Understanding the Concept of Community: Definition, Elements, and Significance
The concept of community is derived from the Latin word "Communis" and holds different definitions based on scholars' interpretations. It encompasses elements such as locality, we-feeling, security, norms and values, and roles and status within society. Communities are formed for the purpose of serving and living together, sharing common interests, values, and practices. Security and social agreements bind community members together, while norms and values distinguish different communities.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
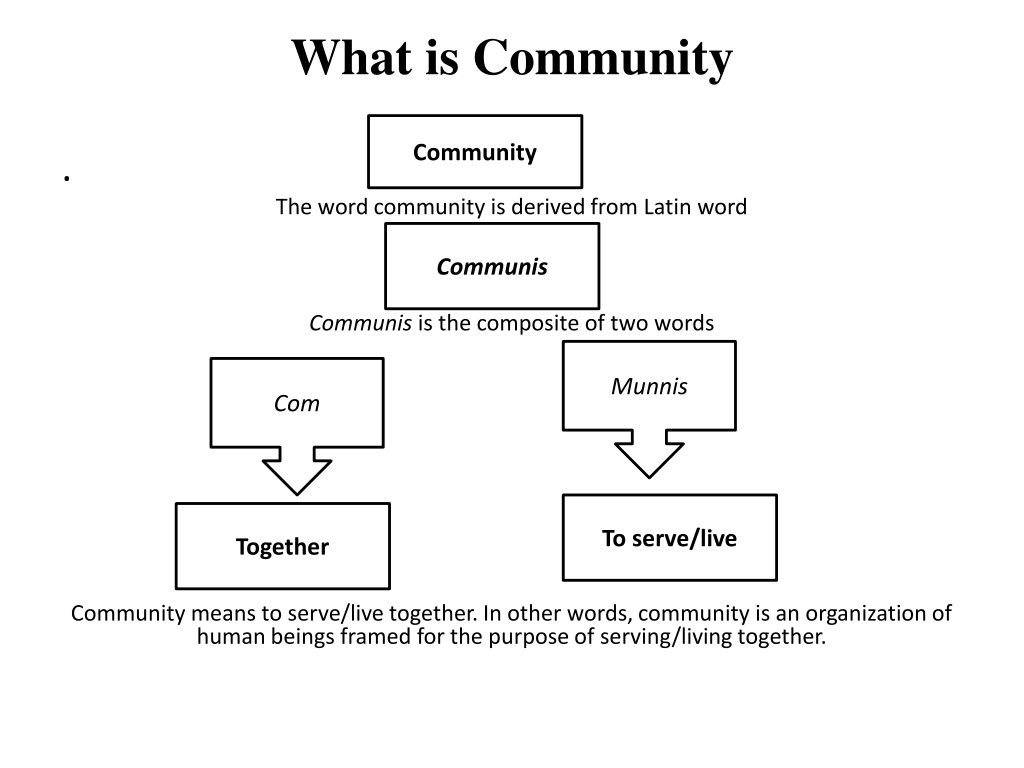
What is Community Community . The word community is derived from Latin word Communis Communis is the composite of two words Munnis Com To serve/live Together Community means to serve/live together. In other words, community is an organization of human beings framed for the purpose of serving/living together.
Definition There is no consensus among the scholars about the very definition of the word community . Therefore, different scholars defined it in different words. Some of them are as follow: 1. Emory Stephen Bogardus (1961) opines that community is a social group with some degree of wefeeling and living in a given area . 2. Pauline Vislick Young (1858) regarded the population of a village, of an area or a group of people, having some common interests such as residence, kinship or religious affiliation as community. 3. Abdul Hameed (1999) has stated that community is a place where people can get the things they need and want. Communities have places for all the things people do. They have places where people learn and pray. They can be villages, towns or cities.
Elements of Community The main elements of community are as follow: 1. Locality/Geographical Area A community is a territorial group. It occupies a definite territory or geographical area. Locality is the physical basis of a community. Without a definite locality, social relations between human beings cannot be established. 2. We-feeling for the Attainment of Wider Goals We-feeling of the individuals in a community means a feeling of belonging to one s another. The people living in a community mostly have shared sentiments and a common way of life. They usually speak the same language, shared customs and cultural traditions, similar values and practices and have relatively alike attitudes.
3. Security Man is a social animal by nature. Man cannot live alone because of insecurity. One major factor that keep the people in the community to live together is security. There is a concept of rights and obligations that make a social agreement between the people which make them a single unit. Due to the social agreement between the community members, they work together to defend themselves against all dangers followed by certain values, norms and common interests.
4. Norms and Values Every community has a system of its own norms and values that make it distinguished from other communities. Like, Muslim community is differentiated from the Christian community because of the system of its values and norms. Similarly, rural community is different from the urban community.
5. Role and Status Every person plays a role and holds a status in the society. Role is the standardized behaviour associated with the status for an individual, whereas status is the position held by a person in relation to others. For example, in our society young persons are expected be submissive to the elders and their opinions do not carry more weight than those of their elders. .
6. Power and Social Control Every community has a system of reward and punishment which are awarded through the social sanctions of society according to whether a person abides by or deviates from his allotted role in the society. Normal persons therefore take necessary guidance from the punishment and reward system of society. .
7. Ranks Every community is stratified into various ranks or categories i.e. higher/superior or lower/inferior in the hierarchical order. Everyone has to perform his/her role in the community that leads the people to be interdependent on each other which keep the community unified and integrated. 8. Facilities The community must provide facilities and friendly living conditions to its members. The members always work for its improvement and development. The urban community is differentiated from the rural community based on facilities available. .
Types of Community Ferdinand Tonnies (1855-1936) German Sociologist Book-Community and Society (1887) He was a major contributor to sociological theory and field studies, best known for his distinction between two types of social groups i.e. Gemeinschaft (community) and Gesellschaft (Society).
Differentiation Gemeinschaft(Community) Rural Life ii. Small population iii. Personal relationships iv. Ascribed Status v. Homogeneity vi. Spirit of cooperation vii. Small scale economy (agrarian) viii. No tolerance of deviance ix. Simple technology x. Larger families xi. Relatively slow social change xii. Example-a village Gesellchaft (Society) Urban Life Large population iii. Impersonal relationships iv. Achieved Status v. Heterogeneity vi. Spirit of interest vii. Large scale economy (industrial) viii. Tolerance of deviance ix. Advanced technology x. Smaller families xi. Relatively rapid social change xii. Example-a city i. i. ii.