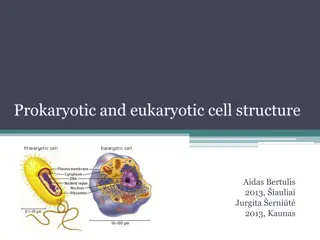
Understanding Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Structure
This comprehensive guide explores the structures and characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Learn about the differences and similarities between these cell types, including features like cell wall composition, membrane-bound organelles, nucleus presence, DNA structure, ribosomes, and m
7 views • 20 slides
Understanding Glandular Specialized Epithelium and Glands
Glandular specialized epithelium forms a class of epithelial tissues with specific functions and structures, composed of cuboidal, columnar, and ciliated columnar epithelial cells. These tissues contain gland cells that are secretary in nature, with zymogen granules in the cytoplasm. Glands are spec
1 views • 35 slides
Understanding the Relationship Between DNA and Protein Specificity
The relationship between an organism's DNA and protein specificity is intricate. DNA encodes the information for the sequence of amino acids in proteins, thereby determining their specificity. This process involves DNA directing the synthesis of specific RNA molecules, which are then translated into
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
Bacteria display unique cellular structures and functions that differ from eukaryotic cells. They have a simple structure with a plasma membrane but lack complex internal membrane systems. The cytoplasm contains inclusion bodies, ribosomes, and genetic material in the nucleoid. Bacteria can be categ
4 views • 21 slides
Understanding the Molecular Composition of Living Cells
Living cells are primarily composed of hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, phosphorus, and sulfur, which form the basis of organic biomolecules. Cells have common features such as cytoplasm, cell membranes, and nuclei. Different types of cells exist, ranging from eukaryotic with organized nuclei to
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Leukopoiesis: The Development of White Blood Cells
Leukopoiesis is the process of white blood cell production, crucial for defending the body against foreign agents. Granulocytes and lymphocytes are key components, with granulocytes found in different locations like the bone marrow, blood, and tissues. The bone marrow pool plays a vital role in the
2 views • 23 slides
Historical Perspectives on DNA as Genetic Material: From Mendelism to Griffith's Experiment
Mendelism's rediscovery in 1900 laid the groundwork for understanding heredity, leading to the association of Mendel's factors with chromosomes. The quest to identify the chemical nature of heredity began with Friedrich Miescher's discovery of nucleic acid in 1869. Despite initial confusion between
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding the Cell Cycle: Growth, Division, and Reproduction
The cell cycle is a fundamental process that allows cells to grow, divide, and reproduce, essential for growth, repair, and maintaining the balance of our bodies. It consists of stages like interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis, each with distinct functions. Interphase is a period of growth and devel
0 views • 28 slides
Introduction to Histology and Cell Structure
Histology is the microscopic study of normal tissues utilizing light and electron microscopes. This field explores the composition and function of cells, focusing on the nucleus, cytoplasm, organelles, and inclusions. Thin tissue sections stained with Haematoxylin and Eosin reveal distinct cellular
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Histology and Cell Structure Fundamentals
Delve into the intriguing world of histology and cell structure, exploring the composition of cells, the functions of various components like the nucleus and cytoplasm, and the significance of organelles. Discover how histology is studied, the types of microscopes used, and the vital role of the cel
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Haemocytes: Types and Functions
Haemocytes are blood cells that play crucial roles in the immune response of insects. They come in different types such as Prohemocytes, Plasmatocytes, and Granulocytes, each with specific characteristics and functions. Prohemocytes are believed to be stem cells giving rise to other cell types, whil
0 views • 9 slides
Cellular Processes and Functions Explained
The cytoplasm is essential for cell function, housing organelles like chloroplasts and vacuoles unique to plants. Mitochondria facilitate cellular respiration, while amino acids form proteins. Enzymes are proteins, and carbohydrates consist of simple sugars. Basic pH numbers range from 8 to 14. Star
0 views • 24 slides
Exploring Biology: Key Terms and Concepts in Cell Biology
Dive into the fascinating world of biology with a focus on essential terms and concepts in cell biology. Learn about the structures and functions of cells, from bacteria to organelles, and understand the fundamental components that make up living organisms. Explore the roles of mitochondria, nucleus
0 views • 18 slides
Fascinating Vocabulary of Cell Biology
Explore the intricate world of cell biology through fancy terminology for basic cell components, such as the cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, nucleus, and more. Discover the unique functions and structures of plant and animal cells as compared to different types of cells within each class. Vi
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Cell Organelles and Their Functions
Cell organelles play vital roles in the functioning of both animal and plant cells. From the cell membrane that controls the exchange of materials to the nucleus that governs cell activities, each organelle contributes uniquely. The cytoplasm provides a supportive environment for organelles, while t
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding DNA Transformation in Bacterial Cells
DNA transformation is a crucial process in genetic engineering, where foreign DNA is introduced into bacterial cells such as E. coli. This process, known as transformation, involves making the cells competent to uptake DNA through physical and chemical treatments. The uptake of DNA occurs after trea
0 views • 34 slides
Understanding the Functions of Cell Organelles
Explore the vital functions of different cell organelles such as the cell membrane, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, ribosomes, vacuole, cell wall, chloroplasts, and chlorophyll in a cell. Learn how each organelle plays a unique role in maintaining
0 views • 38 slides
Understanding Plant Cell Components: Nucleus, Cell Wall, Mitochondria, Cytoplasm, Chloroplasts
Plant cells consist of various components like the nucleus, cell wall, mitochondria, cytoplasm, and chloroplasts, each serving specific functions essential for the plant's growth and survival. The nucleus houses genetic information, the cell wall provides support, mitochondria produce energy, cytopl
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Drug Metabolism: Importance and Mechanisms
Drug metabolism is a crucial process in the body that transforms drugs into forms easily excreted, affecting their efficacy and toxicity. This involves different sites such as the liver, kidney, and plasma, with enzymes in cellular organelles like cytoplasm and mitochondria playing key roles. First-
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Kappa Particles Transmission in Paramecium
Research by Dr. Shashikant R. Sitre delves into the transmission of kappa particles in Paramecium, revealing the presence of these cytoplasmic particles in specific strains. The interaction between killer and sensitive strains, controlled by the dominant K gene, sheds light on cytoplasmic heredity a
0 views • 10 slides
Detailed Overview of Bacteria's Structure and Function
Explore the world of bacteria with a focus on their microscopic nature, general characteristics, ultrastructure of bacterial cells, and components like cell envelope, cytoplasm, and nuclear material. Uncover the diverse forms of bacteria, their mode of nutrition, reproduction methods, and unique fea
0 views • 12 slides
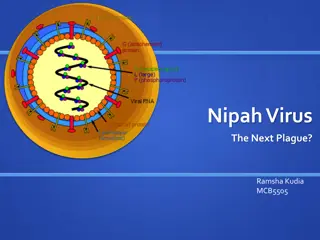
Understanding Nipah Virus: A Comprehensive Overview
Nipah virus, belonging to the Paramyxoviridae family, is a zoonotic virus with high pathogenicity and mortality rates. It falls under the Henipavirus genus, known for infecting a wide range of animal species. Its virion structure consists of non-segmented, negative-sense RNA, and the viral genome co
0 views • 22 slides