Understanding Chemical Reactions and Catalysts
Chemical reactions involve the formation of new substances from reactants, with key processes like oxidation and reduction. Reversible reactions, endothermic and exothermic reactions, and the role of catalysts in speeding up reactions are explored. The significance of chemical symbols, formulas, and equations in representing reactions is also discussed. Controlling reactions through catalysts, concentration, and surface area manipulation are vital aspects in enhancing reaction rates.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chemical Reactions This is the fourth text which will be used for practicing dictation and translation in the written part of the exam. The key words are emphasized in bold and there is a list of them at the end of the presentation.
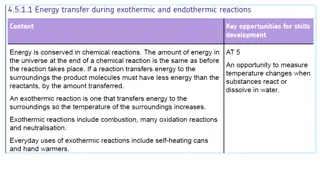
Chemical Reactions When a chemical reaction occurs, new substances (called products) form from the substances taking part in the reaction (called reactants). Burning is an exothermic reaction more heat is given out during the reaction than is taken in. Oxidation occurs when a substance combines with oxygen. Reduction occurs when a substance loses oxygen.
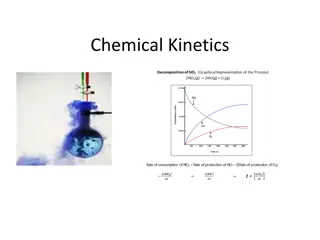
Chemical Reactions Reversible chemical reactions can go forwards and backwards. When heated, nitrogen dioxide (NO2) breaks down into nitrogen monoxide (NO) and oxygen (O2), when cooled the change is reversed. Some reactions take in more heat energy than they give out. These reactions are called endothermic. Electron transfer During the oxidation process, atoms lose electrons and are oxidized. During reduction, atoms gain electrons and are reduced.
Chemical Reactions Each element has a chemical symbol to identify it, and each compound a chemical formula. The formula indicates how the elements in the compound are combined. A chemical equation shows which substances react and the products that result. An atom s valency shows the number of chemical bonds it can form. It is the number of electrons the atom gains, loses or shares when it makes bonds.
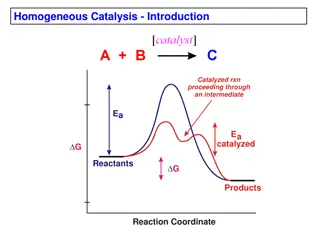
Chemical Reactions Controlling reactions Chemists speed up reactions by making the reacting particles collide with each other more often or with greater energy. Substances called catalysts speed up reactions by helping substances react together. They remain unchanged by the chemical reaction. Increasing the concentration of a reactant speeds up a reaction. Dyeing a material is faster with a concentrated dye there are more dye molecules to collide with the material.
Chemical Reactions The surface area of a solid object is the size of its outer surface. Increasing the surface area of a reacting substance speeds up the chemical reaction. Yeast is a fungus containing enzymes, which are biological catalysts. The enzymes in yeast make starches and sugars break down more rapidly into carbon dioxide and ethanol.
Key words: Product produkt, proizvod Reactant - reaktant Burning sagorevanje Reversible/reversed reverzibilna, povratna Oxidation/reduction oksidacija/redukcija Chemical symbol hemijski simbol Chemical formula hemijska formula Chemical equation hemijska jednacina Chemical bonds hemijske veze
Key words Catalyst katalizator Catalyzation - katalizacija Dye boja Dyeing bojenje Surface area ukupna spoljna povrsina Yeast kvasac Starch skrob To break down razgraditi