Understanding the Core Tenets of Samkhya Philosophy
Samkhya philosophy, one of the oldest systems of Indian philosophy, emphasizes a dualism between prakrti and purusa, with prakrti as the root cause of the world of objects. It maintains a plurality of purusa and remains silent on the concept of God. Prakrti is described as uncaused, independent, abs
1 views • 30 slides
Lewis Two-Sector Model: Sustaining Economic Growth Through Labor Transfer
Lewis Two-Sector Model, based on the assumption of surplus labor in agriculture, explains how transferring labor to the industrial sector boosts economic growth. The model highlights the shift from traditional to modern sectors, increased output, wages, and profits, and self-sustaining growth capabi
0 views • 10 slides
Modern Perspectives on the Philosophy of Mind in Psychology
Explore modern approaches to the philosophy of mind in psychology, including functionalism, the mind-brain identity theory, and the challenges faced by functionalists. Functionalism emphasizes the functional aspect of mental processes and their potential realization in various physical devices, whil
0 views • 20 slides
Explore the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution marked a shift from the medieval worldview to a secular, rational, and materialistic perspective. Key terms such as geocentric and heliocentric conceptions, Cartesian dualism, rationalism, and the scientific method played pivotal roles in shaping this transformative period.
7 views • 10 slides
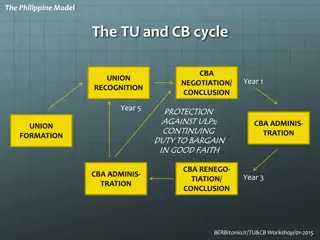
Labor Market Trends and Union Growth in the Philippines
The Philippine model of trade unionism involves a cycle of union recognition, negotiation, and conclusion, with a continuing duty to bargain in good faith. The trade union structure consists of three levels with one level of collective bargaining. The context of trade unions and collective bargainin
0 views • 43 slides
The Theory of Beauty and Criteria for Existence
Understanding the criteria for the existence of beauty encompasses different philosophical perspectives such as Materialism, Idealism, and Dualism. Materialism posits that everything is composed of material, while Idealism asserts that reality is fundamentally mental or immaterial. The debate on the
0 views • 47 slides
The Wave Model: Understanding the Sea's Positive Impact on Wellbeing
Explore how immersing in the sea positively affects wellbeing through the Wave Model, uncovering themes like awareness, time, connectedness, growth, and dualism. The study delves into participants engaging in sea-related activities across various locations, showcasing both positive and negative emot
0 views • 23 slides
The Foundations of the Separation of Powers in Companies
The separation of powers in companies is based on the dualism of organs: the Board and General Meeting. The actual situation in companies diverges between large public companies with autonomous management and smaller private companies with owner-operators. The search for the foundations of the separ
0 views • 15 slides
Exploring Sankhya Philosophy: Metaphysical Dualism and Causation
Delve into the ancient Sankhya philosophy, the oldest school of Indian philosophy founded by Kapila. Discover its metaphysical goal of avoiding monistic materialism and idealism, leading to a dualism between nature and spirit. Explore the concepts of Prakriti (Nature) and Purusha (Self), along with
0 views • 38 slides
Exploring the Metaphysics of Mind: Substance, Properties, and Views
Delve into the realm of metaphysics as it pertains to the nature of reality, with a focus on substance and properties. Explore the concepts of substance dualism, monisms like idealism and materialism, and the debate around mental properties and their relation to physical properties. Consider various
0 views • 8 slides