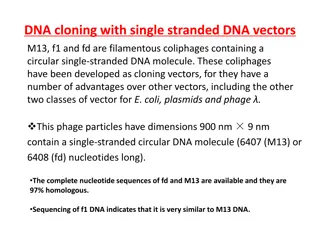
Understanding DNA Cloning with Filamentous Coliphages
Filamentous coliphages M13, f1, and fd are utilized as cloning vectors due to their circular single-stranded DNA molecules and advantages over other vectors. These phages have dimensions of 900 nm x 9 nm and infect bacteria through F pili, releasing up to 1000 phage particles per cell per generation
0 views • 17 slides
Evolutionary Insights of Basidiomycota Dikaryons
Basidiomycota, a successful fungal group with 30,000 known species, predominantly exhibits filamentous vegetative growth while also producing yeast forms. The multi-layered cell wall and regularly septate hyphae with dikaryotic mycelium are key characteristics. Recent experimentation on Schizophyllu
0 views • 20 slides
Evolutionary Trends in Monera Kingdom: Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, and Actinomycetes
Monera, the simplest yet diverse kingdom, is divided into Archaebacteria and Eubacteria. Archaebacteria are ancient, thriving in extreme conditions, while Eubacteria encompass true bacteria with various metabolic capabilities. Actinomycetes, unique filamentous bacteria, play vital roles in soil ecos
0 views • 4 slides
Research on Producing Bio-Composite Materials from Wastewater Using Filamentous Bacteria and Polyhydroxyalkanoates
This project conducted at the University of Delaware aimed to evaluate the potential of using filamentous wastewater microorganisms as reinforcement and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)-accumulating microorganisms as a biorenewable matrix for bio-composite materials. Filamentous bacteria were analyzed fo
1 views • 13 slides
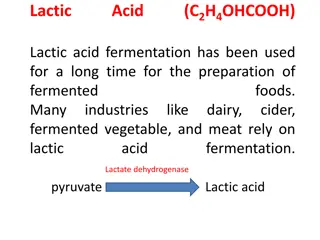
Lactic Acid Fermentation in Food Industry
Lactic acid fermentation is a widely used method for producing fermented foods like dairy, vegetables, and meats. This process involves lactic acid bacteria and filamentous fungi to convert sugars into lactic acid. Various microbial cultures are utilized, and raw materials such as whey, molasses, an
0 views • 23 slides
General Characteristics of Fungi and Mycology Overview
Fungi, diverse eukaryotic organisms, exhibit various characteristics such as heterotrophic nature, distinct cell wall composition, and different modes of reproduction. Mycology, the study of fungi, delves into their classification and functions. Fungal cells may be unicellular or filamentous, with m
0 views • 15 slides
Introduction to Bacterial Cells Morphology in Microbiology
Bacteria are ubiquitous microorganisms with diverse shapes and arrangements. They exist as bacilli (rod-shaped), cocci (spherical), and spirilla (spiral-shaped). Actinomycetes are filamentous bacteria resembling molds. Understanding bacterial cell morphology is crucial in microbiology studies.
0 views • 16 slides
Fungal Classification and Reproduction in Hymenoascomycetidae Subclass
Hymenoascomycetidae subclass includes orders like Erysiphales, Claviceptales, Helotiales, Pezizales, and Tuberales. Erysiphales fungi cause Powdery Mildews with closed ascocarps, while Claviceptales produce filamentous ascospores. Asexual reproduction involves conidiophores, while sexual reproductio
0 views • 8 slides
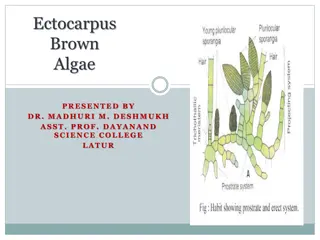
Exploring Ectocarpus: Characteristics and Occurrence
Ectocarpus, a brown algae genus, is diverse with species found worldwide, including 16 in India. It thrives in marine habitats as free-floating, epiphytic, or lithophytic forms. The filamentous plant body is heterotrichous, divided into prostrate and erect systems. Two genetic types, haploid and dip
0 views • 24 slides
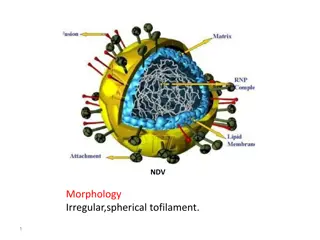
Understanding the Morphology and Genome Organization of NDV
NDV, a pleomorphic virus, has an irregular spherical shape with filamentous features. Its genome consists of a single-stranded RNA with six genes arranged in a specific order. The virus contains a lipoprotein envelope with short spikes and a helical nucleocapsid core to protect the RNA. The genomic
0 views • 35 slides