Romanticism: The Age in Making
Explore the origins and characteristics of Romanticism in this informative lecture, covering the Enlightenment, American Independence, and the shift away from Enlightenment Neo-classicism.
19 views • 20 slides
Class Group Mastery Adapting to 21st Century Learning
The traditional image of a classroom \u2013 rows of desks facing a teacher dispensing knowledge \u2013 is increasingly incompatible with the realities of modern learning. The 21st century demands critical thinkers, collaborators, and innovators, requiring a fundamental shift in how we approach educa
3 views • 3 slides
Liberty & The Age of Enlightenment The American Battlefield Trust
The Age of Enlightenment, with its emphasis on natural law, liberty, progress, and constitutional government, greatly influenced American thinking and the Revolutionary War. Key figures like John Locke and Sir William Blackstone contributed ideas of social contract and law that shaped American gover
2 views • 15 slides
Understanding RIPE and the Social Contract in the Age of Enlightenment
The RIPE Social Contract delves into the theory of social contracts originating from the Age of Enlightenment. It explores the legitimacy of the state's authority over individuals and discusses the expectations and roles of RIPE, NCC, and RIRs within the internet ecosystem. RIPE's objective is to co
0 views • 33 slides
The Life of Siddhartha Gautama: A Journey to Enlightenment
Siddhartha Gautama, born around 583 BC in Nepal, was destined for greatness. Despite being shielded from the harsh realities of life, he was deeply moved by the suffering he witnessed and left his luxurious life at the palace in search of enlightenment. Renouncing his princely status, Siddhartha bec
0 views • 7 slides
Enlightenment Thinkers and Their Ideals
The Age of Revolution was marked by influential Enlightenment thinkers such as Thomas Hobbes, John Locke, Montesquieu, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau. These philosophers explored human nature, government, and society, shaping modern political thought. Hobbes emphasized a pessimistic view, advocating for
2 views • 9 slides
Insights into Buddhism: History, Philosophy, and Schools
Buddhism, a spiritual tradition focused on personal development and attaining deep insight into life, boasts 376 million followers globally. Rooted in the teachings of the Buddha, it emphasizes reaching nirvana through morality, meditation, and wisdom. The history of Buddhism traces back to Siddhart
0 views • 33 slides
Enlightenment, Counter-Enlightenment, and the Supernatural
The relationship between religion and the Enlightenment was characterized by a shift towards viewing them as non-antagonistic entities, despite some lingering conflicts. While the Enlightenment aimed to combat religious bigotry and superstition, it did not eradicate supernatural beliefs entirely, le
0 views • 8 slides
The 1st Great Awakening, Anglicization, & The Enlightenment in APUSH
This content covers key concepts in APUSH related to the 1st Great Awakening, Anglicization, and the Enlightenment. It discusses the religious revival, emergence of new sects, Enlightenment ideas, Anglicization of the colonies, and Britain's mercantilism and imperial aims. The impacts on colonial so
0 views • 10 slides
Medieval Political Thought: Key Thinkers and Concepts
Explore the medieval political thought highlighting prominent thinkers like St. Augustine, St. Thomas Aquinas, and Marsilius of Padua. The period was characterized by universalism, the absence of organized states, and a blend of politics, economics, and religion. Discover the parallelism between Pla
3 views • 6 slides
The Life Journey of Siddhartha Gautama: From Prince to Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, born in 583 BC in Nepal to King Suddhodana and Queen Maya, embarked on a profound life journey. Despite being raised in luxury, he encountered the harsh realities of aging, sickness, and death, prompting him to renounce his princely life in search of spiritual enlightenment. Unde
0 views • 6 slides
Exploring Postmodernism: Art, Literature, and Philosophy
Postmodernism challenges traditional beliefs about language, identity, and reality. It is characterized by skepticism, subjectivism, and a critical view of ideology in politics and economics. Key thinkers like Thomas Pynchon, Donald Barthelme, and Jean-François Lyotard have contributed to shaping t
0 views • 26 slides
The Axial Age: Pivotal Thinkers Across Ancient Civilizations
The Axial Age, coined by Karl Jaspers, refers to a period from the 8th to 3rd century BCE where pivotal thinkers emerged independently in Persia, India, China, Greece, and Rome, shaping the spiritual foundations of humanity. Jaspers, a German philosopher and psychiatrist, highlighted the importance
2 views • 21 slides
The Life and Teachings of Buddha
Buddha, born as Siddhartha Gautama around 500BC in Nepal, left a life of luxury to seek enlightenment after encountering the Four Sights. He eventually found enlightenment through the Middle Way, understanding the Four Noble Truths and following the Eightfold Path. His teachings on suffering, imperm
0 views • 9 slides
Renaissance Historiography: Writing Histories in the Enlightenment Era
The Enlightenment period saw a shift in historical writing towards valuing the past for its own sake. Scholars like Francesco Petrarch and Estienne Pasquier explored different approaches to interpreting history, incorporating philology, individual chronicles, and the portrayal of great men and women
0 views • 35 slides
Seeds of Change: Government, Science, and Enlightenment in European History
Explore the evolution of government, scientific revolution, and Enlightenment ideas in Europe through monarchies, the Scientific Revolution's impact on society, and the Age of Reason. Uncover the shift towards questioning authority and the pursuit of logic and reason. Delve into the significance of
0 views • 22 slides
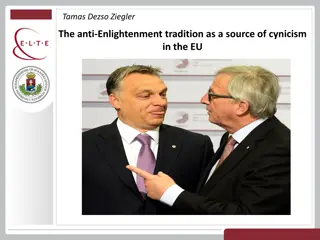
Exploring Anti-Enlightenment Traditions in the EU
This text delves into the concept of the anti-Enlightenment tradition and its influence on cynicism within the European Union. It analyzes the ideological roots, cultural implications, and political manifestations of this tradition, contrasting it with Enlightenment principles such as human rights,
0 views • 9 slides
Enlightenment Philosophers and Their Influence on the French Revolution
The French Revolution was influenced by Enlightenment philosophers like Thomas Hobbes, Rousseau, Voltaire, and Montesquieu. Their ideas on social contracts, collective sovereignty, enlightened absolutism, and the need for checks and balances challenged the traditional Ancien Régime's feudalism, pri
0 views • 26 slides
Enlightenment Political Ideas in Modern France
The Enlightenment era in Modern France brought forth significant political ideas and discussions, including Thomas Hobbes' concept of social contract and Rousseau's emphasis on collective sovereignty. Montesquieu advocated for checks-and-balances in government, while Voltaire promoted enlightened ab
0 views • 21 slides
The 7 Stages of Spiritual Awakening: A Journey to Enlightenment
The path of spiritual awakening is a profound journey that leads to deep inner transformation and enlightenment. visit us :- \/\/mystickentah.com\/
0 views • 13 slides
Causes of the American Revolution and Enlightenment Influence
Explore the causes of the American Revolution, from key events and legislation to influential figures like George Washington and Thomas Jefferson. Discover the impact of Enlightenment thinkers like John Locke and Baron de Montesquieu on the revolutionary ideas that shaped American history.
0 views • 33 slides
Gender and the Enlightenment: Understanding Perspectives on Gender Roles
This study delves into the Enlightenment period, exploring the views on gender, female participation, men and feminism. It discusses key figures like Jean-Jacques Rousseau and their beliefs on gender distinctions. The text examines how education was perceived to shape gender roles within society, sh
0 views • 24 slides
The Age of Revelation: A Time of Ultimate Spiritual Enlightenment
We are experiencing a profound era of revelation like never before in the history of Sonship. This period transcends previous ages by presenting a comprehensive and perfect view of the divine plan. Through cognitive revelation, believers are sharpening their spiritual logic and intellect, embodying
0 views • 33 slides
Science-Based Global Enlightenment in the Quantum-Digital Age
Global Enlightenment in the Quantum-Digital Age explores the urgent need for a science-based approach to address climate change and prevent environmental crises that could lead to a dead planet. It emphasizes the shift from a Hyper-Expansionist socio-economic system to a Sane, Humane, Ecological one
0 views • 25 slides
The Ayrshire Enlightenment: Religious Debates and Cultural Struggles in 18th-Century Scotland
Professor Colin Kidd's slide presentation delves into the religious milieu of Irvine and Greenock during James Galt's upbringing, highlighting the pivotal role of religious debates in shaping society. The contention between traditional Calvinists (Auld Lichts) and more liberal thinkers (New Lichts)
0 views • 12 slides
Insights into the Enlightenment Thinkers: Philosophers of Change
The Enlightenment era marked a shift towards reason and enlightenment, with thinkers like Locke, Hobbes, Montesquieu, Rousseau, and Voltaire advocating for progress, natural law, and individual rights. Each philosopher contributed unique ideas to reshape societal structures, challenging traditional
0 views • 18 slides
Evolution of Criminal Law and Thought: From Pre-Classical Era to Enlightenment
Explore the progression of criminal law and thought from the Pre-Classical School of Thought to the Enlightenment era. Delve into concepts like folkways, mores, and the origins of criminal law, including examples such as societal norms, dress codes, and supernatural explanations for behaviors during
0 views • 23 slides
Enlightenment Thinkers and Their Impact on Society
Explore the ideas and influence of key Enlightenment thinkers such as Montesquieu, Condorcet, Voltaire, and John Locke. Discover their groundbreaking works and beliefs on freedom, governance, equality, and religious tolerance, which shaped the American and French revolutions and continue to resonate
0 views • 31 slides
Enlightenment Philosophes and Their Revolutionary Ideas
Enlightenment philosophes such as Montesquieu, Condorcet, Voltaire, John Locke, Diderot, and Cesare Beccaria came from diverse backgrounds but shared a common desire to change the world. They advocated for freedom of expression, rational criticism, religious tolerance, separation of powers, educatio
0 views • 16 slides
Greek Philosophy: Origins and Influential Thinkers
Greek philosophy originated with the Pre-Socratics in the Ionian School around 600 BC, focusing on naturalistic explanations and cosmological theories. Thales, Anaximander, and Anaximenes were key figures, each proposing unique elemental theories. Pythagoras emphasized the mathematical nature of the
0 views • 19 slides
Enlightenment and Scientific Revolution: Impact and Spread
The Renaissance and Reformation planted seeds for the Scientific Revolution by fostering curiosity and challenging traditional beliefs. The shift from the geocentric to heliocentric theory revolutionized understanding of the universe. The Scientific Method emerged, leading to groundbreaking discover
0 views • 16 slides
Enlightenment and Revolution 1550-1789 Chapter 22 Overview
This chapter provides a comprehensive overview of the Enlightenment and Revolution era between 1550-1789. It covers key concepts including the Scientific Revolution, Enlightenment thinkers such as Galileo Galilei, Isaac Newton, John Locke, Voltaire, and more. The vocabulary section introduces terms
0 views • 32 slides
Critical Analysis of Modernity and Counter-Enlightenment Perspectives
The idea of modernity is scrutinized for its complex relationship with theological concepts, revolution, and progress. In contrast, the counter-Enlightenment emphasizes the diversity of national cultures shaping human behavior and worldviews. Various readings explore modernity's impact on individual
0 views • 10 slides
Perspectives on Faith and Evidence from Notable Thinkers
Explore diverse perspectives on faith, proof, and evidence from influential thinkers like C.S. Lewis, William James, Simone Weil, G.K. Chesterton, Richard Dawkins, and Charles Darwin. Reflect on how faith intersects with reason, evidence, and belief, shaping different worldviews and philosophical ap
0 views • 14 slides
The Growth of Humanism: From Renaissance to Enlightenment
Humanism began to flourish during the Renaissance and the Enlightenment periods, challenging traditional religious beliefs and emphasizing the value of human reason, rights, and autonomy. Influential humanist thinkers questioned the authority of the Church, valued human creativity, and promoted indi
0 views • 26 slides
Enlightenment Ideas and Philosophers
Explore key Enlightenment ideas such as equality, freedom of expression, and religious tolerance through the works of prominent philosophers like Voltaire and Rousseau. These concepts challenged traditional beliefs and laid the foundation for modern democratic societies.
0 views • 12 slides
The Enlightenment and Absolutism: Key Concepts and Figures
The period saw significant developments, including the Scientific Revolution emphasizing reason and systematic observation, leading to the expansion of scientific knowledge. Absolutism showcased monarchs' control, like Peter the Great's westernization of Russia and Louis XIV's Palace of Versailles.
0 views • 22 slides
Perspectives on Different Religions and Paths to Enlightenment
Various religions such as Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam, and Mormonism are explored in terms of their beliefs and paths to spiritual enlightenment. Each religion offers a unique perspective on connecting with a higher power, whether it's through good deeds, karma, following specific teachings, or a comb
0 views • 30 slides
American Government Unit: The Legislative Branch - Lesson Plan Insights
This lesson plan focuses on the American legislative branch, covering topics such as Enlightenment-era political philosophers, dangers of majority rule, and rights within the legal system. Students engage in activities related to the structure of the Constitution, analyze historical thinkers' views,
0 views • 4 slides
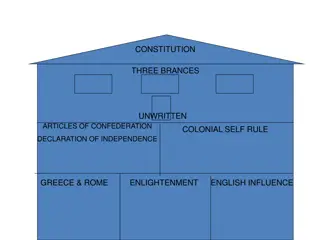
Foundations of Democratic Governance: From Ancient Roots to Modern Principles
Explore the evolution of democratic governance from the foundations laid in Ancient Greece and Rome to the core principles of Enlightenment thinkers and English influences, culminating in the establishment of democratic principles in the Declaration of Independence and the American Constitution. Dis
0 views • 10 slides