Understanding Ploidy and Chromosome Numbers in Organisms
Ploidy refers to the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, impacting the number of possible alleles. Humans are diploid, with 2 sets of 23 chromosomes each from parents, totaling 46 chromosomes. The haploid number for humans is 23, and the monoploid number is also 23. Variations in ploidy levels affect chromosome numbers in organisms. Understanding these concepts is crucial in genetics and biology studies.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PLOIDY Dr.I.Viji Margaret Assistant Professor, PG Dept.of Zoology, Sarah Tucker College, Tirunelveli
Ploidy is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudo autosomal genes. Somatic cells, tissues and individuals can be described according to the number of sets present (the ploidy level):monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets),tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets),hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is used to describe cells with three or more chromosome sets.
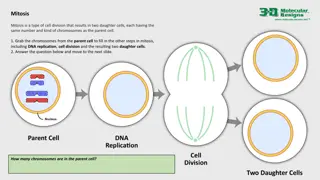
Humans are diploid organisms, carrying two complete sets of chromosomes: one set of 23 chromosomes from their father and one set of 23 chromosomes from their mother. The two sets combined provide a full complement of 46 chromosomes. This total number of chromosomes is called the chromosome number. The zygotic number is defined as the number of chromosomes in zygotic cells. Human zygotes are diploid, hence with a zygotic number of 46.
When a species has a varying chromosome number, e.g. a diploid and tetraploid form, the chromosome number is called diploid number in the diploid form, and tetraploid number in the tetraploid form.
The number of chromosomes found in a single complete set of chromosomes is called the monoploid number(x). The haploid number (n) is unique to gametes (sperm or egg cells), and refers to the total number of chromosomes found in a gamete, which under normal conditions is half the total number of chromosomes in a somatic cell.
The haploid number for humans (half of 46) is 23; and the monoploid number equals 46 divided by the ploidy level of 2, which is also 23. When a human germ cell undergoes meiosis the two sets of 23 chromosomes are split in half to form gametes. After fusion of a male and a female gamete (fertilization) both containing 1 set of 23 chromosomes, the resulting zygote has 46 chromosomes: 2 sets of 23 chromosomes (22 autosomes, and 1allosome).
Variation in euploidy for organisms with x=11 Ploidy Nr of chromosomes Somatic Gametic Diploid 2x=22 2n=22 n=11 Tetraploid 4x=44 2n=44 n=22 Hexaploid 6x=66 2n=66 n=33 Octoploid 8x=88 2n=88 n=44