Atmospheric Thickness and Its Applications
Atmospheric thickness refers to the difference in geopotential height between two pressure surfaces, which is dependent on the mean virtual temperature of the layer in between. This concept plays a key role in determining temperature gradients, identifying fronts, and aiding in weather forecasting,
2 views • 11 slides
Boundary Layer and Drag Forces in Fluid Dynamics
Boundary layer module explains the presence of viscous forces near a surface due to fluid flow, leading to laminar or turbulent boundary layers. Flow separation occurs when a boundary layer detaches from a surface, impacting lift and drag forces. Adverse pressure gradients and flow separation phenom
2 views • 19 slides
Atmospheric Pressure Variations at Different Altitudes
Atmospheric pressure varies with altitude due to the weight of the air column above. This activity explores how Otto von Guericke's experiments with vacuum systems demonstrate the power of air pressure. Theoretical concepts of atmospheric pressure are discussed, highlighting its relation to gravity
3 views • 28 slides
The OSI Model and Layered Tasks in Networking
The content highlights the OSI model and layered tasks in networking, explaining the functions of each layer in the OSI model such as Physical Layer, Data Link Layer, Network Layer, Transport Layer, Session Layer, Presentation Layer, and Application Layer. It also discusses the interaction between l
3 views • 41 slides
Cutting-Edge Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Research at Barcelona Supercomputing Center
Conducted by the Atmospheric Composition Group at Barcelona Supercomputing Center, this cutting-edge research focuses on atmospheric chemistry modeling using advanced tools and frameworks like HERMESv3 and MONARCH. The team's approach integrates various modules to study complex processes influencing
0 views • 16 slides
Bedforms in Unidirectional Flow: Characteristics and Formation
Bedforms in unidirectional flow exhibit various characteristics such as sediment layer thicknesses, boundary layer dynamics, presence of ripples and dunes, and the interplay between flow velocity and sediment deposition. These bedforms, including ripples and dunes, form due to interactions between t
4 views • 13 slides
Insights into the Low-Latitude Boundary Layer in Mercury's Magnetosphere
Study focuses on the low-latitude boundary layer (LLBL) in Mercury's magnetosphere, analyzing magnetosphere and magnetosheath plasma characteristics such as reconnection rates, IMF/magnetic shear, and plasma beta. Results show anti-correlation between LLBL and non-LLBL regions, with different reconn
4 views • 11 slides
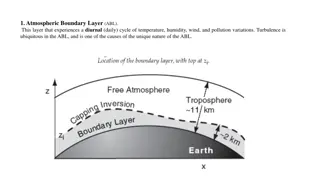
Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Static Stability
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer (ABL) undergoes daily variations in temperature, humidity, wind, and pollution with turbulence being a key factor. Static stability in the environment determines the behavior of air parcels, leading to categorizations of stable, unstable, and neutral conditions based o
2 views • 13 slides
ZFS: Structure and Operations
Explore the comprehensive structure and operations of ZFS, covering aspects like MOS layer, object-set layer, Dnode, Block Pointer, and TRIM operations. Learn about the meta-object set (MOS), dataset and snapshot layer (DSL), and storage pool allocator (SPA) modules within ZFS. Understand how ZVOLs,
5 views • 10 slides
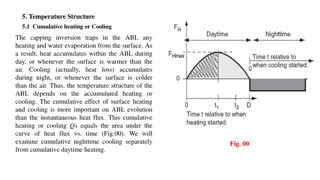
Temperature Structure and Cumulative Heating/Cooling in Atmospheric Boundary Layer
The temperature structure in the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) is influenced by cumulative heating or cooling effects from the surface. During the day, heat accumulates within the ABL, while cooling occurs at night. The cumulative heating or cooling is more crucial for ABL evolution than instanta
3 views • 12 slides
The Planetary Boundary Layer in Atmospheric Science
The Planetary Boundary Layer (PBL) plays a crucial role in atmospheric dynamics, divided into surface, mixed, stable, and residual layers. During the day, the mixed layer experiences convective motions due to surface heating, while the stable layer dominates during the night. Understanding these lay
3 views • 18 slides
Earth's Atmosphere: A Detailed Overview
The Earth's atmosphere is a vital layer of gases that encircles our planet, providing the necessary conditions for life to thrive. It consists of several distinct layers, each with unique characteristics and functions. From the troposphere closest to the surface to the thermosphere extending to grea
5 views • 29 slides
Ground Boundary Impact on Short Tower Turbines: A Conceptual Study
This conceptual study explores the impact of ground boundary on the production of short tower turbines. It investigates whether two turbines with the same rotor diameter but different hub heights can generate the same energy output. The study examines how the ground boundary influences the airflow p
1 views • 8 slides
Atmospheric Composition and Structure
The presentation covers fundamental concepts related to the Earth's atmosphere, including its composition, origin of oxygen, dry and moist layers, standard atmosphere layers, and temperature variations. Key topics discussed include the primordial atmosphere, atmospheric constituents, water vapor dis
1 views • 58 slides
ARP, ICMP, and DHCP in TCP/IP Protocol Stack
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) plays a crucial role in bridging the Layer 2/Layer 3 addressing boundary in the TCP/IP protocol stack, allowing IP to be agnostic about layer 2 addressing while still using layer 2 for packet delivery. Machines ARP for MAC addresses within their local network, where
5 views • 39 slides
Atmospheric Pressure, Wind Variations, and Humidity in Weather Systems
The atmosphere is composed of various elements like gaseous molecules, water vapor, and dust particles. Key weather variables include atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity, wind, cloud cover, and precipitation. Atmospheric pressure is influenced by the weight of air above a point, with average
5 views • 17 slides
Atmospheric Boundary Layer Dynamics and Evolution
The atmospheric boundary layer undergoes transformations from a residual layer to a stable boundary layer through the night, impacting wind behavior and turbulence levels. The virtual potential temperature profile provides insights into these changes.
9 views • 8 slides
Chapter 5: DataLink Layer
In the world of computer communication and networks, the DataLink Layer plays a crucial role in ensuring reliable data transfer. This layer deals with link protocols like Ethernet, frame relay, and 802.11, each offering different services and implementations. The link layer is present in every host,
3 views • 59 slides
Equivalence Principle in Intermediate EM Waves
Basic idea behind the equivalence principle in the context of intermediate electromagnetic waves is explored. The principle enables the replacement of actual sources with equivalent sources at the boundary of a closed surface, maintaining certain field conditions and boundary constraints. The concep
3 views • 40 slides
Future Changes in Atmospheric Rivers in Norway
Research investigates future trends in atmospheric rivers and extreme precipitation in Norway. Findings show increasing frequency and intensity of atmospheric rivers in the Far-Future, particularly during summer, with winter precipitation rising on the mid- and south-west coasts. Utilizing data obse
2 views • 13 slides
Turbulent Boundary Layer Aerodynamics
Phenomena in turbulent boundary layer aerodynamics and aeroelasticity. Observations and equations related to compressible boundary layers are discussed, emphasizing the energy equation and nonlinear partial differential equations.
1 views • 27 slides
Turbulent Boundary Layer Aerodynamics and Aeroelasticity
This content discusses turbulent boundary layer phenomena, transition processes, and compressible boundary-layer equations for flow over a flat plate. It also delves into the considerations for energy equations in compressible flows and the nonlinear partial differential equations involved in bounda
4 views • 25 slides
Fundamentals of Aerodynamics in Aeronautics
This content delves into key topics of aerodynamics including the Navier-Stokes equation, boundary layer concepts, drag force, lift force, viscous flow, and effects of viscosity on boundary layers. It discusses drag prediction methods, boundary layer thickness, and the impact of viscosity on fluid d
1 views • 27 slides
Atmospheric Sciences 101 Atmospheric Sciences 101
Dive into the fascinating world of atmospheric sciences with this comprehensive course. Learn to interpret weather maps, satellite imagery, and radar data. Explore key atmospheric phenomena and their relation to physical principles and laws. Discover how to be a savvy weather consumer by understandi
0 views • 10 slides
Full-Scale Spectrum of Boundary Layer Wind: Insights from Data Analysis
Studying the full-scale spectrum of boundary layer wind using extensive meteorological and sonic data from various sites reveals insights into spectral behaviors at different scales. This analysis aids in building robust models and understanding the crucial spectral gap between 2D and 3D atmospheric
4 views • 18 slides
Significance of the Boundary Layer in Micrometeorology
The boundary layer (BL) plays a critical role in various meteorological processes and human activities. It influences weather forecasts, pollution dispersion, agriculture, energy extraction, and more. Understanding the significance of the BL helps in addressing environmental concerns, optimizing ene
1 views • 6 slides
Impact of Out-of-Boundary Students on School Academic Climate
This research study challenges the impact of out-of-boundary students on a school's academic success, focusing on statistical data and educator opinions in DC Public Schools. Data analysis highlights teachers' preferences between in-boundary and out-of-boundary students.
5 views • 9 slides
Atmospheric Sciences Course: Winter 2023
Gain an understanding of synoptic systems, dynamical concepts, and weather forecasting in the Atmospheric Sciences 370 course for Winter 2023 with Cliff Mass and Rick Steed. Explore the structure and evolution of weather phenomena, developing essential skills in atmospheric analysis and forecasting
0 views • 6 slides
Boundary Characterization of Matrix-Exponential Distributions
The boundary characterization of the set of matrix-exponential distributions with real poles. Understand the representation of ME random variables, their Laplace-Stieltjes transform, and the detailed characterization of the boundary based on distinct real numbers.
1 views • 25 slides
Boundary Surveys to Define and Protect Your Property Lines
Avoid property disputes with professional Boundary Surveys from crasurvey.com.au. Our surveyors deliver precise property boundary mapping to establish legal land ownership and support fencing, construction, and subdivision projects.
5 views • 1 slides
Lunar Atmospheric Composition Experiment: Insights into Moon's Atmosphere
The Lunar Atmospheric Composition Experiment (LACE) on Apollo 17 provided valuable data on the Moon's exosphere, gas molecules, and atmospheric dynamics. LACE's ionization process, mass range scans, and data records offer a deeper understanding of lunar atmospheric composition. Discover the impacts
1 views • 11 slides
Solving Linear Boundary Value Problems with Shooting Method
Explore the application of the shooting method in solving linear boundary value problems for ordinary differential equations. Learn how to convert two-point boundary value problems to initial value problems and solve them effectively. Discover different boundary conditions and methods to find unique
21 views • 23 slides
Atmospheric Thermodynamics Fundamentals
This lecture covers key concepts in atmospheric thermodynamics, including forms of energy, Earth's atmosphere overview, composition, vertical structure, pressure, temperature, density, and important equations like the hydrostatic and hypsometric equations. Gain insights into the fundamentals of atmo
2 views • 21 slides
Far West Calvin Opheim RPG Boundary Percentage Change
Explore the proposed change to the boundary percentage for Far West Calvin Opheim RPG on 11/27/2018, as detailed in ERCOT's recommendations and load forecast observations. Understand the process and considerations involved in adjusting boundary thresholds for transmission planning load forecasts in
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Spherical Coax Boundary Conditions and TEM Properties
Explore the concepts of Spherical Coax along with boundary conditions and TEM properties. Learn about the transmission line type of mode and how to derive potential satisfying boundary conditions. Analyze the fields and understand the complex equations involved in Spherical Coax theory.
2 views • 13 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Static Stability
Explore the Atmospheric Boundary Layer (ABL) and the concept of static stability, which play crucial roles in the dynamic nature of the earth's atmosphere. Learn about the diurnal variations in temperature, humidity, wind, and turbulence in the ABL, as well as how static stability influences the ver
3 views • 12 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Thermodynamics: Dry Air, Stability, Buoyancy
Explore the concepts of dry air, stability, and buoyancy in atmospheric thermodynamics through this detailed lecture. Learn about the definitions of dry air, stability of dry air with adiabatic lapse rate, and the role of buoyancy in atmospheric conditions. Dive into the dynamics of potential temper
2 views • 15 slides
Understanding Boundary Conditions in Physics
Explore the concept of boundary conditions in physics through a series of equations and descriptions. Delve into symmetric boundary conditions and complete sets of functions, illustrated with helpful images. Uncover the complexities and nuances of these fundamental principles in this detailed analys
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Virtual Potential Temperature and Mixed Layer Dynamics
Explore the concepts of virtual potential temperature and mixed layer dynamics in meteorology. Learn about potential temperature, virtual temperature, and their significance in atmospheric stability. Delve into the characteristics of the mixed layer, its turbulence drivers, and how it influences wea
4 views • 9 slides
Electoral Area D Boundary Configuration Study
Conducted in Electoral Area D, the Boundary Configuration Study reviewed existing services, obtained residents' opinions, and explored potential municipal boundary configurations through public engagement. The study analyzed services like water, sewer, fire protection, policing, and roads to recomme
1 views • 17 slides