Understanding Semantics: Analyzing Meaning in Linguistics
Semantics is a branch of linguistics focusing on the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences. It involves analyzing semantic features, roles, and relationships between words to understand conceptual meanings. Explore the association between words and their associative meanings, with a spotlight on thematic roles such as agents, themes, instruments, experiencers, and more.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Agenda Natural Language Understanding (NLU) Semantics Definition Semantic Analysis Semantic features Semantic role (thematic role) Relationship between words Theories in Semantics Reading Material Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 2 28 September 2024
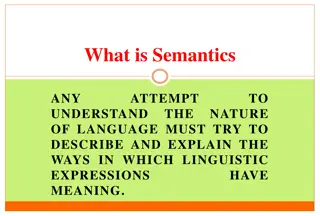
Semantics Definition Semantics is a branch of linguistics dealing with the meaning of words, phrases and sentences. [Kamil Wi niewski, Aug. 12th, 2007, Semantics (http://www.tlumaczenia-angielski.info/linguistics/lexical- semantics.htm)] Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 3 28 September 2024
Semantics (Cont..) It is concerned with the conceptual meaning and not the associative meaning. Conceptual meaning Tells us what a word in fact denotes, as for example Friday the 13th is a day between Thursday the 12th and Saturday the 14th, and that is the conceptual meaning of the phrase Friday the 13th. Associative meaning Yet, for many people the idea of the day Friday 13th brings either thoughts of bad luck or misfortune or happiness. Pragmatics deals with associative meaning. Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 4 28 September 2024
Semantic Analysis Meaning of a word, phrase or sentence can be analyzed from its different aspects: Semantic features Semantic role (thematic role) Relationship between words Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 5 28 September 2024
Semantic Features Basic elements which enable the differentiation of meaning of words. Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 6 28 September 2024
Semantic Role (thematic role) Describe the way in which words are used in sentences and the functions they fulfill. Agent The entity that performs an action is known as an agent, Theme While the entity involved in an action is called the theme (or patient). Instrument When an agent uses an entity in order to do something this entity is called an instrument. Experiencer When a person in a sentence does not perform any action, but only has a perception, state of feeling then the role is described as experiencer. Location The location is where an entity is, Source Is the initial position of the entity, the place where it moves from Goal The goal is where the entity moves to. Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 7 28 September 2024
Semantic Role (Cont..) Agent (Anne Marshall), Theme (the ball), Instrument (her new golf club), Experiencer (she), Location (the hole), Source (the woods), Goal (the grassy area), (2010 George Yule. The Study of Language (4th edition), Cambridge University Press). Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 8 28 September 2024
Relationship Between Words Synonyms Are two words with very similar, almost identical meaning, such as buy and purchase, or cab and taxi. In some cases however, although the meaning seems nearly identical there is a difference in the word usage or the level of formality and therefore the words can not always be substituted. Antonyms In this type of relationship between words two words have opposite meanings, the words such as male/female, old/new, interesting/boring are antonyms. Gradable antonyms are opposites along a scale in that when someone says I am not high it does not necessarily mean I am short . Non-gradable antonyms do not present such flexibility: when we say I am married the only antonym available in this sentence would be I am single . Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 9 28 September 2024
Relationship Between Words (Cont..) Hyponymy Sometimes the meaning of one word is included in the meaning of another, broader term. Then the relationship between words can be described as hyponymy as in the case of words: vegetable and carrot. A carrot is necessarily a vegetable, therefore the meaning of the word vegetable is included in the word carrot, so carrot is a hyponym of vegetable. Superordinate In this relation the word vegetable is the superordinate (higher level term) of the word carrot. The relationship of hyponymy and superordination can be illustrated by the following diagram: Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 10 28 September 2024
Relationship Between Words (Cont..) Homophones are words which have different written forms, but the same pronunciation such as: right/write, to/too/two, bear/bare. Homophones are often mistaken for homonyms, but Homonyms Words which have the same written or spoken forms and unrelated meanings, as for example: bat (flying creature) and bat (used in baseball), race (contest) and race (ethnic group). Polysemy When a word has multiple related meanings then linguists speak of polysemy as with head for instance: head as a part of body; mind, or mental ability; a person in charge. Metonymy There exist a close connection of certain entities in everyday experience. The connection can be that of container-content, whole-part, or others. It is clearly visible in the following example he drank the whole bottle when it is obvious that he did not drink the container, but the content of the bottle. Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 11 28 September 2024
Theories in Semantics Model Theoretic Semantics Truth-Conditional Semantics Lexical & Conceptual Semantics Lexical Semantics Computational Semantics (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semantics) Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 12 28 September 2024
Reading/References Yule G. 1996. The study of language. Cambridge: CUP. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semantics) Daniel Jurafsky, Speech and Language Processing: An Introduction to Natural Language Processing, Computational Linguistics and Speech Recognition Kamil Wi niewski, Aug. 12th, 2007, Semantics (http://www.tlumaczenia-angielski.info/linguistics/lexical-semantics.htm) Natural Language Processing (NLP) by Rahman Ali, Lect: QACC, UOP 13 28 September 2024