Understanding Cellular Pathology: Response to Stress and Disease Predisposition
Explore the hallmarks of cellular pathology, including factors influencing disease predisposition such as genetics, environmental factors, and lifestyle. Delve into the cellular response to stress, adaptive and pathological reactions, and key stressors disrupting cellular homeostasis. Uncover how ce
0 views • 51 slides
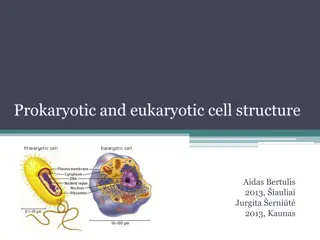
Understanding Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Structure
This comprehensive guide explores the structures and characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Learn about the differences and similarities between these cell types, including features like cell wall composition, membrane-bound organelles, nucleus presence, DNA structure, ribosomes, and m
7 views • 20 slides
Understanding Motor Proteins and Cytoskeletal Dynamics in Cell Biology
Motor proteins, such as myosin, kinesin, and dynein, utilize chemical energy to move along cellular tracks, influencing processes like muscle contraction, organelle movements, and cellular migration. With the ability to translocate using ATP hydrolysis, these proteins play crucial roles in various c
5 views • 14 slides
Understanding the Cell Membrane: Structure and Function
The cell membrane is essential for life, defining cell boundaries, maintaining internal conditions, and regulating substance transport. Composed of lipids and proteins, this dynamic structure allows for selective permeability. Explore its importance in cellular processes.
4 views • 30 slides
Understanding Resting Membrane Potential and Excitability in Cells
Explore the concepts of resting membrane potential (RMP), excitability in cells, and the electrochemical basis behind them. Learn about the characteristics of excitable and non-excitable tissues, the factors influencing RMP, and the role of ion distribution in generating the negative charge inside c
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Cellular Respiration and Metabolism in Living Organisms
Cellular respiration is a vital process in all living cells, producing energy through chemical reactions. Metabolism, consisting of anabolism and catabolism, maintains growth and function. ATP plays a central role as energy currency in cells. Through stages like glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, cellu
1 views • 16 slides
Understanding Cellular Respiration and Oxygen Delivery
Cellular respiration, a vital process for organ survival, involves mitochondria performing cellular respiration by utilizing glucose and oxygen. Glucose is derived from diet or body breakdown, while oxygen enters through the respiratory system, facilitated by red blood cells in the circulatory syste
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Active Transport: Energy-Driven Cellular Processes
Active transport is a vital process in cells that require energy in the form of ATP to move materials across the plasma membrane against their concentration gradient. This process involves pumps, endocytosis, and exocytosis. The sodium-potassium pump in nerve cells is a classic example of active tra
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Cell Membrane Transport: Diffusion and Facilitated Diffusion
Cell membrane transport plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular functions by regulating the movement of substances across the membrane. Diffusion, a passive transport process, allows molecules to move from areas of high concentration to low concentration without energy expenditure. Within diffu
2 views • 20 slides
Bacterial Cell Structure and Composition Overview
Bacterial cells exhibit variations in size, typically ranging from 0.75 to 1.5 micrometers. The cell envelope, comprising glycocalyx, cell wall, and cell membrane, plays crucial roles in protection and cell function. The cell membrane, a thin barrier rich in phospholipids and proteins, is integral t
1 views • 28 slides
Understanding Cellular Transport and the Role of Cell Membrane
Explore the process of cellular transport, where materials are exchanged between organisms and their environments. Discover the types of materials transported into and out of cells, from water to waste materials. Delve into the significance of the cell membrane as the final point of transfer and its
0 views • 61 slides
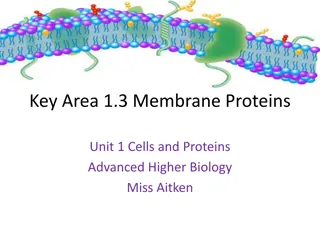
Understanding Membrane Proteins and Cell Membrane Permeability
Cell membranes consist of phospholipid bilayers with embedded proteins, including integral and peripheral proteins. Integral proteins span the membrane, while peripheral proteins interact with the surface. Only non-polar molecules can pass through the membrane directly, while charged ions, polar mol
0 views • 30 slides
Understanding Cell Membrane Structure and Function
This educational content delves into the structure and function of the cell membrane, covering topics such as the fluid mosaic model, permeability, carrier-mediated processes, and membrane proteins. It explains the composition of the cell membrane, selective permeability, and the roles of integral a
0 views • 36 slides
Neo.Go Mobile Application Integration Settings
This guide provides detailed instructions for integrating the Neo.Go mobile application with Neo security system panels using Ethernet or Cellular communication. It covers programming steps, data plan considerations, and settings for both Cellular and Ethernet communications. Ensure a proper data pl
0 views • 26 slides
Comprehensive Overview of Treatment Membranes in Water Quality Risk Assessment Training
Comprehensive overview of treatment membranes in water quality risk assessment training, covering various membrane types, applications, and considerations. Membranes play a crucial role in removing a range of contaminants from water sources, with different membrane types suited for specific applicat
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWAN) and Cellular Network Principles
Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWAN) utilize cellular network technology like GSM to facilitate seamless communication for mobile users by creating cells in a geographic service area. Cellular networks are structured with backbone networks, base stations, and mobile stations, allowing for growth and c
2 views • 17 slides
Overview of Cellular Respiration Pathways and ATP Generation
Cellular respiration involves key processes like the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA), Electron Transport Chain, and ATP generation pathways. The TCA cycle utilizes Acetyl-CoA to produce energy-rich molecules, while the Electron Transport Chain facilitates ATP synthesis through oxidative phosphorylati
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Cell Membrane: Maintaining Homeostasis in Cells
Cells maintain homeostasis to function effectively. The cell membrane plays a crucial role in this process by regulating material exchange, separating the cell from its environment, and ensuring internal balance. Understanding how cells exchange materials through the membrane is key to comprehending
1 views • 16 slides
Cellular Fractionation: Techniques and Applications
Cellular fractionation is a crucial process for separating cellular components to study intracellular structures and proteins. It involves homogenization, centrifugation, and purification steps to isolate organelles based on their properties like density and shape. This method provides valuable insi
6 views • 11 slides
Understanding Membrane Treatment in Water Filtration Systems
Membrane treatment plays a crucial role in water filtration systems by removing various contaminants such as turbidity, microbiology, and chemical impurities. This overview covers different types of membranes like plate and frame, spiral wound, tubular, and hollow fiber, highlighting their functions
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
Bacteria display unique cellular structures and functions that differ from eukaryotic cells. They have a simple structure with a plasma membrane but lack complex internal membrane systems. The cytoplasm contains inclusion bodies, ribosomes, and genetic material in the nucleoid. Bacteria can be categ
4 views • 21 slides
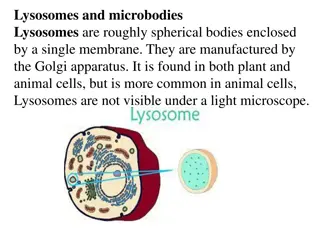
Understanding Lysosomes: Functions and Characteristics
Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles containing digestive enzymes that break down various biomolecules. They maintain an acidic internal environment, protecting the cell from enzymatic activity. Lysosomes play a crucial role in cellular waste disposal, macromolecule digestion, and intracellula
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding the Fluid Mosaic Model of Plasma Membrane Structure
The fluid mosaic model proposed by S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a fluid combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. This model explains how phospholipids form a stable barrier, the role of saturated and unsaturated fa
2 views • 6 slides
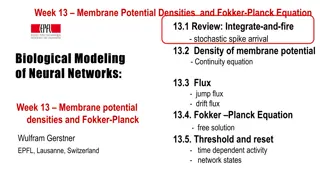
Exploring Membrane Potential Densities and the Fokker-Planck Equation in Neural Networks
Delve into the concepts of membrane potential densities and the Fokker-Planck Equation in neural networks, covering topics such as integrate-and-fire with stochastic spike arrival, continuity equation for membrane potential density, jump and drift flux, and the intriguing Fokker-Planck Equation.
0 views • 29 slides
Understanding Cellular Injury and Its Manifestations
Cellular injury can occur due to various factors like physical trauma, chemicals, radiation, and biologic agents. This process can lead to reversible or irreversible damage in cells, affecting their normal functions and possibly leading to cell death. Manifestations of cellular injury include cellul
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Cellular Membrane Transport in Biology/Chemistry Interface 2
Explore the teachable unit on membrane transport in an introductory biology class for majors to understand how cells exchange substances with their environment. The unit covers selective membrane permeability, membrane transport mechanisms, proteins involved, physiological importance, and outcomes o
0 views • 23 slides
Evolution of Membrane Models: From Early Observations to Fluid-Mosaic Structure
Researchers in the early 20th century noted the permeability of lipid-soluble molecules into cells, paving the way for membrane studies. The development of membrane models progressed from the sandwich model to the widely accepted fluid-mosaic model. The complexity of the plasma membrane, comprising
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Membrane Potential and Action Potentials in Excitable Cells
Membrane potential, resting potential, and action potentials play crucial roles in the functioning of excitable cells like neurons, muscle cells, and endocrine cells. Voltage-gated channels, depolarization, and repolarization are key processes involved in generating and propagating action potentials
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Membrane Transport in Plant Cells
Plant cells rely on membrane transport to facilitate the movement of molecules across their plasma membrane. This process involves passive and active transport mechanisms, with the help of specialized proteins such as channels, carriers, and pumps. Channels serve as selective pores for ions and wate
0 views • 20 slides
Comparison of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells in Cell Biology
Cells are the fundamental units of life, but viruses are an exception as they lack cells. Eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus with a nuclear membrane housing chromosomes, while prokaryotic cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles. Eukaryotic cells are larger, containing membrane-
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding the Structure of Eggs in Poultry Management
Eggs in poultry management consist of the yolk, albumen, shell membrane, and shell. The yolk is the yellow center surrounded by the vitelline membrane. The albumen makes up most of the egg and has two layers - outer thin white and inner thick white with chalazae. The shell membrane and shell protect
0 views • 14 slides
Cellular Processes and Functions Explained
The cytoplasm is essential for cell function, housing organelles like chloroplasts and vacuoles unique to plants. Mitochondria facilitate cellular respiration, while amino acids form proteins. Enzymes are proteins, and carbohydrates consist of simple sugars. Basic pH numbers range from 8 to 14. Star
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Biomembranes: Composition, Structure, and Functions
Biomembranes, specifically the plasma membrane, play a crucial role in cell function by separating and protecting the cell, facilitating communication with the environment, and regulating transport processes. Composed of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, membranes have a fluid mosaic structure wi
0 views • 13 slides
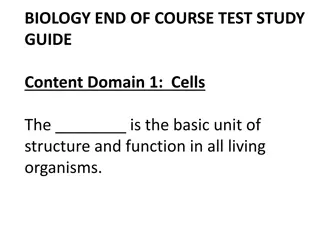
Understanding Cells: The Basic Units of Life
Exploring the fundamental importance of cells in living organisms, this study guide delves into the structure and function of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. It highlights the distinction between these cell types, their respective characteristics, and the defining features of living things. Emphas
0 views • 93 slides
Understanding Cellular Respiration: Energy Production in Organisms
Organisms can be classified into autotrophs that use sunlight for photosynthesis and heterotrophs that rely on consuming food. Regardless of food source, all organisms obtain energy through cellular respiration, a process that converts stored chemical energy into ATP. This energy currency is essenti
0 views • 21 slides
Energy-Efficient Handover Triggering for Cellular Networks
Mobile devices play a crucial role in today's world, with a surge in mobile subscriptions and applications. However, energy consumption, particularly battery life, remains a challenge. The study focuses on Application-Based Handover Triggering (AHT) as a solution to optimize energy usage in cellular
0 views • 24 slides
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: A Comparative Overview
Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack membrane-bound organelles, reproducing through binary fission. Eukaryotic cells are more complex, larger, with a nucleus enclosed in a nuclear envelope. They have various organelles and a cell wall. The plasma membrane defines cell boundaries, regulating the pa
0 views • 13 slides
Membrane Filtration in Dairy Products: Utilization of Whey and Skim Milk
Utilizing membrane filtration in dairy processing transforms whey, a byproduct of cheese production, into valuable products like refined proteins. Ultrafiltration (UF) allows for the fractionation of whey into protein-rich and lactose-containing streams, increasing protein content significantly. The
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding the Composition and Function of the Plasma Membrane in Animal Cells
The plasma membrane is a vital component of animal cells, serving as a barrier that regulates the passage of substances. Composed mainly of lipids and proteins, it plays a crucial role in cell structure and function. This article explores the chemical composition, molecular structure, and significan
0 views • 16 slides
Exploring Animal Cell Organelles and Functions
Dive into the intricate world of animal cell organelles and their functions. From the plasma membrane to the nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and more, uncover the essential components that drive cellular processes. Discover the roles these organelles play in
0 views • 7 slides