Understanding the Importance of Skin and Hides in Livestock Industry
Skin and hides are crucial by-products of large and small animals, with differences in thickness and weight. They are sourced from slaughtered and fallen animals, processed through drying, tanning, and conditioning to produce leather. Leather has outstanding strength, flexibility, and weather insula
0 views • 16 slides
Skin and Hides Utilization in Livestock Products Technology
Skin and hides are important by-products obtained from slaughtered and fallen animals, with different characteristics and yields. The process involves flaying to separate the hide from the animal's body, followed by various treatments to produce leather. Leather, with its excellent strength, flexibi
0 views • 29 slides
External Morphology and Functions of Balanoglossus
Balanoglossus is an elongated, wormlike animal with a unique body structure divided into proboscis, collar, and trunk regions. The body wall consists of an outer epidermis, inner musculature, and peritoneum, providing protection and support. The proboscis is a club-shaped structure, the collar conta
0 views • 7 slides
Development of Wool Follicles in Sheep: A Detailed Overview
Wool production in sheep involves the development of wool follicles starting from the basal layer of the epidermis. The process includes the formation of follicles during gestation, thickening of the basal layer into a plug, growth of accessory structures like glands, and the differentiation of cell
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Coagulase Test in Microbiology
Coagulase test is a crucial microbiological technique used to differentiate Staphylococcus aureus, which produces coagulase, from other species like S. epidermis and S. saprophyticus that do not. This test helps in identifying the presence of bound and free forms of coagulase, aiding in the accurate
0 views • 56 slides
Basics of Fingerprinting: Biological Formation of Ridges
Fingerprints are formed due to the proliferation of cells in the epidermis, resulting in ridges and patterns unique to each individual. The process begins in the embryonic stage with the development of volar pads on fingertips, palms, and soles. As the skin matures, primary and secondary ridges are
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding the Common Integuments and Skin Anatomy
The common integuments encompass the skin, hairs, skin glands, claws, hooves, and horns, playing vital roles in protection, thermoregulation, and drug administration. The skin's structure consists of the epidermis and dermis layers, renewing continuously to maintain its functions. Additionally, nail
0 views • 11 slides
Introduction to Practical Pharmacognosy: Study of Medicines from Natural Sources
Pharmacognosy is the study of medicines derived from natural sources, exploring drugs from plants through the lenses of botany, chemistry, and pharmacology. This includes the classification of vegetable drugs based on taxonomic, chemical, and morphological characteristics. Understanding key points f
0 views • 19 slides
Diseases of Skin Overview and Primary Lesions by Dr. Sonam Bhatt, Assistant Professor VMD Basu Patna
Skin, the largest organ of the body, plays a crucial role in regulating temperature and acting as a protective barrier. It consists of the epidermis, dermis, and subcutis, along with skin appendages like hair and claws. Skin lesions can be categorized into primary and secondary, with primary lesions
0 views • 18 slides
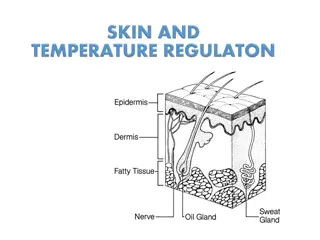
Understanding Thermoregulation in Animals and Humans
Thermoregulation is the process of regulating body temperature in organisms. It can be seen in two types of animals - ectothermic and endothermic. Ectothermic animals rely on external energy sources to maintain body temperature, while endothermic animals use internal metabolic energy. The skin plays
0 views • 22 slides
Maize Root Anatomy: An In-depth Examination
Maize root anatomy involves various specialized structures such as the epidermis, cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and vascular tissue. The epidermis is crucial for absorption and protection, while the cortex plays a role in providing support and storage. The endodermis acts as a barrier and regulates
0 views • 9 slides