Understanding Diabetes Mellitus and Dental Plaque
Diabetes mellitus is an endocrine disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels due to insufficient insulin production or ineffectiveness. Type 1 diabetes is insulin-dependent and typically develops in childhood, while Type 2 diabetes is non-insulin dependent and often seen in overweight adults. Symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, and tiredness. Dietary guidelines emphasize reducing saturated fats and choosing high-fiber foods. Dental plaque, composed of bacteria, food, and saliva, is the main cause of dental diseases like periodontal disease and tooth decay.
Uploaded on Sep 11, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
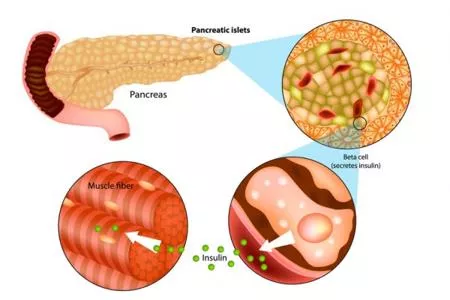
Definition Diabetes mellitus is an endocrine disorder with abnormally high levels of glucose in the blood. This occurs because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or the insulin produced is ineffective
Types of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 Insulin- dependent diabetes (IDD) Often hereditary and generally develops during childhood, adolescence and young adulthood The pancreas does not produce insulin Oral medication and insulin injections as well as diet and exercise are used to control IDD Cannot be reversed
Types of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Non-insulin dependent diabetes (NIDD) Develops mainly during later adulthood, especially among overweight adults The pancreas produces insulin that cannot be used by the body Oral medication and insulin injections as well as diet and exercise are used to control NIDD, or diet and exercise alone can also control this condition Can be reversed when a person loses weight
Symptoms Frequent urination Excessive thirst Weight loss Tiredness Lack of concentration Blurred vision
Dietary Guidelines (HL) Reduce intake of foods high in saturated fat eg. cheese, butter, especially important to reduce type 2 diabetes Choose diabetic confectionery eg. diabetic chocolate, artificial sweeteners, to avoid blood glucose levels spiking Increase intake of high-fibre foods eg. wholegrain bread release glucose into the bloodstream slowly and steadily Choose low GI (glycaemic index) foods eg. porridge. High GI foods eg. cakes. Low GI foods release glucose into the bloodstream slowly and steadily Eat, regular, balanced meals to stabilise blood sugar levels help avoid hypoglycaemia or hyperglycaemia
Learning Check 2011, HL, Section B, Q2
Definition Plaque, which is composed of bacteria, food and saliva, is the main cause of dental disease. Plaque forms a coating on the outside of teeth and gums. Periodontal disease and dental caries or tooth decay occurs when plaque is allowed to remain on teeth.
Periodontal Disease Bacteria in plaque produce toxins which causes inflammation of the gums and destruction of the bone holding the teeth in place Periodontal disease occurs when plaque builds up along the gum line The teeth become loose over time and may have to be extracted
Dental cavities/tooth decay Bacteria in plaque react with food particles to produce an acid, which attacks the tooth enamel, weakening it Dental cavities occur when plaque is allowed to remain on teeth Over time a cavity(hole) will develop in the enamel, which eventually may expose the toot s nerve, leading to a tooth ache
Dietary Changes Reduce the risk of dental disease Avoid high sugar foods eg. cakes, fizzy drinks Use artificial sweeteners eg . Canderel instead of sugar Choose high fibre breakfast cereals, eg Weetabix instead of high sugar options Choose water instead of fizzy drinks Avoid foods with hidden sugars eg corn syrup
Dental Care Reducing the risk of dental disease Brush teeth at least twice per day and if possible after each meal Floss teeth daily Visit the dentist at least twice per year Choose a flouride toothpaste, flouride strengthens teeth and helps prevent tooth decay Use an antiseptic mouthwash to reduce build-up of bacteria and freshen breath