes and if humans can identify them all. Various linguistic theories are referenced, emphasiz
0 views • 27 slides
Understanding Brucellae: Characteristics and Infection Routes
Brucellae are intracellular parasites causing brucellosis in humans, characterized by acute bacteremia followed by a chronic phase. The four zoonotic species are B. melitensis, B. abortus, B. suis, and B. canis. Their morphology, growth characteristics, antigenic structure, and common infection rout
0 views • 18 slides
John Calvin's Doctrine of Predestination: A Summary
John Calvin's doctrine of predestination revolves around the absolute power of God, the corrupted nature of humans due to original sin, and the concepts of the Elect and the Reprobates. Calvin believed in unconditional election, limited atonement, irresistible grace, and the perseverance of the elec
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Ploidy and Chromosome Numbers in Organisms
Ploidy refers to the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, impacting the number of possible alleles. Humans are diploid, with 2 sets of 23 chromosomes each from parents, totaling 46 chromosomes. The haploid number for humans is 23, and the monoploid number is also 23. Variations in ploid
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Not Humans Subjects Research (NHSR) Determinations
Maria Drayton, an IRB Analyst at the University of Maryland, presents important information on Not Humans Subjects Research (NHSR). This includes definitions, IRB review requirements, evaluation criteria, and actions to take based on research determinations. The process involves careful consideratio
0 views • 19 slides
Comprehensive Overview of Rabies: Causes, Symptoms, and Impact
Rabies, also known as hydrophobia, lyssa, or lytta, is a severe viral disease affecting mammals, including humans, leading to damage to the nervous system and inevitable death. The disease is caused by a large RNA neurotropic virus of the genus lyssavirus. Rabies is transmitted through the infected
0 views • 22 slides
Evolution of Early Humans in Africa: A Journey Through Time
Explore the fascinating timeline of human evolution in Africa, from Australopithecines walking upright to the emergence of Homo habilis and Homo erectus. Discover how these early humans adapted, developed tools, and utilized fire, shaping the course of human history.
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Canine Attachment and Cross-Species Relationships
Dogs exhibit strong social attachment to humans, forming enduring bonds that serve as a secure base. This attachment benefits both organisms, providing resources for survival and establishing social structures. Imprinting studies suggest that animals, like humans, develop proximity-seeking behaviors
0 views • 29 slides
Overview of Salmonella Infections and Pathogenicity
Salmonella bacteria, often transmitted through contaminated food or drink, can cause various infections in humans and animals. They are identified by their morphology, and classified into different species and subtypes. The pathogenesis of Salmonella infections varies, with some species infective pr
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding the Mechanism of Second Dentition in Humans
Second dentition is a natural process involving the development of a second set of teeth in humans. This complex phenomenon includes factors like root development, periodontal changes, and functional occlusion. The process is crucial for normal craniofacial development and has implications for ortho
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Avian Influenza: Symptoms, Transmission, and Prevention
Avian influenza, commonly known as bird flu, is a contagious disease caused by flu viruses that primarily affect birds but can also spread to humans. Learn about the symptoms in humans, how the virus spreads, and preventive measures to stay safe. Stay informed and take necessary precautions to reduc
1 views • 15 slides
Antibiotic Resistance in Humans: Impact of Antibiotic Use on Farms
Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern, with evidence suggesting a link between antibiotic use in farm animals and resistant infections in humans. Explore a case study of a Salmonella outbreak in Denmark, where antibiotic treatment failed, leading to fatalities. Learn about the role of selection
0 views • 25 slides
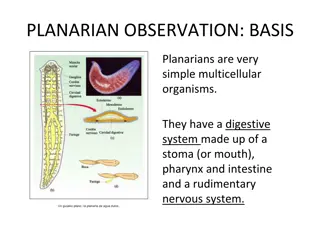
Planarian Observation: Nervous System Activity Study
Planarian Observation involves studying the effects of different substances on a planarian's nervous system. Through remote laboratory experiments, observations are made on the movement of planarians in various solutions compared to a control solution. Results are analyzed to determine the effects o
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Kyasanur Forest Disease: A Veterinary Perspective
Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD) is a tick-borne viral hemorrhagic fever caused by the Flavivirus, primarily affecting monkeys and humans in certain endemic areas of India. The disease was first identified in 1957 in Karnataka and is characterized by symptoms like fever and bleeding disorders. The viru
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Zoonotic Hepatitis A Virus Infections
Zoonotic hepatitis A virus infections primarily affect humans and nonhuman primates, with transmission occurring through fecal-oral route. This article delves into the reservoir, mode of transmission, clinical signs, and diagnosis of hepatitis A, shedding light on its impact on both species. Nonhuma
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Human Interaction in Interactive Systems
In the study of human factors in interactive systems, understanding the capabilities and limitations of users is crucial. This involves examining human input-output channels, memory, thinking processes, and problem-solving abilities. Humans interact with technology through senses like vision, hearin
0 views • 110 slides
Understanding Purine Degradation and Gout
Purine degradation pathway involves the breakdown of dietary nucleic acids, mainly from meat, into uric acid through specific enzymatic steps. Excessive uric acid production can lead to conditions like gout and hyperuricemia. Humans excrete uric acid in the urine as the final product, while other an
1 views • 12 slides
Overview of Rift Valley Fever: Symptoms in Animals and Humans
Rift Valley Fever (RVF) is an acute viral hemorrhagic fever primarily affecting domesticated animals and humans. The disease is caused by the RVF virus transmitted through mosquito bites or contact with infected animal tissues. In animals, clinical signs vary with high mortality rates in young lambs
0 views • 10 slides