Ginzburg Landau phenomenological Theory
The Ginzburg-Landau phenomenological theory explains superconductivity and superfluidity as distinct thermodynamic phases. It focuses on phase transitions characterized by singularities in specific heat at the transition temperature. Derived from BCS theory, it quantifies condensation energy, emphas
1 views • 38 slides
Crystal Field Theory in Transition Metal Complexes
Crystal Field Theory (CFT) explains the colors and magnetic properties of transition metal complexes. It focuses on the energy changes in d-orbitals of metal ions caused by surrounding ligands. This theory, developed in 1929, provides insights into the bonding interactions in complex compounds. The
10 views • 44 slides
Understanding Social Learning Theory and the Power of Example
Social Learning Theory, introduced by Bandura, emphasizes learning through observation and modeling. It explores how individuals acquire behavioral dispositions, trial-and-error experiences, and the impact of stimuli in the environment. The theory focuses on the importance of attention, retention, a
1 views • 17 slides
Evolution of Mathematical Theories and Proof Systems
Development of mathematical theories such as model theory, proof theory, set theory, recursion theory, and computational complexity is discussed, starting from historical perspectives with Dedekind and Peano to Godel's theorems, recursion theory's golden age in the 1930s, and advancements in proof t
1 views • 29 slides
Introduction to Organizational Behavior: Management Theories and Practices
Explore the evolution of organizational behavior from early management theories to contemporary practices. Understand the historical foundations and relevance of management theory in shaping workplace dynamics. Delve into key concepts like Scientific Management, Administrative Management, Bureaucrat
1 views • 28 slides
Chromosomal Alterations and Their Impact on Phenotype
Errors in mitosis or meiosis can result in changes in phenotype, often due to alterations in chromosome structure such as deletion, duplication, inversion, and translocation. Nondisjunction can lead to abnormal chromosome number, resulting in disorders like aneuploidy. Polyploidy, with extra complet
0 views • 9 slides
Psychological Theories of Criminality: Understanding the Roots
Psychological theories of criminality delve into the association between intelligence, personality, learning, and criminal behavior. Major theories include Psychodynamic Theory by Freud, Behavioral Theory by Bandura, and Cognitive Theory by Kohlberg. These theories explore how unconscious mental pro
1 views • 20 slides
Genetic Assessment of CNV.J on Chromosome 3q28 - Case Study J
This case study evaluates a copy number variant (CNV) on chromosome 3q28 (190380498_191783134) associated with a loss of genetic material. The assessment includes genomic content analysis, gene involvement categorization, evaluation of established/predicted genes, and detailed scrutiny of the CCDC50
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Sex-Linked Inheritance: Key Concepts and Examples
Sex-linked inheritance refers to the transmission of genetic traits determined by genes located on the sex chromosomes. This type of inheritance differs from autosomal inheritance due to the unique characteristics of the X and Y chromosomes. In organisms with XX/XY sex determination, genes on the X
1 views • 21 slides
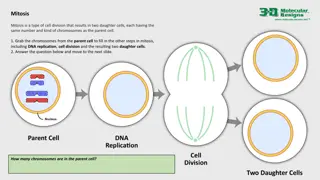
Cell Division Processes: Mitosis and Meiosis Explained
Mitosis and meiosis are two types of cell division processes with distinct outcomes in terms of chromosome numbers. Mitosis results in two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis produces four gamete cells with half the chromosome number. This explanation
2 views • 5 slides
Lampbrush and Polytene Chromosomes: Structures and Functions
Lampbrush chromosomes, found in growing oocytes of vertebrates, display large loops of DNA during the diplotene stage, with high gene expression levels. Polytene chromosomes, giant interphase chromosomes in insects, contain multiple strands with distinct banding patterns. Chromocenter serves as the
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding the Theory of Firms: Neoclassical vs. Modern Approaches
The theory of firms is explored through the Neoclassical and Modern perspectives. Neoclassical theory focuses on profit maximization, while Modern theory delves into managerial, principal-agent, and transaction cost theories. The discussion covers criticisms of Neoclassical theory and the essential
1 views • 79 slides
Theories of Causation in Psychological and Social Sciences
Overview of theories of causation categorized into psychological, social psychological, and sociological perspectives. Psychological theories focus on instinctive, biological, and psychological qualities of abusers, including Attachment Theory, Psychodynamic Theory, Social Learning Theory, and Situa
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Political Theory through a Contextual Approach
Exploring G.H. Sabine's perspective on political theory through a contextual approach, emphasizing the importance of historical context and societal influences. Sabine argues that while political theory evolves with its contemporary politics, it should be analyzed within its specific time and social
0 views • 9 slides
Evolution of Light Theory: From Wave Theory to Quantum Theory
At the turn of the century, the discovery of the photoelectric effect challenged the wave theory of light, leading to the development of the quantum theory by Max Planck and Albert Einstein. This new theory introduced the concept of discrete energy units known as quanta, bridging the gap between wav
1 views • 62 slides
Understanding Plasmids: DNA Molecules Free of Chromosome
Plasmids are DNA molecules existing free of the chromosome in a cell. They can be circular or linear and carry genes beneficial to the host. Plasmids replicate from unique origins and regulate copy numbers through various mechanisms. Different replication mechanisms, such as theta and RC, are used,
0 views • 31 slides
Dp-branes, NS5-branes, U-duality, and M-Theory Overview
Overview of Dp-branes, NS5-branes, and U-duality derived from nonabelian (2,0) theory with Lie 3-algebra. Introduction to M-theory, including M2-branes and M5-branes in the strong coupling limit. Discussion on BLG theory, Lorentzian Lie 3-algebra, and the ABJM theory for M2-branes.
1 views • 32 slides
Understanding Time-Independent Perturbation Theory in Quantum Mechanics
Perturbation theory is a powerful tool in solving complex physical and mathematical problems approximately by adjusting solutions from a related problem with known solutions. This theory allows for more accurate approximate solutions by treating the difference as a small perturbation. An example inv
0 views • 19 slides
Ethical Theories: Divine Command vs. Virtue Theory Explained
Divine Command Theory asserts that morality is derived from God's commands, contrasting with Virtue Theory which focuses on developing moral virtues to achieve human flourishing and excellence. Divine Command Theory relies on religious texts, while Virtue Theory emphasizes the cultivation of virtues
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Chromosome Territories in the Nucleus
Chromosome territories refer to specific regions in the nucleus where chromosomes are organized. While chromosomes appear as condensed structures during cell division, they have a different appearance in non-dividing cells like neurons. Scientists have used microscopy to study chromosome organizatio
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Chromosomes: Key Components, Functions, and Significance
Chromosomes, essential in mitosis and meiosis, are condensed forms of DNA vital for heredity, mutation, and evolution. Learn about their structure, role in inheritance, and impact on species development through historical discoveries. Discover the importance of chromosome sets and genomes in gametic
0 views • 38 slides
Understanding Numerical Chromosome Aberrations in Humans
Numerical chromosome aberrations involve the gain or loss of whole chromosomes, impacting the genome size and potentially leading to genetic mutations. Nondisjunction, where chromosomes fail to separate properly during cell division, can result in aneuploidy - the presence of an extra or missing chr
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Human Chromosome Nomenclature and Structure
In humans, each cell typically contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, with 22 autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. Chromosomes can be classified based on their structure, centromere position, and banding patterns. The location of the centromere on each chromosome is important for gene mapping and i
0 views • 17 slides
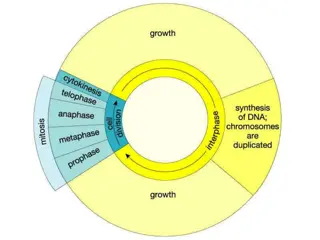
Understanding the Cell Cycle and Mitosis Process
The cell cycle consists of two main periods: Interphase and Mitosis. During Interphase, the cell prepares for division by growing in size and copying chromosomes. Mitosis, the division of the nucleus, results in the formation of two daughter cells with identical chromosome copies. Centrioles and cen
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Chromosome Aberrations in Genetics
Chromosome aberrations are deviations from the normal set of chromosomes, which can involve changes in chromosome number, gene arrangement, and appearance. These aberrations can be associated with genetic diseases and species differences. They encompass alterations in the number of genes within a ch
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Ploidy and Chromosome Numbers in Organisms
Ploidy refers to the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, impacting the number of possible alleles. Humans are diploid, with 2 sets of 23 chromosomes each from parents, totaling 46 chromosomes. The haploid number for humans is 23, and the monoploid number is also 23. Variations in ploid
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Down Syndrome: Causes, Effects, and Characteristics
Down syndrome, also known as Trisomy 21, is a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra 21st chromosome. Discovered by Dr. John Langdon Down in 1866, this condition affects individuals in various ways, influencing their development and abilities. People with Down syndrome may learn skills
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding X-Linked Inheritance and Diseases
X-linked inheritance involves genes on the X chromosome, leading to unique inheritance patterns and characteristics. X-linked diseases vary in expression between males and females due to differences in chromosome composition. X-linked dominant traits are rare but can have significant impacts on affe
1 views • 21 slides
Understanding Down Syndrome: Types, Characteristics, and Impacts
Down syndrome is a genetic condition caused by an extra chromosome, typically chromosome 21. This leads to physical and cognitive challenges, with individuals exhibiting unique abilities. The syndrome presents with distinctive physical features, such as flattened face, almond-shaped eyes, and poor m
2 views • 14 slides
Understanding Fermi Liquid Theory in Interacting Fermion Systems
Fermi liquid theory, also known as Landau-Fermi liquid theory, is a theoretical model that describes the normal state of metals at low temperatures. Introduced by Landau and further developed by Abrikosov and Khalatnikov, this theory explains the similarities and differences between interacting ferm
0 views • 23 slides
Computational Learning Theory: An Overview
Computational Learning Theory explores inductive learning algorithms that generate hypotheses from training sets, emphasizing the uncertainty of generalization. The theory introduces probabilities to measure correctness and certainty, addressing challenges in learning hidden concepts. Through exampl
0 views • 43 slides
Automata Theory and Theory of Computation Overview
This course overview covers concepts in automata theory and theory of computation, including formal language classes, grammars, recognizers, theorems in automata theory, decidability, and intractability of computational problems. The Chomsky hierarchy, interplay between computing components, modern-
0 views • 42 slides
Cell Division Mechanisms in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells divide through binary fission, while eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis with nuclear division and cytokinesis. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and divide by replicating DNA and forming two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotic chromosomes, associated with histone proteins, undergo co
0 views • 56 slides
Theories of Interest in Microeconomics II
Explore various theories of interest in economics, including the Classical Theory, Liquidity Preference Theory by Keynes, Productivity Theory, Abstinence Theory, Time-Preference Theory, Fisher's Time Preference Theory, and the Loanable Fund Theory. These theories offer different perspectives on the
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Mutations: Types, Causes, and Significance
Explore the world of gene mutations and chromosome mutations, including point mutations, frameshift mutations, and changes in chromosome structure. Learn about the significance of mutations, how they can be inherited or acquired, and their impact on genetic information. Uncover examples of neutral,
0 views • 9 slides
Exploring the Evolution of Atomic Theory
Delve into the historical journey of atomic theory starting from Democritus and Aristotle's views to modern advancements proving some aspects of Dalton's theory incorrect. Learn about key laws and theories such as the Particle Theory of Matter, Dalton's Atomic Theory, and JJ Thomson's discoveries, s
0 views • 30 slides
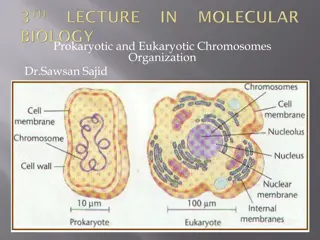
Understanding Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosome Organization
Chromosomes are vital structures in cells, holding genetic material. Prokaryotic cells have a nucleoid containing DNA while eukaryotic cells have DNA enclosed in a nucleus. Proteins like H-NS, HU, FIS, and IHF play crucial roles in maintaining chromosome structure and gene expression. Unlike eukaryo
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Linkage and Crossover in Genetics
Genes determining individual characteristics are carried in chromosomes, with some genes linked and inherited together. This linkage affects how genes assort in offspring, following principles of inheritance like Mendel's laws. The Chromosome Theory of Linkage explains how the distance between genes
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding the Chromosome Theory of Sex Determination
The concept of sex differentiation in organisms, the role of gamete size, hermaphroditism vs. dioecious species, and the chromosome theory of inheritance are explored. Discover how the presence of specific chromosomes determines sex in insects and how individual genes on sex chromosomes impact sexua
0 views • 17 slides
Macromechanical Analysis of Lamina and Tsai-Hill Failure Theory Overview
The Tsai-Hill failure theory is based on the strengths of a unidirectional lamina, incorporating longitudinal and transverse tensile and compressive strengths, as well as in-plane shear strength. This theory, derived from the distortion energy theory, provides criteria for determining lamina failure
0 views • 15 slides