Understanding Viral Pathogenesis: Insights into Disease Development
Viral pathogenesis explores the intricate relationship between viruses and their hosts, encompassing factors like viral effects on cells, entry mechanisms, tissue tropism, immune responses, and the outcomes of infection. This process involves a series of interactions leading to either virus clearanc
1 views • 29 slides
Understanding Virus-Cell Interactions: Mechanisms and Consequences
Viruses interact with host cells in various ways, encoding genes that manipulate cell functions for their benefit. These interactions can range from benign to lethal outcomes. Factors influencing these interactions include viral factors, cellular responses, and the presence of virulence factors. Dif
0 views • 37 slides
Understanding No Enveloped DNA Viruses: Papillomaviruses and Polyomaviruses
Explore the characteristics and implications of no enveloped DNA viruses, such as Papillomaviruses causing common warts and Polyomaviruses inducing tumors in animals. Learn about their genetic properties, potential for carcinogenesis, and infections in different host systems.
6 views • 18 slides
Understanding Viruses, Viroids, and Prions: A Comprehensive Overview
Explore the fascinating world of viruses, viroids, and prions, from their discovery to their genetic material and hosts. Learn about the structure, genome, and sizes of viruses, as well as their interactions with different host cells. Gain insights into these acellular disease-causing agents and the
0 views • 17 slides
The Origin of Viruses: Theories and Evidence
Viruses are acellular parasites with a complex replication mechanism. Studies on their origin present challenges due to the lack of fossils. Three main hypotheses include regressive, cellular origin, and co-evolution. The regressive hypothesis suggests viruses originated from complex ancestors that
2 views • 25 slides
Understanding the Structure and Symmetry of Viruses along with Cultivation Methods
Viruses, defined as obligate intracellular parasitic organisms, exhibit general properties such as small size, filterability, simple structure, and absence of cellular components. They vary widely in size and lack independent metabolism. The cultivation of viruses plays a crucial role in studying th
3 views • 37 slides
The Transmission and Movement of Plant Viruses
Plant viruses are transmitted through various means such as cell-to-cell movement via plasmodesmata and systemic spread through vascular tissues. The viral proteins and mechanisms facilitating these movements are crucial for viral infection and spread within plant hosts. Understanding the different
0 views • 47 slides
Virus Entry Mechanisms: Understanding Pathogenesis and Spread
Exploring the diverse ways viruses enter the body through various routes such as respiratory tract, oropharynx, skin, genitourinary tract, and eyes, shedding light on the steps of the virus life cycle shaping pathogenesis. Viral diseases result from the intricate interaction between viral and host f
4 views • 20 slides
Understanding Influenza: Key Concepts and Impact on Public Health
Influenza is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses, with symptoms spread through droplets in the air or on surfaces. Vaccination and surveillance play vital roles in controlling flu outbreaks. Understanding the structure and types of influenza viruses, along with the importanc
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Enveloped and Non-enveloped DNA Viruses
Non-enveloped DNA viruses, surrounded by a protein capsid, are resistant to sterilization and thrive in acidic environments. Adenoviruses, a common non-enveloped type, spread through close contact and contaminated objects. Additionally, Papilloma and Polyoma viruses, causing persistent infections an
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Orthomyxoviridae: Key Points on Influenza Viruses
Influenza viruses belong to the Orthomyxoviridae family and are major contributors to respiratory epidemics and pandemics. They consist of three genera - Influenza A, B, and C - with distinct morphological characteristics and genetic makeup. By exploring the properties, classification, and morpholog
0 views • 62 slides
Understanding Antiviral Chemotherapy: Importance and Types
Antiviral chemotherapy plays a crucial role in preventing and treating viral infections, especially when public health measures and vaccines are not sufficient. This form of treatment has been successful in combating diseases like HIV by inhibiting viral replication and targeting specific functions
1 views • 34 slides
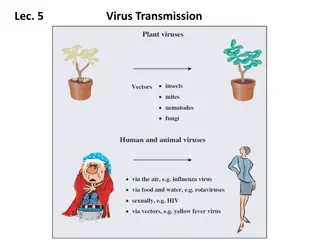
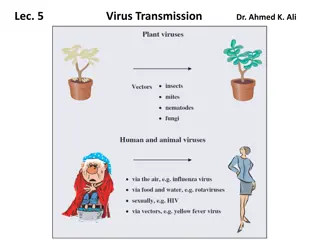
Understanding the Transmission of Viruses: Routes and Implications
Viruses are intracellular parasites that require transmission to a new host to evade immune responses. This transmission process, whether through respiratory droplets, fecal-oral routes, or sexual contact, is crucial in the viral life cycle. Different modes of transmission, such as horizontal and ve
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Viruses: Basics and Morphology
Viruses are the smallest unicellular organisms that are obligate intracellular. They lack cellular organization like bacteria, and their multiplication is complex. Viruses have either DNA or RNA and are classified based on their nucleic acid. Their structure includes nucleic acid and a capsid compos
0 views • 29 slides
Understanding Viral Gastroenteritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Transmission
Viral gastroenteritis, commonly known as viral diarrhea, is a prevalent infection affecting mainly infants and young children. The disease is self-limiting, with symptoms like diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Key viral etiologies include Rota viruses, Astroviruses, Norovirus, and Enteric aden
0 views • 19 slides
Get Rid of Bacteria and Viruses with Effective F10 Germicidal Barrier Ointment
F10 Germicidal Barrier Ointment by Chemical Essentials is a game-changer in the battle against bacteria, fungi, and viruses. This antiseptic preparation is specially formulated to tackle open and contaminated wounds while preventing re-infestation.\n
1 views • 5 slides
Understanding Computer Viruses and Preventive Measures
Computer viruses are malicious software that can cause significant harm to your device by spreading through various means such as online downloads and email attachments. They can disrupt systems, leak data, and cause operational issues. Learn how to identify signs of a computer virus and prevent inf
1 views • 9 slides
Understanding Foodborne Illness: Causes and Symptoms
Foodborne illnesses are diseases transmitted to humans through contaminated food, causing symptoms like nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, fever, and diarrhea. These illnesses are mainly caused by pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites, often spread through mishandling of
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Computer Viruses and Their Types
Computer viruses, created by malicious hackers, are programs that can replicate themselves and harm computer systems by damaging data files. They can cause various issues like slow response, crashes, and distorted graphics. Common virus types include time bombs, logical bombs, worms, and boot sector
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Computer Viruses: Types, Prevention, and Top 5 Destructive Viruses
Computer viruses are malicious software programs that can cause significant harm. Learn about different types of viruses, symptoms of infection, stages of a virus, prevention measures, and the top 5 most destructive viruses of all time.
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Computer Viruses: Threats and Categories
Learn about computer viruses, their history, classification, and impact. Explore different types like file viruses, polymorphic viruses, and stealth viruses. Understand the categories based on impact and discover macroviruses related to office applications.
1 views • 47 slides
Understanding How Viruses, Bacteria, and Fungi Impact Human Health
Explore the intricate world of viruses, bacteria, and fungi and how they interact with living organisms. Learn about the structure and functions of viruses, the role of bacteria in diseases, and the implications of fungi on human health. Discover the different ways these microorganisms affect us and
0 views • 37 slides
Understanding Viruses: Origin, Structure, and Importance in Research
Viruses are microscopic organisms that rely on living cells to replicate and cause a range of illnesses in humans, animals, and plants. Studying viruses has led to significant scientific breakthroughs, providing insights into essential biological mechanisms and disease processes. Theories on the ori
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Viruses and Bacteria: A Biology Presentation by Mandie Lynn Walls
Explore the world of viruses and bacteria through this engaging biology presentation put together by Mandie Lynn Walls. Learn about the structure of viruses, different types of viruses like T4 Bacteriophage and Herpes Virus, the distinction between viruses and bacteria such as E. coli, vaccination m
0 views • 39 slides
Novel RNA Viruses in Oysters Revealed by Virome Study
Oysters, as high-yield mariculture varieties, were investigated for novel RNA viruses using virome analysis. Eighteen new RNA viruses were identified, with evidence of genetic recombination. This study highlights the importance of advanced sequencing technologies in discovering viral pathogens in aq
0 views • 11 slides
Overview of Poxviridae Family: Structure, Classification, and Genus Details
Poxviridae is a family of large viruses known for causing vesicular skin diseases in both animals and humans. This family includes various poxviruses of veterinary and medical importance, each classified under different subfamilies and genera like Orthopoxvirus and Capripoxvirus. The viruses possess
0 views • 44 slides
Understanding Viral Hepatitis: Causes, Types, and Clinical Symptoms
Viral hepatitis is caused by various hepatotropic viruses, including Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. This type of liver inflammation can manifest acutely or chronically, leading to symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal pain, nausea, and fatigue. Hepatitis A virus, in particular, is primarily transmitted
0 views • 36 slides
Overview of Myxoviruses: Classification, Morphology, and Orthomyxoviridae
Myxoviruses are a group of viruses that bind to mucin receptors on red blood cells, causing hemagglutination. They are classified into orthomyxoviridae and paramyxoviridae, with influenza viruses being major pathogens. Influenza viruses consist of three genera and have distinct morphological feature
0 views • 25 slides
Unveiling the Intriguing World of Ancient Retroviruses and Human Evolution
Exploring the fascinating realm of ancient retroviruses, evolutionary biologists are resurrecting extinct deadly viruses to study their impact on human evolution and modern diseases. By investigating the genetic material of viruses, particularly endogenous retroviruses, researchers aim to trace evol
0 views • 13 slides
Decades of Marine RNA Virosphere Research
Research spanning over two decades has delved deep into the marine RNA virosphere, shedding light on the complex marine ecosystem and the characteristics of RNA viruses. Discoveries in deep marine virus taxonomy have led to significant taxonomic changes and advancements in virus classification and g
0 views • 10 slides
Exploring the Fundamentals of Plant Pathology: Understanding Viruses in Plant Diseases
Delve into the world of plant pathology with Mr. Vikash Kumar, as you learn about the nature, structure, and transmission of viruses affecting plants. Explore the important characteristics of plant viruses, their unique properties, and how they interact within plant cells. Gain insights into viral d
0 views • 14 slides
Overview of Non-Enveloped DNA Viruses and Their Impact on Human Health
Non-enveloped DNA viruses are surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid, making them difficult to sterilize and highly resilient in various environments. This article explores the characteristics and impact of non-enveloped DNA viruses such as Adenoviruses, Papilloma and Polyoma Viruses, and Huma
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Virus Transmission via Vectors
Viruses must be transmitted to new hosts for their survival. This transmission occurs through vectors like arthropods, which acquire and transmit viruses during feeding. The mechanism involves viruses attaching to the vectors' mouthparts or entering their circulatory system to reach salivary glands
0 views • 14 slides
Survey of Structural Properties of Different Classes of Viruses
Viruses are small obligate intracellular parasites that require living hosts for multiplication. They lack ribosomes and metabolic enzymes, relying on host cells for replication. Viruses vary in size, shape, and genome organization, with classification based on morphology, physicochemical properties
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Viruses: A Brief Overview of Virology
Viruses are small intracellular microorganisms consisting of nucleic acid and proteins, often enclosed in a lipid bilayer membrane acquired from host cells. They lack cellular structure and organelles and rely on host cells for replication. Control measures for viruses include leveraging knowledge o
0 views • 20 slides
Discovery and Classification of Viruses: Milestones in Virology History
Russian biologist Dimitry Ivanovsky's 1892 discovery of viruses through a Chamberland filter, followed by Martinus Beijerinck's 1898 identification of filterable, non-cultivable agents as viruses, marked key milestones in virology. The subsequent work of Beijerinck, Twort, and d'Herelle further adva
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding the Basics of Virology: Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
Virology explores the world of viruses, infectious agents with living and nonliving characteristics. Viruses, noncellular genetic elements, depend on host cells for replication and lack metabolic functions on their own. Viroids and prions are novel entities related to viruses. Viruses are classified
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Virus Transmission via Vectors in Hosts
Viruses must be propagated and transmitted to new hosts for survival. They can be spread via vectors like arthropods, which acquire and transmit viruses during feeding. This transmission can occur quickly through the vector's mouthparts or more slowly via circulation in the vector's body. Plant viru
0 views • 14 slides
Arboviruses: A Comprehensive Overview of Arthropod-Borne Viruses
Arboviruses, transmitted by bloodsucking arthropods, are a diverse group of RNA viruses with varied classifications like Togaviridae, Flaviviridae, Bunyaviridae, Reoviridae, and Rhabdoviridae. In India, Dengue, Chikungunya, and Japanese Encephalitis are prevalent arboviruses. Togaviridae, including
0 views • 70 slides
Overview of Virus Structure and Classification
Viruses were first observed by Edward Jenner in 1798, who noticed their role in providing immunity. They are smaller than bacteria and consist of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat. Viruses are obligate cellular parasites, replicating only inside living cells. The structure of viruses inc
0 views • 38 slides