The Cold War Expansion and Nuclear Arms Race
The Cold War intensified as the Soviet Union detonated an atomic bomb, leading to heightened tensions. Communist advancements, including the takeover of communist China, shocked the world. Nuclear arsenals expanded with the development of the hydrogen bomb, sparking concerns of an arms race. Eisenhower introduced new policies, favoring massive retaliation against communist threats. Stalin's death eased tensions temporarily, but the Cold War continued globally with deep divisions between the U.S. and Soviet Union.
Uploaded on Sep 13, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
25.3 The Cold War Expands
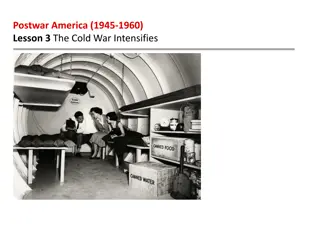
The Arms Rave Heightens Tensions September 2 1949- In struments in an American B-29 aircraft flying over Alaska detected atmospheric radiation. Conclusion: Soviet Union had set off an atomic bomb.
Communist Advances Shock the Nation News that Soviets had the bomb was followed by communist China takeover.
Nuclear Arsenals Expand 3 months later: Truman orders H-Bomb (hydrogen) Einstein and Oppenheimer opposed development stating it would lead to an arms race. Tests by both sides Atomic testing in the American west, at sites such as the Nevada desert, led to increased atmospheric radiation and long range health problems for people living in downwind of test sites.
Eisenhower Introduces New Policies Eisenhower accepted much of Truman s foreign policy. Believed strongly in a policy to actively contain communism. Secretary of State John Dulles, and experienced diplomat who had helped organize the United Nations after WWII. Eisenhower believed that Truman's approach to foreign policy had dragged the United States into an endless series of conflicts begun by the Soviet Union.
Eisenhower Favors Massive Retaliation Focused on stockpiling nuclear weapons and building planes, missles, and submarines needed to deliver them. Criticism: Conservative: downgrading conventional forces would weaken American defense Liberals feared that preparing for nuclear war made such a war more likely. Mass Retaliation: U.S. would respond to communist threats to its allies by threatening to use crushing. Overwhelming force, perhaps even nuclear weapons. Dulles believed that only by going to the brink of war could the United States protect its allies, discourage communist aggression and prevent war. brinkmanship
Stalins Death Eases Tensions Nikita Khrushchev- emerged as the new head of Soviet Union. Communist Determined opponent of the U.S.
The Cold War Goes Global U.S. and Soviet Union: deeply divided
Unrest Explodes Behind the Iron Curtain Two uprising shook Eastern Europe. First, workers in Poland rioted against Soviet rule and won greater control of their government. Since the Polish government did not attempt to leave the Warsaw Pact, Soviet leaders permitted the actions. nationwide revolt against the government of the Hungarian People's Republic and its Soviet-imposed policies, lasting from 23 October until 10 November 1956. Though leaderless when it first began, it was the first major threat to Soviet control since the USSR's forces drove Nazi Germany from its territory at the end of World War II.
revolt began as a student demonstration, which attracted thousands as they marched through central Budapest to the Parliament building, calling out on the streets using a van with loudspeakers. A student delegation, entering the radio building to try to broadcast the students' demands, was detained. When the delegation's release was demanded by the demonstrators outside, they were fired upon by the State Security Police ( VH) from within the building. One student died and was wrapped in a flag and held above the crowd. This was the start of the revolution. As the news spread, disorder and violence erupted throughout the capital. revolt spread quickly across Hungary and the government collapsed
Thousands organized into militias, battling the Soviet troops. Pro- Soviet communists were often executed or imprisoned and former political prisoners were released and armed. Radical impromptu workers' councils wrested municipal control from the ruling Hungarian Working People's Party and demanded political changes. A new government formally disbanded the VH, declared its intention to withdraw from the Warsaw Pact, and pledged to re-establish free elections. By the end of October, fighting had almost stopped and a sense of normality began to return.
The U.S. Defuses the Suez Canal Egypts president Gamal Nasser tried to use the U.S. Soviet rivalry to his advantage. The Suez Crisis was an event in the Middle East in 1956. It began with Egypt taking control of the Suez Canal which was followed by a military attack from Israel, France, and Great Britain. The canal had been owned by the Suez Canal Company, which was controlled by French and British interests Egyptian president, Gamal Abdel Nasser, nationalized the Suez Canal.
The Suez Canal is an important man-made waterway in Egypt. It connects the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. This is important for ships traveling from Europe to and from the Middle East and India. The Suez Canal was built by French developer Ferdinand de Lesseps. It took over 10 years and an estimated one and a half million workers to complete. The canal was first opened on November 17, 1869.
In 1954 Gamal Abdel Nasser took control of Egypt. One of Nasser's goals was to modernize Egypt. He wanted to build the Aswan Dam as a major part of the improvement. The United States and the British had agreed to loan Egypt the money for the Dam, but then pulled their funding due to Egypt's military and political ties to the Soviet Union. Nasser was angry. Seizing the Canal In order to pay for the Aswan Dam, Nasser decided to take over the Suez Canal. It had been controlled by the British in order to keep it open and free to all countries. Nasser seized the canal and was going to charge for passage in order to pay for the Aswan Dam. Israel, France, and Great Britain Collude The British, the French, and the Israelis all had issues with Nasser's government at the time. They decided to use the canal as a reason to attack Egypt. They secretly planned that Israel would attack and seize the canal. Then the French and the British would enter as peacekeepers taking control of the canal.
Israel Attacks Just like they had planned, the Israeli's attacked and grabbed the canal. Then the British and French jumped in. They told both sides to stop, but when Egypt wouldn't they bombed Egypt's air force. The Crisis Ends The Americans were angry with the French and the British. At the same time of the Suez Crisis, the Soviet Union was invading Hungary. The Soviet Union had also threatened to enter the Suez Crisis on the side of the Egyptians. The United States ended up forcing the Israelis, the British, and the French to withdraw in order to prevent conflict with the Soviet Union.
Eisenhower Promises Strong Action Eisenhower Doctrine stated that a country could ask for military support from the United States if it was threatened by another country. It was based on a speech President Eisenhower gave to Congress and was a warning to the Soviet Union. Once the Central Intelligence Agency was established, it proved to be a great source of America s information during the Cold War with the Soviet Union. The Central Intelligence Agency was given 46 million dollars by President Eisenhower in 1955 to have the CIA Headquarters built in Langley, Virginia. By 1961 the CIA supported the invasion of Cuba at the Bay of Pigs by providing the Cuban exiles with weapons and training. Later, the Central Intelligence Agency discovered that Cuba had Soviet missiles pointed at the United States on nuclear missile carriers; this created the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962. During the Cold War the CIA played the biggest role in counter-espionage ever, but once the Cold War began thaw the focus fell on the CIA control.
The Cold War Blasts Off Into Space The Space Race began in 1955 when both countries announced that they would soon be launching satellites into orbit. The Soviets took the US announcement as a challenge and even established a commission whose goal was to beat the US in putting a satellite into space. On October 4, 1957 the Russians placed the first successful satellite into orbit. It was called Sputnik I. The Russians had taken the lead in the Space Race. The Americans successfully launched their first satellite four months later called the Explorer I.