Understanding the Structure and Importance of DNA
Explore the essential components and structure of DNA, including nucleotides, RNA, and the significance of DNA in carrying genetic information across generations. Learn about the four DNA nucleotides, how mononucleotides are formed, and the discovery of DNA's structure. Dive into base pairing and the crucial role of hydrogen bonds in maintaining DNA integrity.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Objectives Be able to describe the structure of a nucleotide Be able to describe the structure of RNA Be able to describe the structure of DNA
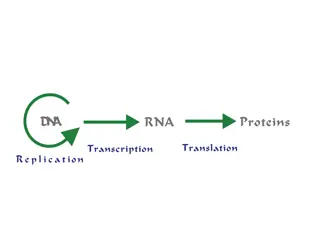
Why is DNA so important? DNA carries genetic information It passes on the features of organisms from one generation to the next The code on DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein the primary structure
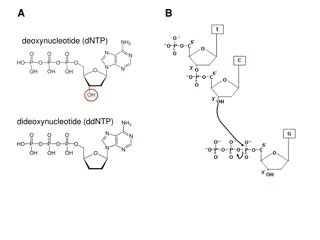
DNA is made up of many nucleotides The organic base contains nitrogen Pentose (5 carbon) sugar
There are 4 different DNA nucleotides, each with a different base- what are the 4 bases? http://images.spaceref.com/news/adenine.jpg A- adenine T- thymine G- guanine C-cytosine https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/88/Thymine-3D-balls.png/100px-Thymine-3D-balls.png https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/1f/Guanine-3D-balls.png https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/73/Cytosine-3D-balls.png
How is a mononucleotide formed? The pentose sugar, organic base and phosphate group are all joined by condensation reactions to form a mononucleotide
A condensation reaction between two nucleotides forms a phosphodiester bond Phosphate group of one mononucleotide is joined to the deoxyribose group of another in a condensation reaction
A polynucleotide contains many nucleotides
How did we discover the structure of DNA? http://www.dnaftb.org/19/animation.html Questions: What stands out from Chargaff s findings? What would be the problem with pairing A-T or C-G? CLICK THROUGH ANIMATION
Base pairing The bases on the two strands of DNA attach to each other by hydrogen bonds The hydrogen bonds hold the two strands together Adenine always pairs with thymine Guanine always pairs with cytosine
A complementary to T C complementary to G
Base pairing (DNA interactive- Animations- Base Pairing) Hydrogen bonds
A nucleotide showing the positions of the 3-prime and 5-prime carbon atoms on the pentose sugar http://biology-forums.com/gallery/33_23_06_11_4_12_30.jpeg
The double helix Look at the model
Why is DNA so stable? the phosphodiester backbone protects the more chemically reactive organic bases hydrogen bonds link the base pairs forming bridges. As there are 3 H-bonds between cysteine and guanine, more C-G pairings make the molecule more stable.
Function of DNA Make a note as we go through
Separate strands are joined by hydrogen bonds, these are easily broken to allow stands to separate for DNA replication & protein synthesis
It is extremely large, allowing lots of genetic information to be stored.
Very stable and can be passed from generation to generation (rarely mutates)
Bases are protected by the sugar phosphate backbone- prevents corruption by outside chemical or physical forces
The sequence of DNA bases codes for the primary structure of proteins.
Base pairing allows DNA to replicate and to transfer information to mRNA
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
RNA A polymer A single, relatively short polynucleotide chain Pentose sugar is always ribose Bases are adenine, uracil, guanine and cytosine
Research task mRNA rRNA tRNA Which bases is it made up of? Draw/describe the structure What does it do?