Understanding Flower Variations in Plants
Explore the diverse world of flowers in plants through examples and explanations of their reproductive parts and processes. Discover how some plants have both male and female flowers, while others have separate sex flowers. Learn about perfect flowers, the female and male parts of a flower, and the process of reproduction in flowering plants.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
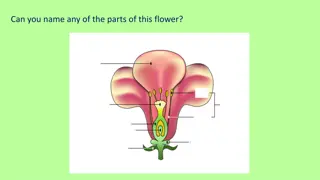
Are all flowers on all plants the same? Respond here give examples Flower Dissection - Reproduction in flowering plants: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=493WeySyf-8
National curriculum links: Describe the life process of reproduction in some plants WALT: recognise that flowers are not all the same and identify how they are different Success criteria: I can identify, name and describe in detail the function of the reproductive parts of a flower and the processes involved in plant reproduction. I can describe how the flowers of some plants are different, including only male or female parts. I can explain how the process of reproduction differs in plants that have single sex flowers. Key vocabulary: reproduction, reproduce, flower, organ, carpel, stamen, pollen, pollinator, pollination, fertilisation
Drag the statements about the flowers into the groups. True False True False
Key information: Most flowering plants have flowers with both male and female parts perfect flowers such as tulip, daisy and rose. Some plants have separate male and female flowers on the same plant, such as corn and courgette. A smaller number of plants have male and female flowers on separate plants, such as willow, maple and holly. All flowering plants do not produce perfect flowers complete with male and female organs, but that there are some flowering plants with different sex flowers on the same or separate plants. Video links to refresh your last weeks learning : Sexual Reproduction in Plants | Plants | Biology | FuseSchool https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R8_ScKzLAfE
Recap : Write here the female and male parts of the flower: ________ is a female part and ___________ male part of a flower . What is a perfect flower ? A perfect flower has both_______________ What is a the process of reproduction in flowering plants?
Some examples so you can understand clearly. Zucchini plants have both male and female blooms, which have distinct, visible differences. Male Zucchini Flowers the male flowers have a single, long stamen that is covered in pollen. Female Zucchini Flowers Female blossoms have a stigma with multiple stems inside. Quick check: look at the stem length. The male blossom has a long, slender stem, while the female blossom is on a short stem.
Male and female flowers grow on separate kiwifruit plants. Male flowers (top) produce pollen from the numerous stamens. Female flowers (bottom) have a well-developed ovary with long sticky stigmas in the centre. Although female flowers have stamens, they do not produce functional pollen.
Flower Structure and its Parts | Biology | Learn Videos For Kids | Science Videos for Kids: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y1rR6a-o6b0 What did you notice about male and female flowers from the same plant? Please write your details here:
Parts of a Flower Some video links to help you understand the lesson 1) The Parts Of A Flower And Pollination https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lVdflux8pJY 2) Parts of Flower : Pollination video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SiFaN2xQg5g
Task: sketch designs for a model of separate male and female flowers that are located on the same plant 1. Design a model to explain the differences between male and female flowers. 2. Produce a detailed sketch of your design. 3. Include the names of the flower parts and their arrangement in the flower. Extension: Think about how the female flower will be pollinated and the seed fertilised, how you can model this effectively. Key vocabulary: reproduction, reproduce, flower, organ, carpel, stamen, pollen, pollinator, pollination, fertilisation
MODEL FLOWER PLANNING Plan and sketch your model to explain the differences between male and female flowers. Parts to include Model design Male flower Female flower